J Adv Prosthodont.
2010 Sep;2(3):111-115. 10.4047/jap.2010.2.3.111.
A study on the in-vitro wear of the natural tooth structure by opposing zirconia or dental porcelain
- Affiliations
-
- 1Advanced Prosthodontics, Graduate School of Clinical Dentistry, Korea University, Seoul, Korea. neoplasia96@korea.ac.kr
- 2Institute for Clinical Dental Research, Korea University, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Prosthodontics, Korea University Anam Hospital, Korea University, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Dental Biomaterials Science, School of Dentistry, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2118117
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jap.2010.2.3.111
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study was conducted to evaluate clinical validity of a zirconia full-coverage crown by comparing zirconia's wear capacity over antagonistic teeth with that of feldspathic dental porcelain.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
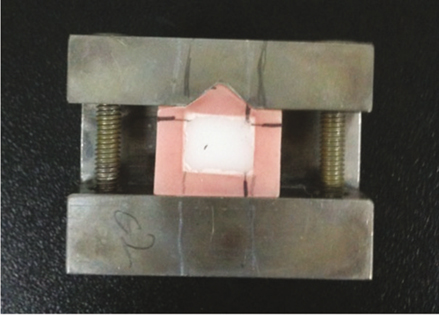
The subject groups were divided into three groups: the polished feldspathic dental porcelain group (Group 1), the polished zirconia group (Group 2), and the polished zirconia with glazing group (Group 3). Twenty specimens were prepared from each group. Each procedure such as plasticity, condensation, and glazing was conducted according to the manufacturer's manual. A wear test was conducted with 240,000 chewing cycles using a dual-axis chewing simulator. The degree of wear of the antagonistic teeth was calculated by measuring the volume loss using a three-dimensional profiling system and ANSUR 3D software. The statistical significance of the measured degree of wear was tested with a significant level of 5% using one-way ANOVA and the Tukey test.
RESULTS
The degrees of wear of the antagonistic teeth were 0.119 +/- 0.059 mm3 in Group 1, 0.078 +/- 0.063 mm3 in Group 3, and 0.031 +/- 0.033 mm3 in Group 2. Statistical significance was found between Group 1 and Groups 2 and between Group 2 and 3, whereas no statistical significance was found between Group 1 and Group 3.
CONCLUSION
Despite the limitations of this study on the evaluation of antagonistic teeth wear, the degree of antagonistic tooth wear was less in zirconia than feldspathic dental porcelain, representing that the zirconia may be more beneficial in terms of antagonistic tooth wear.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ardlin BI. Transformation-toughened zirconia for dental inlays, crowns and bridges: chemical stability and effect of low-temperature aging on flexural strength and surface structure. Dent Mater. 2002. 18:590–595.2. Sobrinho LC, Cattell MJ, Glover RH, Knowles JC. Investigation of the dry and wet fatigue properties of three all-ceramic crown systems. Int J Prosthodont. 1998. 11:255–262.3. Campbell SD, Sozio RB. Evaluation of the fit and strength of an all-ceramic fixed partial denture. J Prosthet Dent. 1988. 59:301–306.4. Nakamura T, Ohyama T, Imanishi A, Nakamura T, Ishigaki S. Fracture resistance of pressable glass-ceramic fixed partial dentures. J Oral Rehabil. 2002. 29:951–955.5. Komine F, Tomic M, Gerds T, Strub JR. Influence of different adhesive resin cements on the fracture strength of aluminum oxide ceramic posterior crowns. J Prosthet Dent. 2004. 92:359–364.6. Blatz MB. Long-term clinical success of all-ceramic posterior restorations. Quintessence Int. 2002. 33:415–426.7. Piconi C, Maccauro G. Zirconia as a ceramic biomaterial. Biomaterials. 1999. 20:1–25.8. Guazzato M, Albakry M, Ringer SP, Swain MV. Strength, fracture toughness and microstructure of a selection of all-ceramic materials. Part I. Pressable and alumina glass-infiltrated ceramics. Dent Mater. 2004. 20:441–448.9. Fisher RM, Moore BK, Swartz ML, Dykema RW. The effects of enamel wear on the metal-porcelain interface. J Prosthet Dent. 1983. 50:627–631.10. Krejci I, Lutz F, Gautschi L. Wear and marginal adaptation of composite resin inlays. J Prosthet Dent. 1994. 72:233–244.11. Krejci I, Mueller E, Lutz F. Effects of thermocycling and occlusal force on adhesive composite crowns. J Dent Res. 1994. 73:1228–1232.12. DeLong R, Sakaguchi RL, Douglas WH, Pintado MR. The wear of dental amalgam in an artificial mouth: a clinical correlation. Dent Mater. 1985. 1:238–242.13. Sakaguchi RL, Douglas WH, DeLong R, Pintado MR. The wear of a posterior composite in an artificial mouth: a clinical correlation. Dent Mater. 1986. 2:235–240.14. Krejci I, Lutz F. In vitro evaluation of two composite material for posterior restorations. Stomatol DDR. 1990. 40:326–332.15. De Gee AJ, Pallav P, Davidson CL. Effect of abrasion medium on wear of stress-bearing composites and amalgam in vitro. J Dent Res. 1986. 65:654–658.16. Sulong MZ, Aziz RA. Wear of materials used in dentistry: a review of the literature. J Prosthet Dent. 1990. 63:342–349.17. DeLong R, Sasik C, Pintado MR, Douglas WH. The wear of enamel when opposed by ceramic systems. Dent Mater. 1989. 5:266–271.18. Harrison A. Wear of combinations of acrylic resin and porcelain, on an abrasion testing machine. J Oral Rehabil. 1978. 5:111–115.19. Mahalick JA, Knap FJ, Weiter EJ. Occusal wear in prosthodontics. J Am Dent Assoc. 1971. 82:154–159.20. Gallegos LI, Nicholls JI. In vitro two-body wear of three veneering resins. J Prosthet Dent. 1988. 60:172–178.21. Seghi RR, Rosenstiel SF, Bauer P. Abrasion of human enamel by different dental ceramics in vitro. J Dent Res. 1991. 70:221–225.22. Coornaert J, Adriaens P, De Boever J. Long-term clinical study of porcelain-fused-to-gold restorations. J Prosthet Dent. 1984. 51:338–342.23. Wiley MG. Effects of porcelain on occluding surfaces of restored teeth. J Prosthet Dent. 1989. 61:133–137.24. Oh WS, Delong R, Anusavice KJ. Factors affecting enamel and ceramic wear: a literature review. J Prosthet Dent. 2002. 87:451–459.25. DeLong R, Douglas WH, Sakaguchi RL, Pintado MR. The wear of dental porcelain in an artificial mouth. Dent Mater. 1986. 2:214–219.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- COMPARISON OF WEAR RESISTANCE AMONG RESIN DENTURE TEETH OPPOSING VARIOUS RESTORATIVE MATERIALS
- 3D quantitative analysis and SEM qualitative analysis of natural antagonist enamel opposing CAD-CAM monolithic zirconia or lithium disilicate tooth-supported crowns versus enamel opposing natural enamel
- In vitro wear behavior between enamel cusp and three aesthetic restorative materials: Zirconia, porcelain, and composite resin
- Wear of primary teeth caused by opposed all-ceramic or stainless steel crowns
- Clinical study on the comparison of gold and zirconia wear in an implant-supported fixed prosthesis