Clin Endosc.
2012 Nov;45(4):358-361.
ESD Hands-on Course Using Ex Vivo and In Vivo Models in South Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Institute for Digestive Research, Digestive Disease Center, Soonchunhyang University Hospital, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. schcjy@schmc.ac.kr
Abstract
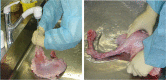
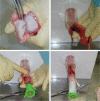
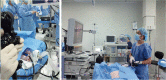
- Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) is an established treatment for gastric neoplasias especially in regions with a high volume of gastric cancer. Although ESD has many advantages over endoscopic mucosal resection, ESD is technically more difficult and can result in severe complications. Therefore establishment of an effective training system is required to help endoscopists climb the ESD learning curve. Although a standard training system for ESD remains to be established, some centers are incorporating ex vivo and/or in vivo animal models to provide a safe and effective means of ESD training. However, it is unknown if these animal models are more effective than other programs. Moreover the efficacy of the animal model may vary according to socio-economic status and the volume of gastric cancer. In this article we introduce the basic and advanced ESD training model using the ex vivo and in vivo animal model from South Korea and review the associated literature from other regions.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Vazquez-Sequeiros E, de Miquel DB, Olcina JR, et al. Training model for teaching endoscopic submucosal dissection of gastric tumors. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2009; 101:546–552. PMID: 19785494.
Article2. Parra-Blanco A, Arnau MR, Nicolás-Pérez D, et al. Endoscopic submucosal dissection training with pig models in a Western country. World J Gastroenterol. 2010; 16:2895–2900. PMID: 20556835.
Article3. Tanaka S, Morita Y, Fujita T, et al. Ex vivo pig training model for esophageal endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) for endoscopists with experience in gastric ESD. Surg Endosc. 2012; 26:1579–1586. PMID: 22223113.4. Hon SS, Ng SS, Lee JF, Li JC, Lo AW. In vitro porcine training model for colonic endoscopic submucosal dissection: an inexpensive and safe way to acquire a complex endoscopic technique. Surg Endosc. 2010; 24:2439–2443. PMID: 20333407.
Article5. Teoh AY, Chiu PW, Wong SK, Sung JJ, Lau JY, Ng EK. Difficulties and outcomes in starting endoscopic submucosal dissection. Surg Endosc. 2010; 24:1049–1054. PMID: 19911227.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (ESD) Training and Performing ESD with Accurate and Safe Techniques
- Is Ex Vivo Training before In Vivo Training Effective in Learning Gastric Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection?
- Ex Vivo and In Vivo Models for Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection Training
- Diode Laser—Can It Replace the Electrical Current Used in Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection? (with Video)
- Effectiveness of a novel ex vivo training model for gastric endoscopic submucosal dissection training: a prospective observational study conducted at a single center in Japan