J Cardiovasc Ultrasound.
2010 Jun;18(2):66-69. 10.4250/jcu.2010.18.2.66.
Papillary Fibroelastoma Presenting as a Left Ventricular Mass
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Pusan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. dongskim@inje.ac.kr
- 2Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Ulsan Hospital, Ulsan, Korea.
- KMID: 2135442
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4250/jcu.2010.18.2.66
Abstract
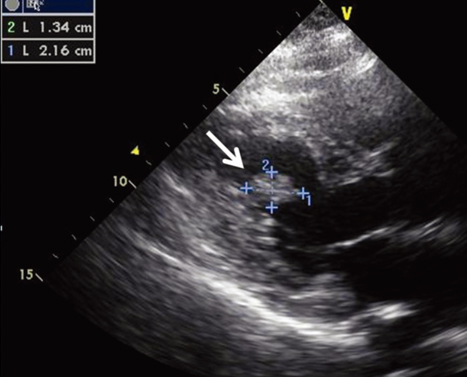
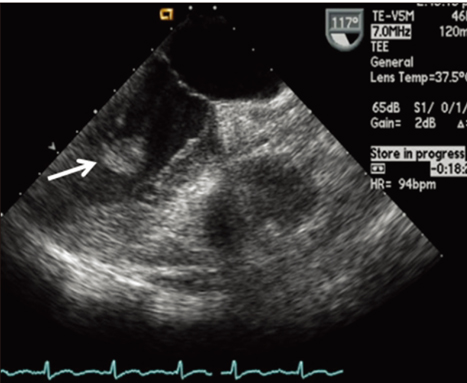
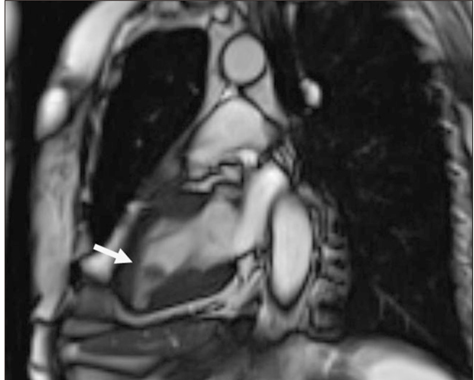
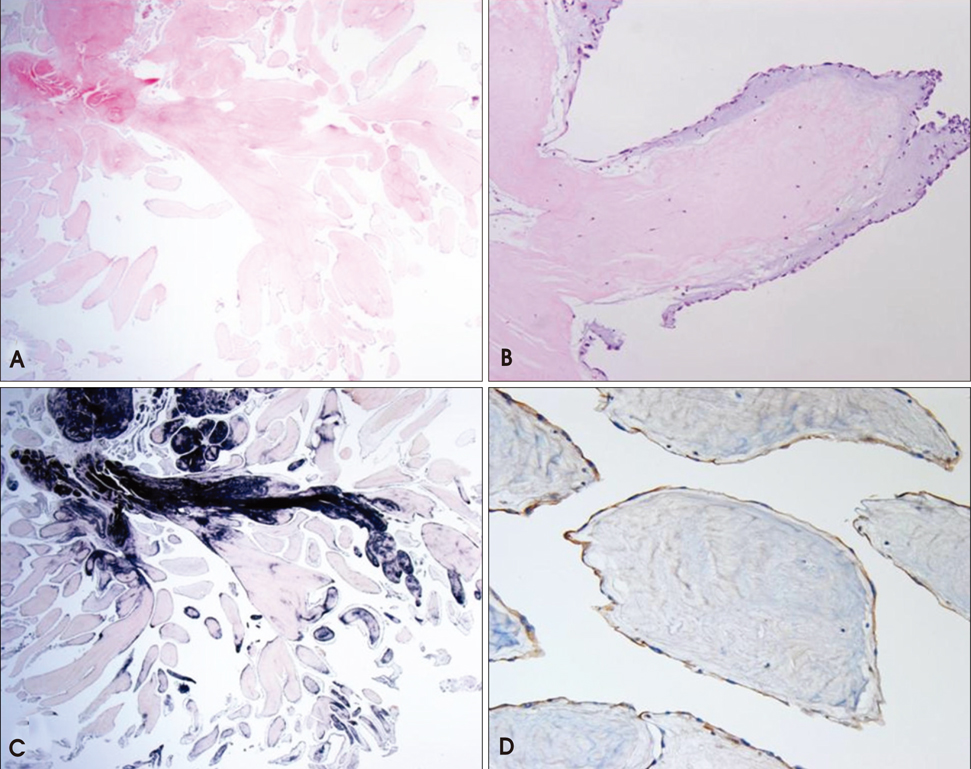
- Cardiac papillary fibroelastoma (CPF) is a benign cardiac tumor that usually affects cardiac valves. It is usually discovered incidentally on routine echocardiography. However, left ventricular CPF is rare. This report describes the case of a 73-year-old female, referred to a cardiology department for evaluation of a mass of the left ventricle. The mass was found routine echocardiography. The transthoracic echocardiography revealed a 2.2x1.3 cm highly oscillating mass, attached by stalk on the inferior wall of the left ventricle. Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging demonstrated a non-enhanced, 1.8x1.0 cm mass on the inferior wall of the left ventricle. The patient underwent surgical resection of the mass, histopathologic examination of the mass confirmed the diagnosis of a CPF.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Multiple Papillary Fibroelastomas and Thrombus in the Left Heart
Guang-Won Seo, Sang-Hoon Seol, Bo-Min Park, Tae-Jin Kim, Jae-Kyun Kim, Pil-Sang Song, Dong-Kie Kim, Ki-Hun Kim, Yeon Mee Kim, Doo-Il Kim
J Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2014;22(1):40-42. doi: 10.4250/jcu.2014.22.1.40.
Reference
-
1. Reynen K. Frequency of primary tumors of the heart. Am J Cardiol. 1996. 77:107.
Article2. Edwards FH, Hale D, Cohen A, Thompson L, Pezzella AT, Virmani R. Primary cardiac valve tumors. Ann Thorac Surg. 1991. 52:1127–1131.
Article3. Gowda RM, Khan IA, Nair CK, Mehta NJ, Vasavada BC, Sacchi TJ. Cardiac papillary fibroelastoma: a comprehensive analysis of 725 cases. Am Heart J. 2003. 146:404–410.
Article4. Mutlu H, Demir IE, Leppo J, Levy WK. Nonsurgical management of a left ventricular pedunculated papillary fibroelastoma: a case report. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2008. 21:877.e4. 877.e7.
Article5. Moustafa S, Sauvé C, Pagé P, Serri K. Incidental finding of a papillary fibroelastoma of the mitral valve chordae. Eur J Echocardiog. 2008. 9:745–746.
Article6. al-Mohammad A, Pambakian H, Young C. Fibroelastoma: case report and review of the literature. Heart. 1998. 79:301–304.
Article7. Klarich KW, Enriquez-Sarano M, Gura GM, Edwards WD, Tajik AJ, Seward JB. Papillary fibroelastoma: echocardiographic characteristics for diagnosis and pathologic correlation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1997. 30:784–790.
Article8. Parmley LF, Salley RK, Williams JP, Head GB 3rd. The clinical spectrum of cardiac fibroma with diagnostic and surgical considerations: noninvasive imaging enhances management. Ann Thorac Surg. 1988. 45:455–465.
Article9. Burke A, Virmani R. Tumors of the heart and great vessels. Atlas of tumor pathology 3rd Series. 1996. 1st ed. Washington DC, USA: American Registry of Pathology;47–54.10. Hong G, Byun YS, Kang S, Rim SJ, Chung N, Cho SY, Kim SS. A case of cardiac lipoma. J Korean Soc Echocardiogr. 2002. 10:8–10.
Article11. Sun JP, Asher CR, Yang XS, Cheng GG, Scalia GM, Massed AG, Griffin BP, Ratliff NB, Stewart WJ, Thomas JD. Clinical and echocardiographic characteristics of papillary fibroelastomas: a retrospective and prospective study in 162 patients. Circulation. 2001. 103:2687–2693.
Article12. Seol SH, Kim DS, Han YC, Kim KH, Kim YB, Kim DK, Kim U, Yang TH, Kim DI. Nonsurgical management of a tricuspid valvular pedunculated papillary fibroelastoma. Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2009. 7:44.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Papillary Fibroelastoma of the Left Ventricular Outflow Tract Causing Stroke
- Cardiac Papillary Fibroelastoma in Left Ventricular Trabeculation as a Potential Cause of Cerebral Infarction: A Case Report
- Anesthetic Management of the Excision of Left Ventricular Papillary Fibroelastoma : A case report
- Papillary Fibroelastoma Originating from the Left Ventricle: A case report
- Aortic Valve Papillary Fibroelastoma Triggering Chest Pain: A case report