Korean J Urol.
2009 Jan;50(1):23-27. 10.4111/kju.2009.50.1.23.
Effect of Extracorporeal Magnetic Innervation (ExMI) Pelvic Floor Therapy on Urinary Incontinence after Radical Prostatectomy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Chungnam National University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. uro17@cnuh.co.kr
- 2Department of Urology, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2140109
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/kju.2009.50.1.23
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: To evaluate the safety and clinical effects of extracorporeal magnetic innervation (ExMI) for urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Thirty-two patients with urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy were randomly assigned to receive either ExMI treatment or pelvic floor training alone. For the ExMI group, treatment was initiated 1 week after catheter removal and the treatment sessions were for 20 minutes, twice a week, for 8 weeks. For the control group, only pelvic floor muscle exercises were performed. Patients were followed up at 1 week and 1, 2, 3, and 6 months. Outcomes were assessed by 24-hour pad weight testing, the number of pads used daily, and a quality-of-life survey (I-QoL).
RESULTS
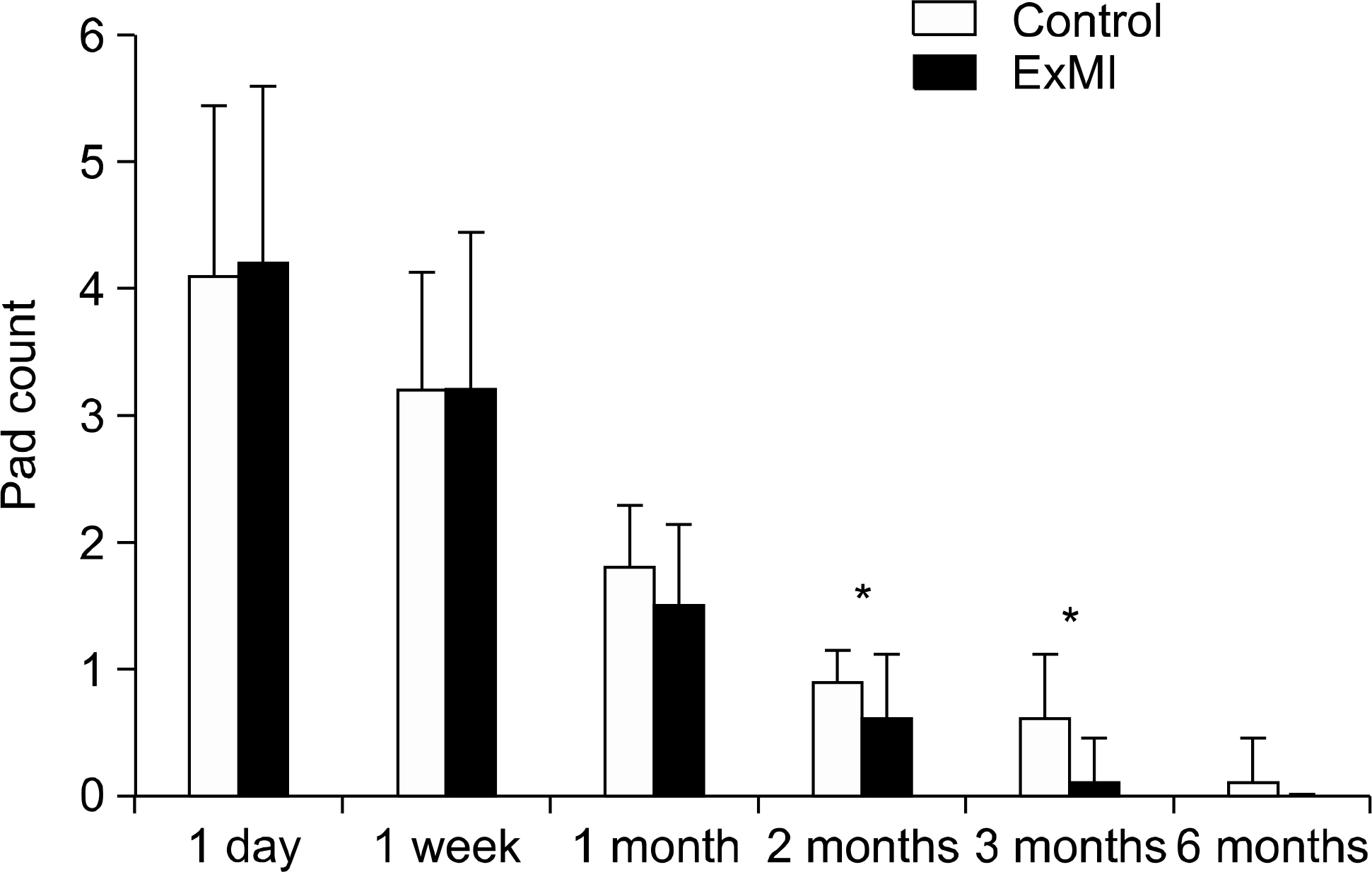
Leakage weight during the 24 hours after removing the catheter was 655g and 646g for the ExMI and control groups, respectively. At 1 month, it was 147g and 187g; at 2 months, 33g and 81g (p=0.001); and at 3 months, 9g and 45g (p=0.001), respectively. Finally, 6 months later, leakage weight was less than 10g in both groups. The number of pads used daily after removing the catheter was 4.2 and 4.1 for the ExMI and control groups, respectively. At 1 month, it was 1.5 and 1.8; at 2 months, 0.6 and 0.9 (p=0.033); and at 3 months, 0.1 and 0.6 (p=0.002), respectively. Finally, 6 month later, pads counts were 0 and 0.1. I-QoL scores decreased after surgery, but gradually improved in both groups. No other side effects or adverse events were observed.
CONCLUSIONS
ExMI provided earlier recovery of continence than in the control group after radical prostatectomy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1.Foote J., Yun S., Leach GE. Postprostatectomy incontinence. Pathophysiology, evaluation, and management. Urol Clin North Am. 1991. 18:229–41.2.Wagner TH., Patrick DL., Bavendam TG., Martin ML., Buesching DP. Quality of life of persons with urinary incontinence: development of a new measure. Urology. 1996. 47:67–71.
Article3.Peyromaure M., Ravery V., Boccon-Gibod L. The management of stress urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy. BJU Int. 2002. 90:155–61.
Article4.Van Kampen M., De Weerdt W., Van Poppel H., De Ridder D., Feys H., Baert L. Effect of pelvic-floor re-education on duration and degree of incontinence after radical prostatectomy: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2000. 355:98–102.
Article5.Chao R., Mayo ME. Incontinence after radical prostatectomy. detrusor or sphincter causes. J Urol. 1995. 154:16–8.
Article6.Leach GE., Yip CM., Donovan BJ. Post-prostatectomy incontinence: the influence of bladder dysfunction. J Urol. 1987. 138:574–8.
Article7.Srougi M., Nesrallah LJ., Kauffmann JR., Nesrallah A., Leite KR. Urinary continence and pathological outcome after bladder neck preservation during radical retropubic prostatectomy: a randomized prospective trial. J Urol. 2001. 165:815–8.
Article8.Kaye KW., Creed KE., Wilson GJ., D'Antuono M., Dawkins HJ. Urinary continence after radical retropubic prostatectomy. Analysis and synthesis of contributing factors: a unified concept. Br J Urol. 1997. 80:444–501.
Article9.Hunter KF., Moore KN., Cody DJ., Glazener CM. Conservative management for postprostatectomy urinary incontinence. Cochrance Database Syst Rev. 2007. 2:CD001843.
Article10.Filocamo MT., Li Marzi V., Del Popolo G., Cecconi F., Marzocco M., Tosto A, et al. Effectiveness of early pelvic floor rehabilitation treatment for post-prostatectomy incontinence. Eur Urol. 2005. 48:734–8.
Article11.Yamanishi T., Yasuda K., Sakakibara R., Hattori T., Ito H., Murakami S. Pelvic floor electrical stimulation in the treatment of stress incontinence: an investigational study and a placebo controlled double-blind trial. J Urol. 1997. 158:2127–31.
Article12.Han HS., Kim JI., Park SS. The effect of electrical stimulation and biofeedback for female urinary incontinence. Korean J Urol. 2001. 42:1063–7.13.Yamanishi T., Yasuda K., Suda S., Ishikawa N. Effect of functional continuous magnetic stimulation on urethral closure in healthy volunteers. Urology. 1999. 54:652–5.
Article14.Galloway NT., El-Galley RE., Sand PK., Appell RA., Russell HW., Carlin SJ. Update on extracorporeal magnetic innervation (ExMI) therapy for stress urinary incontinence. Urology. 2000. 56(6 Suppl 1):82–6.
Article15.Yokoyama T., Nishiguchi J., Watanabe T., Nose H., Nozaki K., Fujita O, et al. Comparative study of effects of extracorporeal magnetic innervation versus electrical stimulation for urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy. Urology. 2004. 63:264–7.
Article16.Nowak M., Jordan M., Haberl S., Herwig R., Kuehhas F., Brausi M, et al. Prospective study of extracorporeal magnetic innervation pelvic floor therapy (EXMI) versus standard pelvic floor training following radical prostatectomy: impact on timing and magnitude of recovery of continence. Eur Urol. 2007. 6(Suppl):): 143.17.Yamanishi T., Yasuda K., Suda S., Ishikawa N. Effect of functional continuous magnetic stimulation on urethral closure in healthy volunteers. Urology. 1999. 54:652–5.
Article18.Janez J., Plevnik S., Suhel P. Urethral and bladder responses to anal electrical stimulation. J Urol. 1979. 122:192–4.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Long Term Effect of Extracorporeal Magnetic Innervation Therapy with Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercise for Stress Urinary Incontinence
- Early Experience with Extracorporeal Magnetic Innervation (ExMI) Therapy for Stress Urinary Incontinence
- A Study on the Improvement of Urinary Incontinence Symptoms and Sexual Function in Patients with Urinary Incontinence before and after Extracorporeal Magnetic Innervation (ExMI) Therapy
- Effect of Extracorporeal Magnetic Innervation Therapy in the Patient with Stress Urinary Incontinence
- Comparative Study of the Pelvic Floor Magnetic Stimulation with BIOCON-2000TM in Female Urinary Incontinence Patients