Ann Rehabil Med.
2015 Oct;39(5):718-725. 10.5535/arm.2015.39.5.718.
Short-Term Effect of Percutaneous Bipolar Continuous Radiofrequency on Sacral Nerves in Patients Treated for Neurogenic Detrusor Overactivity After Spinal Cord Injury: A Randomized Controlled Feasibility Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. aodwntjr1@naver.com
- 2Department of Medical Statistics, Catholic University of Daegu School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2148202
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2015.39.5.718
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To investigate the short-term effects of bipolar radiofrequency applied to sacral nerves to treat neurogenic detrusor overactivity in patients with spinal cord injury.
METHODS
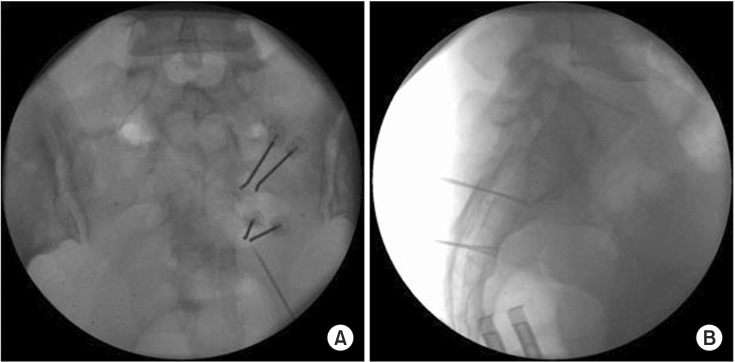
Ten patients with spinal cord injury with neurogenic detrusor overactivity were recruited. These subjects were randomized to two groups: intervention (n=5) and control (n=5), members of which received conventional treatment. Voiding diary, International Consultation on Incontinence Questionnaire (ICIQ) and the urinary incontinence quality of life scale (IQOL) data were obtained and an urodynamic study (UDS) was performed before and after intervention. In the intervention group, percutaneous bipolar continuous radiofrequency (CRF) was performed on both the S2 and S3 nerves in each patient.
RESULTS
In a comparison of daily frequency and number of urinary incontinence and ICIQ and IQOL scores at baseline and at 1 and 3 months after intervention, all variables achieved a significant effect for time (p<0.05). Regarding UDS parameters, pre/post intervention differences between baseline and 3-month post-intervention for volume at maximal detrusor pressure during filling and reflex detrusor volume at first contraction were significantly different between the two groups (p<0.05). However, pre/post intervention differences in maximum cystometric capacity and maximum detrusor pressure during filling were not significant between the two groups (p>0.05).
CONCLUSION
Percutaneous bipolar CRF applied to sacral nerves might be an effective therapy for neurogenic overactive bladder that reduces urinary incontinence and improves quality of life.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ku JH. The management of neurogenic bladder and quality of life in spinal cord injury. BJU Int. 2006; 98:739–745. PMID: 16978269.
Article2. Hansen RB, Biering-Sorensen F, Kristensen JK. Urinary incontinence in spinal cord injured individuals 10-45 years after injury. Spinal Cord. 2010; 48:27–33. PMID: 19488052.
Article3. Lieberman JA 3rd. Managing anticholinergic side effects. Prim Care Companion J Clin Psychiatry. 2004; 6(Suppl 2):20–23. PMID: 16001097.4. Wyndaele JJ. Complications of intermittent catheterization: their prevention and treatment. Spinal Cord. 2002; 40:536–541. PMID: 12235537.
Article5. Houle AM, Vernet O, Jednak R, Pippi Salle JL, Farmer JP. Bladder function before and after selective dorsal rhizotomy in children with cerebral palsy. J Urol. 1998; 160(3 Pt 2):1088–1091. PMID: 9719282.6. Toczek SK, McCullough DC, Gargour GW, Kachman R, Baker R, Luessenhop AJ. Selective sacral rootlet rhizotomy for hypertonic neurogenic bladder. J Neurosurg. 1975; 42:567–574. PMID: 1151454.
Article7. Brindley GS. The first 500 patients with sacral anterior root stimulator implants: general description. Paraplegia. 1994; 32:795–805. PMID: 7708419.
Article8. Mulcahy JJ, Young AB. Percutaneous radiofrequency sacral rhizotomy in the treatment of the hyperreflexic bladder. J Urol. 1978; 120:557–558. PMID: 712897.
Article9. Mulcahy JJ, Young AB. Long-term follow-up of percutaneous radiofrequency sacral rhizotomy. Urology. 1990; 35:76–77. PMID: 2296824.10. Ferreira RS, Levi d'Ancona CA, Dantas-Filho VP, Rodrigues Netto N Jr, Miyaoka R. Percutaneous radiofrequency sacral rhizotomy in the treatment of neurogenic detrusor overactivity in spinal cord injured patients. Actas Urol Esp. 2011; 35:325–330. PMID: 21477886.
Article11. Cho KH, Lee SS. Radiofrequency sacral rhizotomy for the management of intolerable neurogenic bladder in spinal cord injured patients. Ann Rehabil Med. 2012; 36:213–219. PMID: 22639745.
Article12. Avery K, Donovan J, Peters TJ, Shaw C, Gotoh M, Abrams P. ICIQ: a brief and robust measure for evaluating the symptoms and impact of urinary incontinence. Neurourol Urodyn. 2004; 23:322–330.
Article13. Oh SJ, Park HG, Lim SH, Hong SK, Martin ML, Ting BL, et al. Translation and linguistic validation of Korean version of the Incontinence Quality of Life(I-QoL) instrument. J Korean Continence Soc. 2002; 6:10–23.
Article14. Wagner TH, Patrick DL, Bavendam TG, Martin ML, Buesching DP. Quality of life of persons with urinary incontinence: development of a new measure. Urology. 1996; 47:67–72. PMID: 8560665.
Article15. van Leijsen SA, Kluivers KB, Mol BW, Broekhuis SR, Milani FL, van der Vaart CH, et al. Protocol for the value of urodynamics prior to stress incontinence surgery (VUSIS) study: a multicenter randomized controlled trial to assess the cost effectiveness of urodynamics in women with symptoms of stress urinary incontinence in whom surgical treatment is considered. BMC Womens Health. 2009; 9:22. PMID: 19622153.
Article16. Purves D, Augustine GJ, Fitzpatrick D, Katz LC, Lamantia A, McNamara JO, et al. Neuroscience. 2nd ed. Sunderland: Sinauer Associates Inc.;2001.17. Meirowsky AM, Scheibert CD, Hinchey TR. Studies on the sacral reflex arc in paraplegia; response of the bladder to surgical elimination of sacral nerve impulses by rhizotomy. J Neurosurg. 1950; 7:33–38. PMID: 15402631.18. Townsend CM, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM, Mattox KL. Sabiston textbook of surgery: the biological basis of modern surgical practice. 18th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders;2008.19. Cosman ER, Nashold BS, Ovelman-Levitt J. Theoretical aspects of radiofrequency lesions in the dorsal root entry zone. Neurosurgery. 1984; 15:945–950. PMID: 6514169.
Article20. Cosman ER Jr, Cosman ER Sr. Electric and thermal field effects in tissue around radiofrequency electrodes. Pain Med. 2005; 6:405–424. PMID: 16336478.
Article21. Cosman ER Jr, Gonzalez CD. Bipolar radiofrequency lesion geometry: implications for palisade treatment of sacroiliac joint pain. Pain Pract. 2011; 11:3–22. PMID: 20602716.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Radiofrequency Sacral Rhizotomy for the Management of Intolerable Neurogenic Bladder in Spinal Cord Injured Patients
- Semiconditional Electrical Stimulation of Pudendal Nerve Afferents Stimulation to Manage Neurogenic Detrusor Overactivity in Patients with Spinal Cord Injury
- Efficacy and Safety of OnabotulinumtoxinA in Patients With Neurogenic Detrusor Overactivity Caused by Spinal Cord Injury: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- Efficacy and Adverse Events Associated With Use of OnabotulinumtoxinA for Treatment of Neurogenic Detrusor Overactivity: A Meta-Analysis
- Differences in Urodynamic Variables for Vesicoureteral Reflux Depending on the Neurogenic Bladder Type