Effects of a Coaching Program on Comprehensive Lifestyle Modification for Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Nursing, Cheongju University, Cheongju, Korea.
- 2Department of Nursing, Dankook University, Cheonan, Korea. kyunglee@dankook.ac.kr
- KMID: 2129558
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.6.672
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of using a Coaching Program on Comprehensive Lifestyle Modification with pregnant women who have gestational diabetes.
METHODS
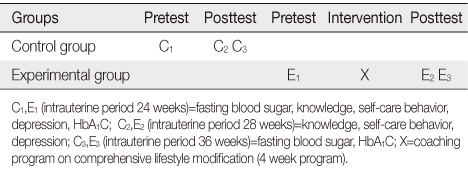
The research design for this study was a non-equivalent control group quasi-experimental study. Pregnant women with gestational diabetes were recruited from D women's hospital located in Gyeonggi Province from April to October, 2013. Participants in this study were 34 for the control group and 34 for the experimental group. The experimental group participated in the Coaching Program on Comprehensive Lifestyle Modification. The program consisted of education, small group coaching and telephone coaching over 4weeks. Statistical analysis was performed using the SPSS 21.0 program.
RESULTS
There were significant improvements in self-care behavior, and decreases in depression, fasting blood sugar and HbA1C in the experimental group compared to the control group. However, no significant differences were found between the two groups for knowledge of gestational diabetes mellitus.
CONCLUSION
The Coaching Program on Comprehensive Lifestyle Modification used in this study was found to be effective in improving self-care behavior and reducing depression, fasting blood sugar and HbA1C, and is recommended for use in clinical practice as an effective nursing intervention for pregnant women with gestational diabetes.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 7 articles
-
The effects of health care programs for gestational diabetes mellitus in South Korea: a systematic review
Seo Jin Park, Jina Lee
Korean J Women Health Nurs. 2020;26(4):274-284. doi: 10.4069/kjwhn.2020.10.28.Effects of a Postnatal Care Program on Self-efficacy, Self-management, and Glycemic Control in Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Yeong Kyung Jeon, Hyo Jin Kim, Mi Yeon Yang, Da Yeong Jung, Kum Young Yoon, Gie Ok Noh
Korean J Women Health Nurs. 2018;24(4):367-378. doi: 10.4069/kjwhn.2018.24.4.367.Effects of a Group Coaching Program on Depression, Anxiety and Hope in Women with Breast Cancer Undergoing Chemotherapy
So Ryoung Seong, Moon-kyung Cho, Jeeyoon Kim, Yeo Ok Kim
Asian Oncol Nurs. 2017;17(3):188-199. doi: 10.5388/aon.2017.17.3.188.Psychosocial support interventions for women with gestational diabetes mellitus: a systematic review
Seulgi Jung, Yoojin Kim, Jeongok Park, Miyoung Choi, Sue Kim
Korean J Women Health Nurs. 2021;27(2):75-92. doi: 10.4069/kjwhn.2021.05.13.Effects of nonpharmacological interventions on the psychological health of high-risk pregnant women: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Hyeji Yoo, Sukhee Ahn
Korean J Women Health Nurs. 2021;27(3):180-195. doi: 10.4069/kjwhn.2021.09.17.The Effects of Snack Control Education and Telephone Coaching on Self-Management, Social Support, Self-Efficacy, and Blood Glucose in Diabetes Patients
Hye Eun Park
J Korean Diabetes. 2021;22(4):274-283. doi: 10.4093/jkd.2021.22.4.274.Prepregnancy Glucose Levels Within Normal Range and Its Impact on Obstetric Complications in Subsequent Pregnancy: A Population Cohort Study
Ho Yeon Kim, Ki Hoon Ahn, Geum Joon Cho, Soon-Cheol Hong, Min-Jeong Oh, Hai-Joong Kim
J Korean Med Sci. 2023;38(35):e286. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e286.
Reference
-
1. The Korean Diabetes Association. Diabetes fact sheet in Korea 2013 [Internet]. Seoul: Author;2013. cited 2013 October 12. Available from: www.diabetes.or.kr/temp/diabetes_factsheet_2013111.pdf.2. Reece EA. The fetal and maternal consequences of gestational diabetes mellitus. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2010; 23(3):199–203. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/14767050903550659.3. Jang HC. Diagnosis of gestational diabetes mellitus. Clin Diabetes. 2006; 7(4):296–301.4. Park JE. Effective education strategies for women with gestational diabetes mellitus. J Korean Diabetes. 2012; 13(3):148–151. http://dx.doi.org/10.4093/jkd.2012.13.3.148.5. Choi ES, Oh JA, Hur MH, Lee IS, Choi SY. The knowledge and learning needs about gestational diabetes in pregnant women. J Korean Acad Womens Health Nurs. 2000; 6(1):96–108.6. Katon JG, Russo J, Gavin AR, Melville JL, Katon WJ. Diabetes and depression in pregnancy: Is there an association? J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2011; 20(7):983–989. http://dx.doi.org/10.1089/jwh.2010.2662.7. McKellar JD, Humphreys K, Piette JD. Depression increases diabetes symptoms by complicating patients' self-care adherence. Diabetes Educ. 2004; 30(3):485–492.8. Whitmore J. Coaching for performance: GROWing human potential and purpose: The principles and practice of coaching and leadership. 4th ed. London, UK: Nicholas Brealey Publishing;2009.9. Hayes E, Kalmakis KA. From the sidelines: Coaching as a nurse practitioner strategy for improving health outcomes. J Am Acad Nurse Pract. 2007; 19(11):555–562. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-7599.2007.00264.x.10. Whittemore R, Melkus GD, Sullivan A, Grey M. A nurse-coaching intervention for women with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Educ. 2004; 30(5):795–804.11. Navicharern R, Aungsuroch Y, Thanasilp S. Effects of multifaceted nurse-coaching intervention on diabetic complications and satisfaction of persons with type 2 diabetes. J Med Assoc Thai. 2009; 92(8):1102–1112.12. Olsen JM, Nesbitt BJ. Health coaching to improve healthy lifestyle behaviors: An integrative review. Am J Health Promot. 2010; 25(1):e1–e12. http://dx.doi.org/10.4278/ajhp.090313-LIT-101.13. Jeon HO, Kim O. The effects of an internet based coaching program for obesity management in hypertensive patients. Korean J Adult Nurs. 2011; 23(2):146–159.14. Hwang JY. The effects of group coaching program on self-esteem, subjective-wellbeing, depression for middle-aged housewives [master's thesis]. Seoul: Kwangwoon University;2012.15. Armstrong C, Wolever RQ, Manning L, Elam R 3rd, Moore M, Frates EP, et al. Group health coaching: Strengths, challenges, and next steps. Glob Adv Health Med. 2013; 2(3):95–102. http://dx.doi.org/10.7453/gahmj.2013.019.16. Kim S, Kim HS, Cheong HY. Effects of a coaching-based childbirth program on anxiety and childbirth self-efficacy among primigravida women. Korean J Women Health Nurs. 2011; 17(4):369–377. http://dx.doi.org/10.4069/kjwhn.2011.17.4.369.17. Gu MO. The effect of a self regulation education program for the promotion and maintenance of self care behavior in the chronically ill patients: For diabetic patients. J Nurs Acad Soc. 1996; 26(2):413–427.18. Bae JI. Construction of a postpartum depression model [dissertation]. Seoul: Ewha Womans University;1996.19. Korea Association of Diabetes Nurse Educator. Gestational diabetes [Internet]. Seoul: Author;2013. cited 2013 September 8. Available from: http://kadne.cafe24.com/bbs/board.php?bo_table=sub3_13&wr_id=8.20. Park JY. A study for developing an effective group coaching process. J Korean Coaching Res. 2010; 3(1):41–64.21. Lee YR, Kang MA, Kim PG. The effects of an admission-education program on knowledge, self-efficacy, self-care and glucose control in type 2 diabetes patients. J Korean Acad Soc Nurs Educ. 2008; 14(1):12–19.22. Paek KS. The effect of a diabetic education program on self-care behavior and glucose metabolism in type 2 diabetic patients. J Korean Community Nurs. 2001; 12(2):390–396.23. Wolever RQ, Dreusicke M, Fikkan J, Hawkins TV, Yeung S, Wakefield J, et al. Integrative health coaching for patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized clinical trial. Diabetes Educ. 2010; 36(4):629–639. http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/0145721710371523.24. Polonsky WH, Earles J, Smith S, Pease DJ, Macmillan M, Christensen R, et al. Integrating medical management with diabetes self-management training: A randomized control trial of the diabetes outpatient intensive treatment program. Diabetes Care. 2003; 26(11):3048–3053.25. Radder JK, van Roosmalen J. HbA1c in healthy, pregnant women. Neth J Med. 2005; 63(7):256–259.26. Yoo JS, Lee SJ, Lee HC, Kim MJ. The effect of a comprehensive lifestyle modification program on glycemic control and body composition in patients with type 2 diabetes. Asian Nurs Res (Korean Soc Nurs Sci). 2007; 1(2):106–115. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/s1976-1317(08)60013-4.27. Kim H, Kim S. Effects of an integrated self-management program on self-management, glycemic control, and maternal identity in women with gestational diabetes mellitus. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2013; 43(1):69–80. http://dx.doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.1.69.28. Homko CJ, Santamore WP, Whiteman V, Bower M, Berger P, Geifman-Holtzman O, et al. Use of an internet-based telemedicine system to manage underserved women with gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2007; 9(3):297–306. http://dx.doi.org/10.1089/dia.2006.0034.29. Thom DH, Ghorob A, Hessler D, De Vore D, Chen E, Bodenheimer TA. Impact of peer health coaching on glycemic control in low-income patients with diabetes: A randomized controlled trial. Ann Fam Med. 2013; 11(2):137–144. http://dx.doi.org/10.1370/afm.1443.30. Katon J, Williams MA, Reiber G, Miller E. Antepartum A1C, maternal diabetes outcomes, and selected offspring outcomes: An epidemiological review. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 2011; 25(3):265–276. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3016.2011.01195.x.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Lifestyle Modification Coaching Program for Secondary Stroke Prevention
- Effective Education Strategies for Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
- The Effects of a Comprehensive Life Style Modification Program on Glycemic Control and Stress Response in Type 2 Diabetes
- Diabetes in pregnancy
- Nutrition Care in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus