Korean J Lab Med.
2006 Feb;26(1):1-8. 10.3343/kjlm.2006.26.1.1.
Evaluation of COSMOsensor Glucose Monitoring System
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Sungkyunkwan University College of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. sy117.lee@samsung.com
- KMID: 2143189
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/kjlm.2006.26.1.1
Abstract
-
BACKGROUND: Glucometer is a most widely-used point-of-care testing (POCT) analyzer and plays an important role in diabetes management. We evaluated the performance of the recently developed glucometer, COSMOsensor (Cosmogenome Inc., Seoul, Korea), comparing it with three foreign-made glucometers.
METHODS
COSMOsensor was evaluated for linearity, precision, comparison of method and analysing time as well as the effect of operator. Other glucometers, Accu-Chek inform (Roche Diagnostics LTD., Mannheim, Germany), Precision(TM)PCx (Abbott Laboratories, Bedford, MA, USA), and Sure- Step.Flexx (LifeScan Inc., Milpitas, CA, USA) were evaluated for the same categories according to NCCLS guidelines.
RESULTS
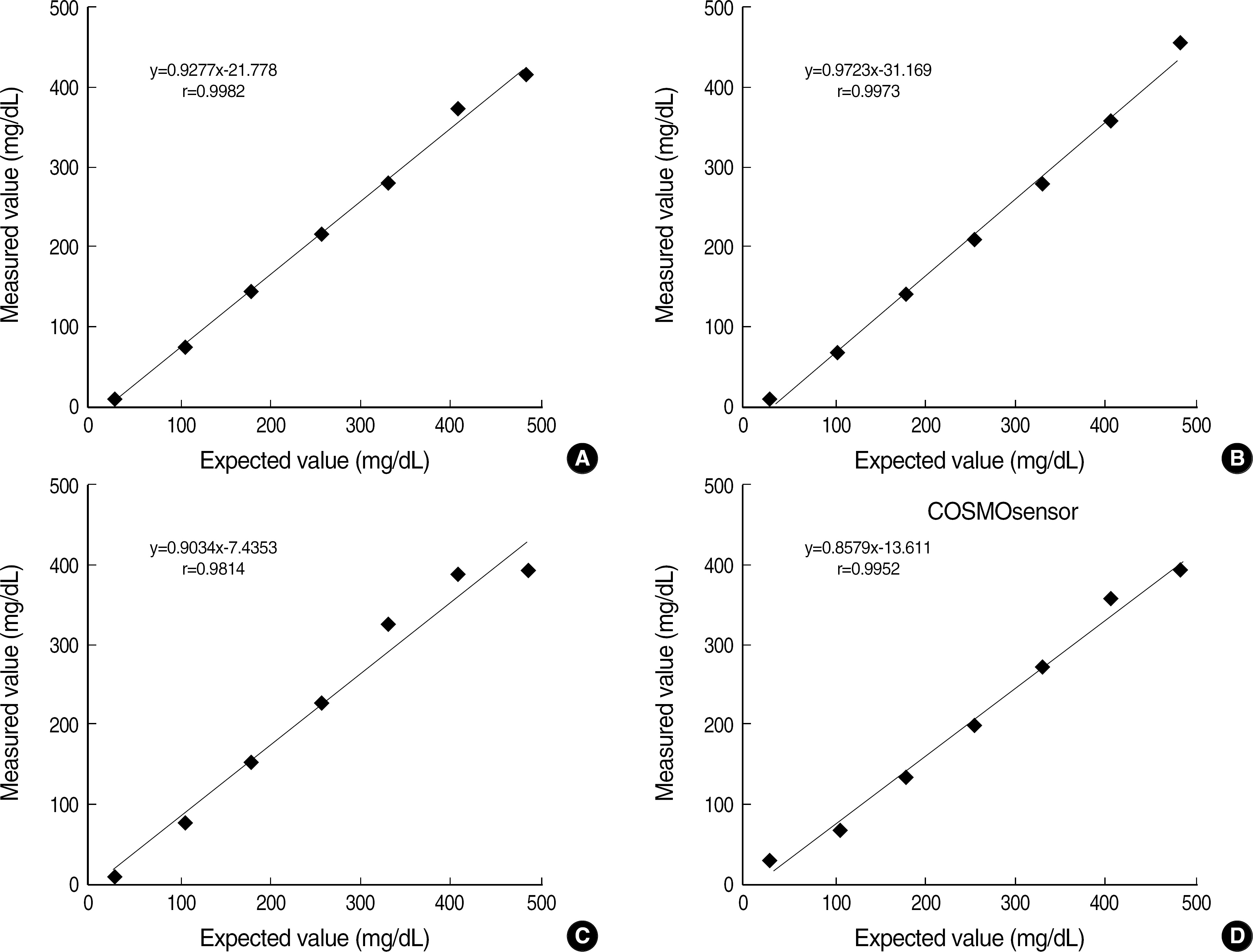
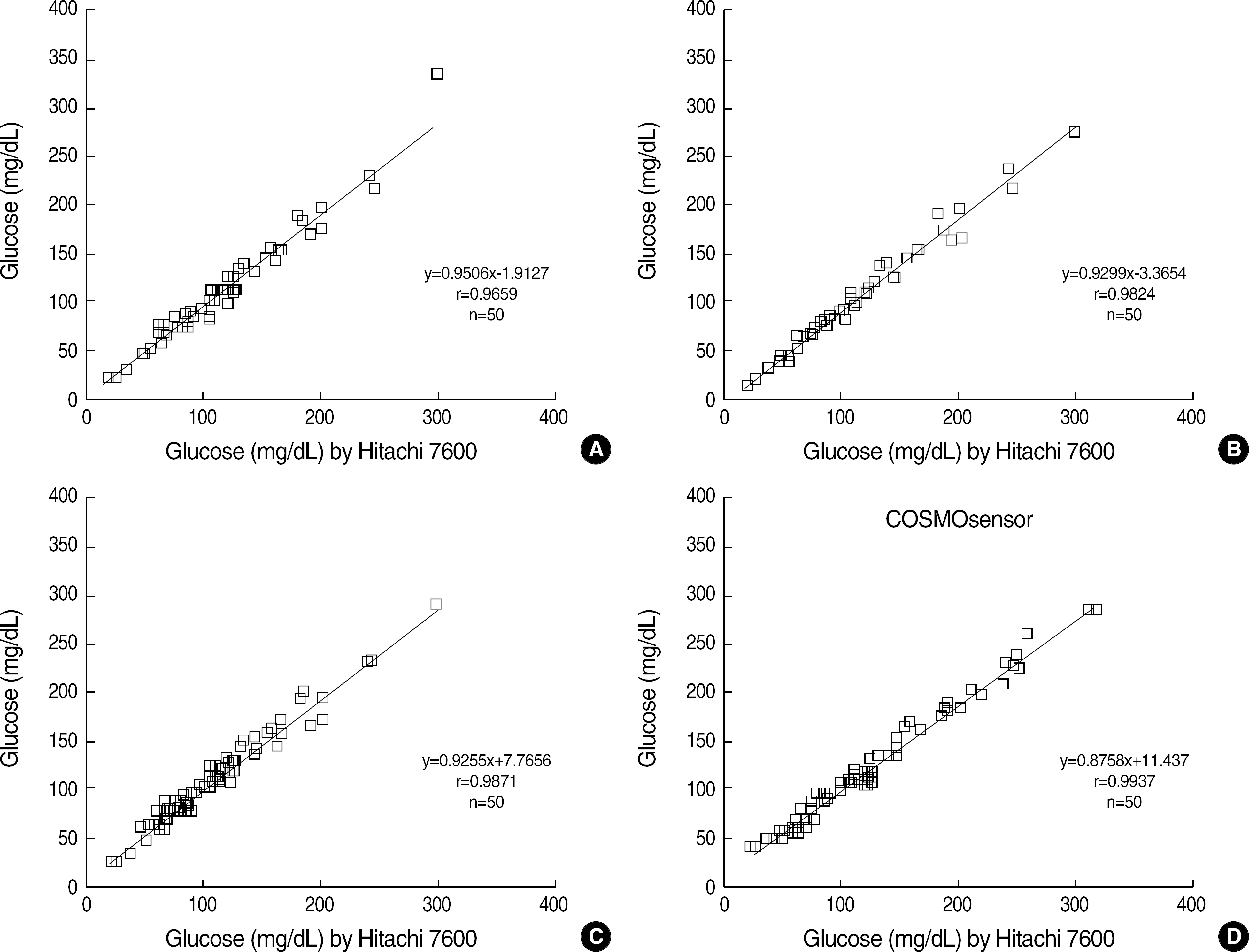
All four glucometers showed a good linearity (r> or =0.9814) and the within-run and total-run coefficients of variation (CVs) were within 3.5%. A high correlation (r> or =0.9659) was also found between the glucometers and Hitachi 7600 (Hitachi Co., Tokyo, Japan) in the central laboratory. Although differences with the reference method were within an allowable range, all glucometers showed variable bias compared with the reference method.
CONCLUSIONS
The COSMOsensor showed a good analytical performance in linearity, precision, and correlation with the reference method, when compared with other foreign-made glucometers. Its rapid turnaround time and easy operation are appropriate for diabetes management and a rapid POCT analyzer. All glucometers showed variable biases, which might be due to different calibration status.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Evaluation of the Wisecheck Glucose Monitoring System
Seonhee Kwon, Ha Nui Kim, Sun-Young Ko, Chi Hyun Cho, Jang Su Kim, Chae Seung Lim
Lab Med Online. 2014;4(1):15-21. doi: 10.3343/lmo.2014.4.1.15.Analytic Performance Evaluation of Blood Monitoring System G400 according to ISO 15197:2013
Doheun Chung, Byungkeun Choi, Byungwook Yoo, Chooyon Cho, Sungho Hong, Jungeun Oh, Yongjin Cho
Korean J Health Promot. 2016;16(4):223-230. doi: 10.15384/kjhp.2016.16.4.223.Analytical Performance Evaluation of Glucose Monitoring System Following ISO15197
Dongheui An, Hee-Jung Chung, Hye-Won Lee, Woochang Lee, Sail Chun, Won-Ki Min
Korean J Lab Med. 2009;29(5):423-429. doi: 10.3343/kjlm.2009.29.5.423.
Reference
-
References
1. Lee SY, Lee NY, Kim JW. Evaluation of 6 glucose testing system. Korean J Lab Med. 2003; 23:170–9.2. Lee SY, Lee SG, Kim JW, Min WK, Park HS. Evaluation of Precision Q.I.DR glucose testing system. Korean J Clin Pathol. 1999; 19:425–32.3. Woo JE, Lee DH, Hwang YS. Evaluation of Companion™ 2, home monitor of blood glucose using electrochemical electrode method. Korean J Clin Pathol. 1994; 14:309–16.4. Min DW, Min WK, Hong KS. Evaluation of 3 monitors of blood glucose: Glucometer II, Reflolux II, Glucoscan-3000. J Lab Med Qual Assur. 1989; 11:245–52.5. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Evaluation of the linearity of quantitative analytical methods; Proposed guideline. Document EP6-P2.Vilanova, Pa: National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards;2001.6. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Evaluation of precision performance of clinical chemistry devices; Approved guideline. Document EP5-A.Vilanova, Pa: National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards;1999.7. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Method comparison and bias estimation using patient samples; Approved guideline. Document EP9-A.Vilanova, Pa: National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards;1995.8. Kim CS, Jeong EK, Park J, Cho MH, Nam JS, Kim HJ, et al. Prevalence of diabetes mellitus (fasting plasma glucose by the ADA criteria and impaired fasting glucose according to anthropometric characteristics and dietary habits:1998 national health and nutrition survey. J Korean Diabetes Assoc. 2005; 29:151–66.9. American Diabetes Association. Self-monitoring of blood glucose. Diabetes Care. 1996; 19:S62–6.10. Skeie S, Thue G, Nerhus K, Sandberg S. Instruments for self-monitoring of blood glucose: comparisons of testing quality achieved by patients and a technician. Clin Chem. 2002; 48:994–1003.
Article11. Blake DR, Narthan DM. Point-of-care testing for diabetes. Point of Care. 2002; 1:155–64.12. Guerci B, Drouin P, Grange V, Bougneres P, Fontaine P, Kerlan V, et al. Self-monitoring of blood glucose significantly improves metabolic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: the Auto-Surveillance Intervention Active (ASIA) study. Diabetes Metab. 2003; 29:587–94.
Article13. Park CY, Ryu MS, Woo JT, Kim SW, Kim JW, Kim YS, et al. Evaluation of GlucoDr™ blood glucose testing system. Clinical Diabetes. 2002; 3:152–63.14. Seo YH, Lee WS, Choi TY, Ahn YH. Clinical and laboratory assessment of a new monitor of blood glucose (Gluco-X). J Lab Med Qual Assur. 1993; 15:85–90.15. Price CP, Hick JM, editors. ed.Point-of-care testing. 1st ed.Washington: American Association for Clinical Chemistry, Inc.;1999.16. Knudson PE, Weinstock RS, Henry JB. Carbohydrates. Henry JB, editor. Clinical diagnosis and management by laboratory methods. 20th ed.Philadelphia: WB Saunders;2001. p. 211–23.17. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Ancillary (bedside) blood glucose testing in acute and chronic care facilities; Approved guidelines. Document C30-A.Vilanova, Pa: National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards;1994.18. Johnson RN, Baker JR. Accuracy of devices used for self-monitoring of blood glucose. Ann Clin Biochem. 1998; 35:68–74.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Application of Continuous Glucose Monitoring System (CGMS) and Patient Education
- Performance Evaluation of B. Braun Omnitest 5 Blood Glucose Monitoring System for Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose
- Analytic Performance Evaluation of Blood Monitoring System G400 according to ISO 15197:2013
- Course quality management based on monitoring by students at a medical school
- Self-Monitoring Blood Glucose Meter: Is Your Glucose Meter Accurate?