Clin Endosc.
2012 Sep;45(3):285-287.
Indications, Knives, and Electric Current: What's the Best?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Incheon St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea. gidoc4u@catholic.ac.kr
Abstract
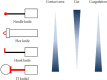
- Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) was developed to overcome the limitations of conventional endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR), and ESD has been also applied for large colorectal neoplasms. Since colorectal ESD is still associated with higher perforation rate, a longer procedure time, and increased technical difficulty, the indications should be strictly considered. Generally, colorectal tumors without deep submucosal invasion or minimal possibility of lymph node metastasis, for which en bloc resection using conventional EMR is difficult, are good candidates for colorectal ESD. The ideal knife for colorectal ESD should avoid making perforations but can make a clean cut of optimal depth at one time. The ideal current for ESD differs depending on the procedure used, the surgical devices used, the tissue to be dissected, and the operator's preference. Application of the optimal indications and improvements in the technical skill and surgical devices are required for easier and safer colorectal ESD.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Saito Y, Uraoka T, Matsuda T, et al. Endoscopic treatment of large superficial colorectal tumors: a case series of 200 endoscopic submucosal dissections (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 66:966–973. PMID: 17524403.
Article2. Fujishiro M, Yahagi N, Kakushima N, et al. Outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal epithelial neoplasms in 200 consecutive cases. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007; 5:678–683. PMID: 17466600.
Article3. Toyonaga T, Man-i M, Fujita T, et al. Retrospective study of technical aspects and complications of endoscopic submucosal dissection for laterally spreading tumors of the colorectum. Endoscopy. 2010; 42:714–722. PMID: 20806155.
Article4. Kitajima K, Fujimori T, Fujii S, et al. Correlations between lymph node metastasis and depth of submucosal invasion in submucosal invasive colorectal carcinoma: a Japanese collaborative study. J Gastroenterol. 2004; 39:534–543. PMID: 15235870.
Article5. Ueno H, Mochizuki H, Hashiguchi Y, et al. Risk factors for an adverse outcome in early invasive colorectal carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2004; 127:385–394. PMID: 15300569.
Article6. Tanaka S, Terasaki M, Kanao H, Oka S, Chayama K. Current status and future perspectives of endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal tumors. Dig Endosc. 2012; 24(Suppl 1):73–79. PMID: 22533757.
Article7. Kim ES, Cho KB, Park KS, et al. Factors predictive of perforation during endoscopic submucosal dissection for the treatment of colorectal tumors. Endoscopy. 2011; 43:573–578. PMID: 21448852.
Article8. Tanaka S. Basic Technique of Endoscopic Mucosal Resection and Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection for Colorectal Tumors: Knack, Pitfall, and Conclusive Evidence of Adjustment. 2006. Tokyo: Mejikaru Byusha.9. Hotta K, Yamaguchi Y, Saito Y, Takao T, Ono H. Current opinions for endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal tumors from our experiences: indications, technical aspects and complications. Dig Endosc. 2012; 24(Suppl 1):110–116. PMID: 22533764.
Article10. Homma K, Otaki Y, Sugawara M, Kobayashi M. Efficacy of novel SB knife Jr examined in a multicenter study on colorectal endoscopic submucosal dissection. Dig Endosc. 2012; 24(Suppl 1):117–120. PMID: 22533765.
Article11. Akahoshi K, Akahane H, Motomura Y, et al. A new approach: endoscopic submucosal dissection using the Clutch Cutter(R) for early stage digestive tract tumors. Digestion. 2012; 85:80–84. PMID: 22269283.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Study of Peritoneal Dialysis: II. Influence of Electric Current in Peritoneal Dialysis
- Comparison of scissor-type knife to non-scissor-type knife for endoscopic submucosal dissection: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- The effects of electrical current from a micro-electrical device on tooth movement
- Stimulatory and Inhibitory Effects of Alternating Current on the Growth of Trichophyton rubrum
- Clinical Characteristics of Electric Cataract