Blood Res.
2015 Dec;50(4):254-256. 10.5045/br.2015.50.4.254.
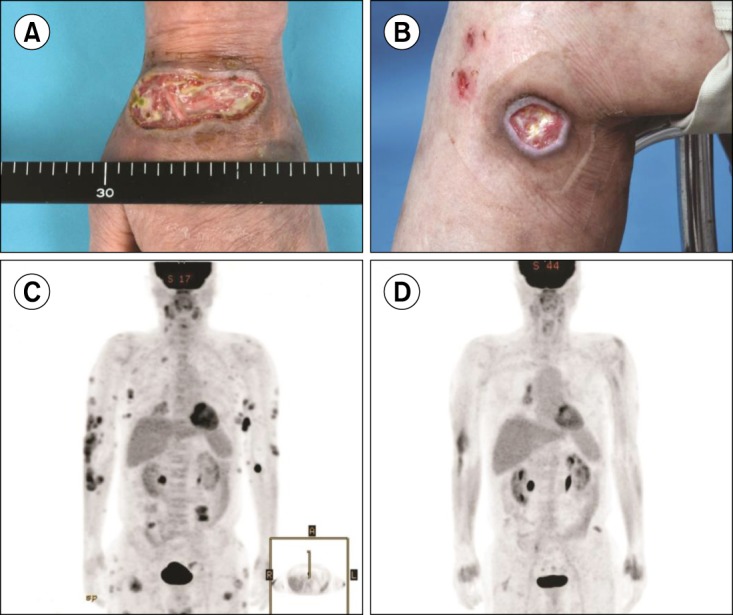
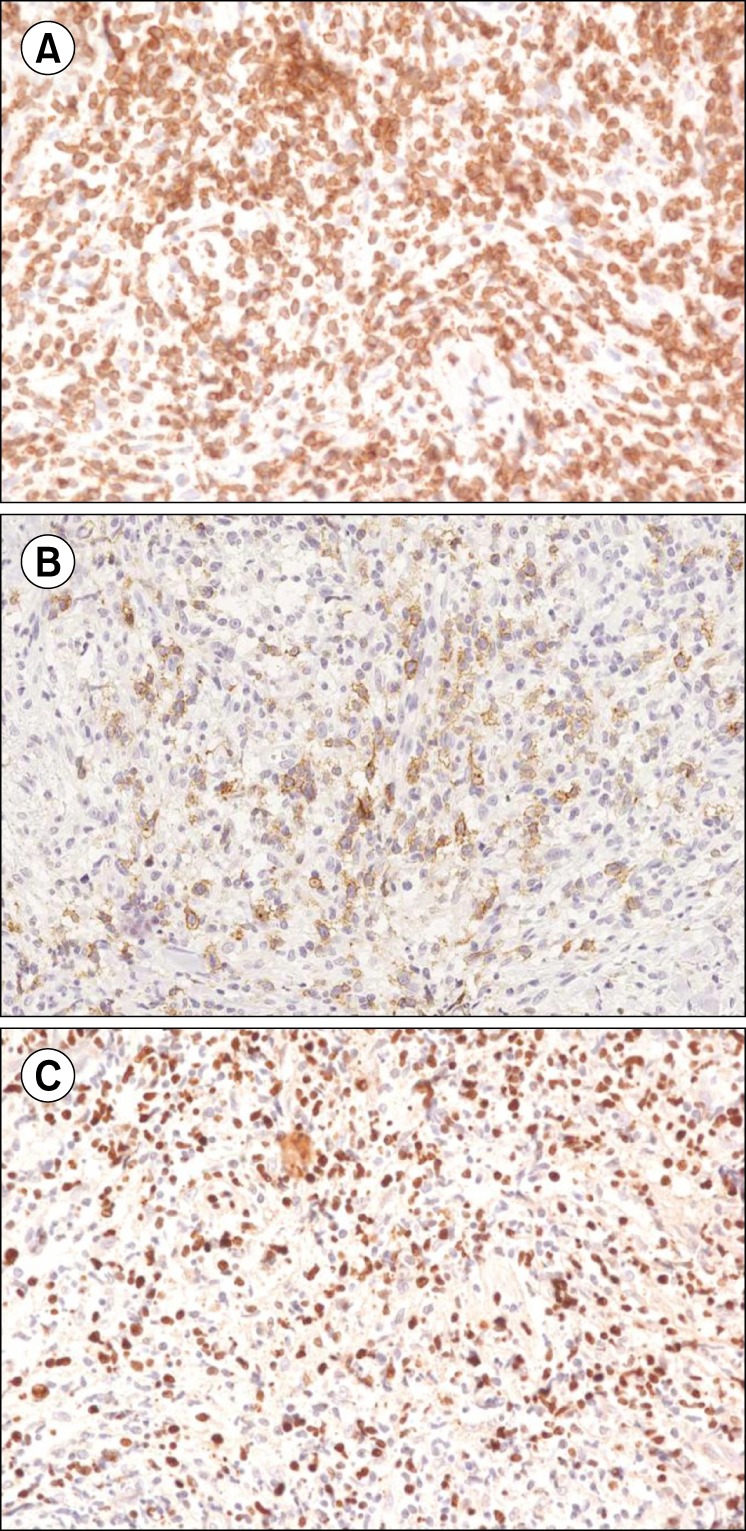
Complete remission in CD30-positive refractory extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma with brentuximab vedotin
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Hematology-Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. gmlrud16.kim@samsung.com
- KMID: 2133761
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/br.2015.50.4.254
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma
Seong Hyun Jeong
Blood Res. 2020;55(Supplement):S63-S71. doi: 10.5045/br.2020.S011.Extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma
Seong Hyun Jeong
Blood Res. 2020;55(S1):S63-S71. doi: 10.5045/br.2020.S011.
Reference
-
1. Yamaguchi M, Suzuki R, Kwong YL, et al. Phase I study of dexamethasone, methotrexate, ifosfamide, L-asparaginase, and etoposide (SMILE) chemotherapy for advanced-stage, relapsed or refractory extranodal natural killer (NK)/T-cell lymphoma and leukemia. Cancer Sci. 2008; 99:1016–1020. PMID: 18294294.
Article2. Younes A, Bartlett NL, Leonard JP, et al. Brentuximab vedotin (SGN-35) for relapsed CD30-positive lymphomas. N Engl J Med. 2010; 363:1812–1821. PMID: 21047225.
Article3. Pro B, Advani R, Brice P, et al. Brentuximab vedotin (SGN-35) in patients with relapsed or refractory systemic anaplastic large-cell lymphoma: results of a phase II study. J Clin Oncol. 2012; 30:2190–2196. PMID: 22614995.
Article4. Horwitz SM, Advani RH, Bartlett NL, et al. Objective responses in relapsed T-cell lymphomas with single-agent brentuximab vedotin. Blood. 2014; 123:3095–3100. PMID: 24652992.
Article5. Kwong YL. Natural killer-cell malignancies: diagnosis and treatment. Leukemia. 2005; 19:2186–2194. PMID: 16179910.
Article6. Falini B, Pileri S, Pizzolo G, et al. CD30 (Ki-1) molecule: a new cytokine receptor of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily as a tool for diagnosis and immunotherapy. Blood. 1995; 85:1–14. PMID: 7803786.
Article7. Hong J, Park S, Baek HL, et al. Tumor cell nuclear diameter and CD30 expression as potential prognostic parameter in patients with extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2012; 5:939–947. PMID: 23119111.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Brentuximab vedotin: clinical updates and practical guidance
- CD30+ Large-Cell Transformation of Mycosis Fungoides Treated with Brentuximab Vedotin
- A multi-center and non-interventional registry of brentuximab vedotin in patients with relapsed or refractory CD30-positive lymphoma: the CISL1803/BRAVO study
- Recent updates on extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma
- A Case of Primary Cutaneous CD30(Ki-1)-positive Large Cell Lymphoma Showing Repetitive Spontaneous Regression and Recurrences