Brain Tumor Res Treat.
2014 Oct;2(2):87-91. 10.14791/btrt.2014.2.2.87.
Immunoglobulin G4-Related Hypertrophic Pachymeningitis with Skull Involvement
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. jhwang@knu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2134277
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14791/btrt.2014.2.2.87
Abstract
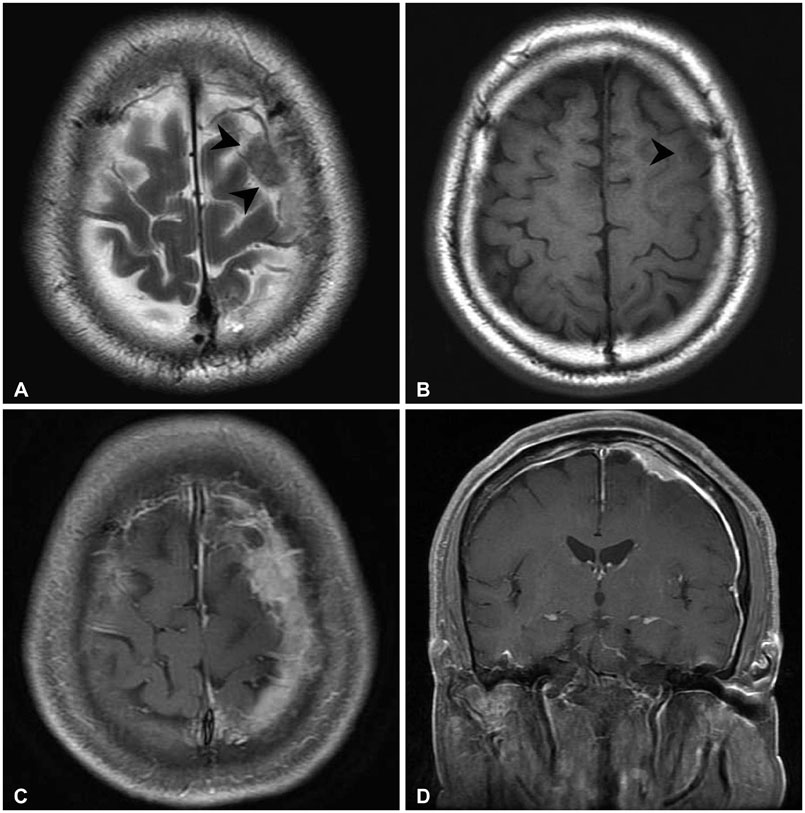
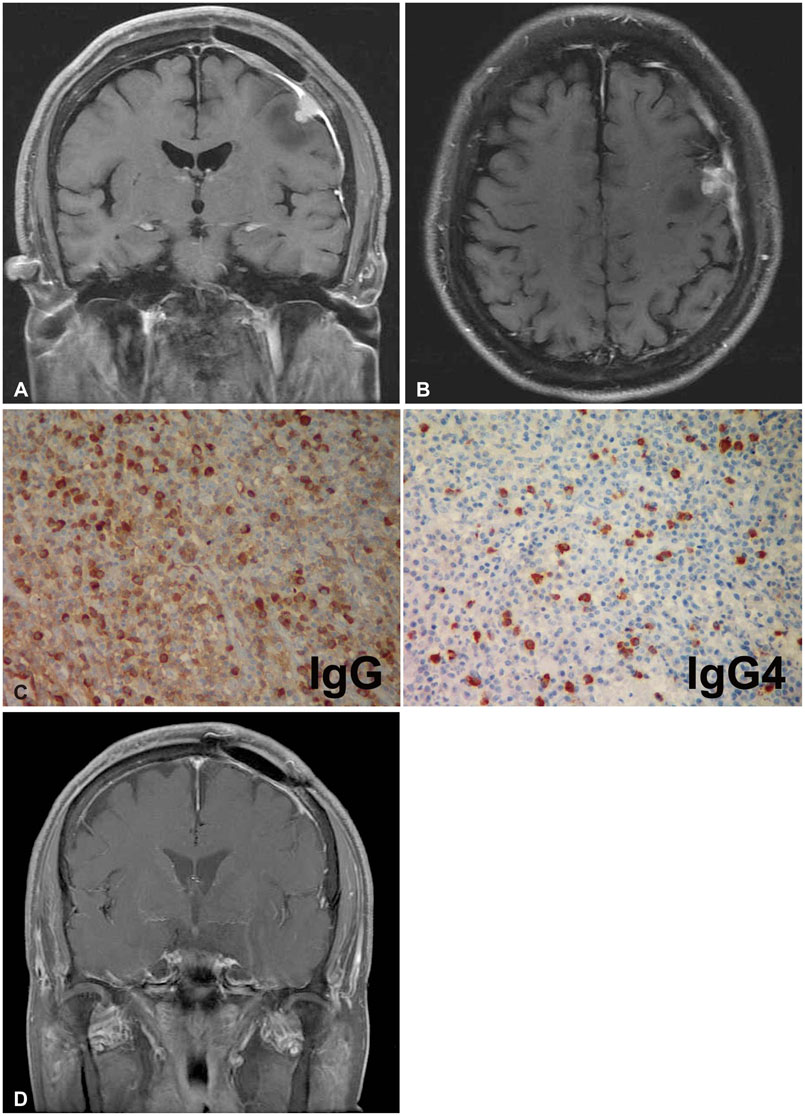
- Immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4)-related hypertrophic pachymeningitis, defined as focally or diffusely thickened dura mater and lymphoplasmacytic infiltration with increased IgG4 bearing plasma cells, is a rare disease. Moreover, cases involving bone are even rarer. In this report, the authors describe a case of IgG4-related hypertrophic pachymeningitis involving the skull in a 65-year-old man presenting with generalized tonic seizures. There is a 2.4 cm diameter extra-axial mass at the vertex of the left frontal convexity and thickened dura mater with contrast enhancement on magnetic resonance (MR) imaging. In addition, the skull adjacent to the mass was focally enhanced. He underwent surgical resection of the enhanced mass and skull. Histopathological findings revealed chronic inflammation with fibrosis, and idiopathic hypertrophic intracranial pachymeningitis was considered. However, eight months after surgery, partial seizures developed and brain MR imaging revealed a recurrence adjacent to the previous mass. We decided to perform additional immunohistochemical staining of the previous specimen, instead of a re-excision. Immunohistochemical staining showed markedly increased IgG4 (+) plasma cells. Consequently, IgG4-related hypertrophic meningitis was confirmed. Since then, steroids and immunosuppressant medications were started. Follow-up MR imaging at 3 months after medication initiation demonstrated complete remission. In conclusion, IgG4-related hypertrophic pachymeningitis should be considered in the differential diagnosis of hypertrophic cranial pachymeningitis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A Case of IgG4 Related Pachymeningitis
Ji In Kim, Jin Taek Song, Hyeong Ju Kwon, Ji-Yong Lee
J Neurocrit Care. 2016;9(2):162-165. doi: 10.18700/jnc.160075.
Reference
-
1. Stone JH, Zen Y, Deshpande V. IgG4-related disease. N Engl J Med. 2012; 366:539–551.
Article2. Della-Torre E, Galli L, Franciotta D, et al. Diagnostic value of IgG4 Indices in IgG4-related hypertrophic pachymeningitis. J Neuroimmunol. 2014; 266:82–86.
Article3. Chan SK, Cheuk W, Chan KT, Chan JK. IgG4-related sclerosing pachymeningitis: a previously unrecognized form of central nervous system involvement in IgG4-related sclerosing disease. Am J Surg Pathol. 2009; 33:1249–1252.4. Kim EH, Kim SH, Cho JM, Ahn JY, Chang JH. Immunoglobulin G4-related hypertrophic pachymeningitis involving cerebral parenchyma. J Neurosurg. 2011; 115:1242–1247.
Article5. Shapiro KA, Bové RM, Volpicelli ER, Mallery RM, Stone JH. Relapsing course of immunoglobulin G4-related pachymeningitis. Neurology. 2012; 79:604–606.
Article6. Mamelak AN, Kelly WM, Davis RL, Rosenblum ML. Idiopathic hypertrophic cranial pachymeningitis. Report of three cases. J Neurosurg. 1993; 79:270–276.7. Hamano H, Kawa S, Horiuchi A, et al. High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 2001; 344:732–738.
Article8. Lin CK, Lai DM. IgG4-related intracranial hypertrophic pachymeningitis with skull hyperostosis: a case report. BMC Surg. 2013; 13:37.
Article9. Lindstrom KM, Cousar JB, Lopes MB. IgG4-related meningeal disease: clinico-pathological features and proposal for diagnostic criteria. Acta Neuropathol. 2010; 120:765–776.
Article10. Parney IF, Johnson ES, Allen PB. "Idiopathic" cranial hypertrophic pachymeningitis responsive to antituberculous therapy: case report. Neurosurgery. 1997; 41:965–971.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Immunoglobulin G4-related hypertrophic pachymeningitis with an isolated scalp mass mimicking a brain tumor: a case report and literature review
- Immunoglobulin G4-Related Hypertrophic Pachymeningitis Presenting with Multiple Lower Cranial Nerve Palsies
- IgG4-Related Hypertrophic Pachymeningitis Mimicking Cerebral Venous Thrombosis
- An Immunoglobulin G4 Related Hypertrophic Pachymeningitis Presented with Recurrent Ophthalmoplegia
- An Immunoglobulin G4-Related Hypertrophic Pachymeningitis Involving Cerebral Parenchyma