Korean J Urol.
2015 Mar;56(3):233-239. 10.4111/kju.2015.56.3.233.
Comparative analysis of benign prostatic hyperplasia management by urologists and nonurologists: A Korean nationwide health insurance database study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Seoul Metropolitan Government-Seoul National University Boramae Medical Center, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. volley@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Urology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Urology, Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Urology, Eulji General Hospital, Eulji University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Urology, Inje University Busan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 6Department of Urology, Chungbuk National University Hospital, Chungbuk National University College of Medicine, Cheongju, Korea.
- 7Department of Urology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 8Department of Urology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2133292
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/kju.2015.56.3.233
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To compare the current management of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) by urologists and nonurologists by use of Korean nationwide health insurance data.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We obtained patient data from the national health insurance system. New patients diagnosed with BPH in 2009 were divided into two groups depending on whether they were diagnosed by a urologist (U group) or by a nonurologist (NU group).
RESULTS
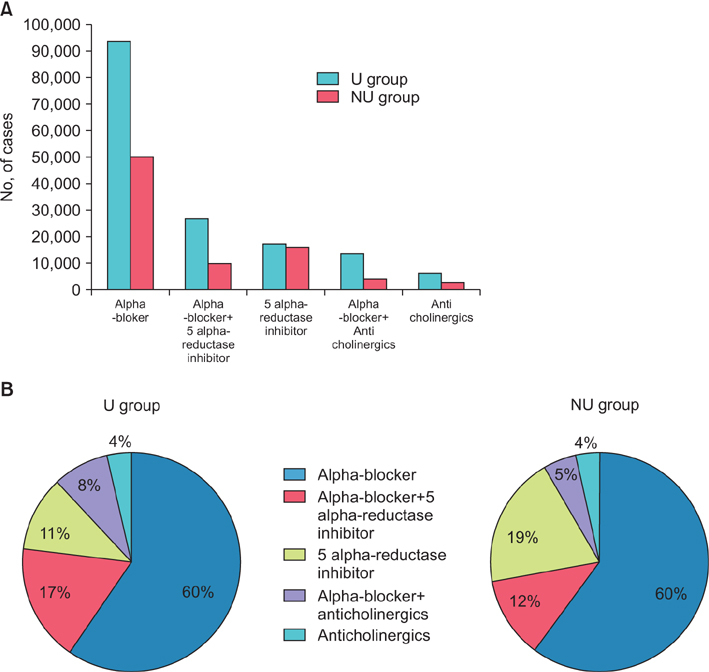
A total of 390,767 individuals were newly diagnosed with BPH in 2009. Of these, 240,907 patients (61.7%) were in the U group and 149,860 patients (38.3%) were in the NU group. The rate of all initial evaluation tests, except serum creatinine, was significantly lower in the NU group. The initial prescription rate was higher in the U group, whereas the prescription period was longer in the NU group. Regarding the initial drugs prescribed, the use of alpha-blockers was common in both groups. However, the U group was prescribed combination therapy of an alpha-blocker and 5-alpha-reductase inhibitor as the second choice, whereas the NU group received monotherapy with a 5-alpha-reductase inhibitor. During the 1-year follow-up, the incidence of surgery was significantly different between the U group and the NU group.
CONCLUSIONS
There are distinct differences in the diagnosis and treatment of BPH by urologists and nonurologists in Korea. These differences may have adverse consequences for BPH patients. Urological societies should take a leadership role in the management of BPH and play an educational role for nonurologists as well as urologists.
MeSH Terms
-
5-alpha Reductase Inhibitors/therapeutic use
Adrenergic alpha-Antagonists/therapeutic use
Adult
Age Distribution
Aged
Aged, 80 and over
Databases, Factual
*Disease Management
Humans
Insurance, Health
Linear Models
Male
Middle Aged
Physicians
Prostatic Hyperplasia/*diagnosis/*therapy
Republic of Korea
Urology/*methods
Young Adult
5-alpha Reductase Inhibitors
Adrenergic alpha-Antagonists
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Recent Trends in Transurethral Surgeries and Urological Outpatient Procedures: a Nationwide Population-based Cohort Study
Jong Keun Kim, Changil Choi, Ui Seok Kim, Hyosang Kwon, Seong Ho Lee, Young Goo Lee, Jun Hyun Han
J Korean Med Sci. 2020;35(38):e315. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e315.
Reference
-
1. McNicholas TA. Lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic obstruction: what are the current practice patterns? Eur Urol. 2001; 39:Suppl 3. 26–30.2. Montorsi F, Mercadante D. Diagnosis of BPH and treatment of LUTS among GPs: a European survey. Int J Clin Pract. 2013; 67:114–119.3. Toguri A, Barkin J. Management of benign prostatic hyperplasia by family physicians. Can J Urol. 2010; 17:Suppl 1. 26–34.4. Cho KH, Roh YK. Primary care physicians shortage: a Korean example. Public Health Rev. 2003; 31:133–148.5. Kang JY, Min GE, Son H, Kim HT, Lee HL. National-wide data on the treatment of BPH in Korea. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2011; 14:243–247.6. Huh JS, Kim YJ, Kim SD. Prevalence of benign prostatic hyperplasia on Jeju island: analysis from a cross-sectional community-based survey. World J Mens Health. 2012; 30:131–137.7. Lee E, Yoo KY, Kim Y, Shin Y, Lee C. Prevalence of lower urinary tract symptoms in Korean men in a community-based study. Eur Urol. 1998; 33:17–21.8. Lee E, Park MS, Shin C, Lee H, Yoo K, Kim Y, et al. A high-risk group for prostatism: a population-based epidemiological study in Korea. Br J Urol. 1997; 79:736–741.9. McVary KT, Roehrborn CG, Avins AL, Barry MJ, Bruskewitz RC, Donnell RF, et al. Update on AUA guideline on the management of benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Urol. 2011; 185:1793–1803.10. Madersbacher S, Alivizatos G, Nordling J, Sanz CR, Emberton M, de la. EAU 2004 guidelines on assessment, therapy and follow-up of men with lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic obstruction (BPH guidelines). Eur Urol. 2004; 46:547–554.11. Strope SA, Elliott SP, Saigal CS, Smith A, Wilt TJ, Wei JT, et al. Urologist compliance with AUA best practice guidelines for benign prostatic hyperplasia in Medicare population. Urology. 2011; 78:3–9.12. Oh CY, Lee SH, Yoo SJ, Chung BH. Korean urologist's view of practice patterns in diagnosis and management of benign prostatic hyperplasia: a nationwide survey. Yonsei Med J. 2010; 51:248–252.13. Modi P, Helfand BT, McVary KT. Medications and surgical interventions for benign prostatic hyperplasia are potential confounders of prostate-specific antigen. Curr Urol Rep. 2010; 11:224–227.14. Cornu JN, Cussenot O, Haab F, Lukacs B. A widespread population study of actual medical management of lower urinary tract symptoms related to benign prostatic hyperplasia across Europe and beyond official clinical guidelines. Eur Urol. 2010; 58:450–456.15. Saigal CS, Joyce G. Economic costs of benign prostatic hyperplasia in the private sector. J Urol. 2005; 173:1309–1313.16. Kang HY, Yang KH, Kim YN, Moon SH, Choi WJ, Kang DR, et al. Incidence and mortality of hip fracture among the elderly population in South Korea: a population-based study using the national health insurance claims data. BMC Public Health. 2010; 10:230.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Korean Urologist's View of Practice Patterns in Diagnosis and Management of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Nationwide Survey
- A Prominently Large Glans penis as a Possible sign of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- Prostate Artery Embolization: Treatment of Symptomatic Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- Patterns in the Diagnosis and Management of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in a Country that does not have Country-Specific Clinical Practice Guidelines
- Chinese Urologists' Views of Practice Patterns in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Nationwide Survey