Tuberc Respir Dis.
2010 Oct;69(4):256-264. 10.4046/trd.2010.69.4.256.
Moxifloxacin Alleviates Oleic Acid-provoked Neutrophilic Respiratory Burst in the Rat Lung through the Inhibition of Cytosolic Phospholipase A2
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physiology, Daegu Catholic University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. leeym@cu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2114619
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2010.69.4.256
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
According to the notion of the immunoregulatory functions of moxifloxacin (MFX), the effect of MFX on the neutrophilic respiratory burst in conjunction with the expression of cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2) was investigated.
METHODS
The effects and possible mechanisms of MFX on neutrophilic respiratory burst in oleic acid (OA)-induced acutely injured rats lung and OA-stimulated, isolated murine neutrophils were probed, associated with the expression of cytosolic phospholipase A2 in vivo and in vitro.
RESULTS
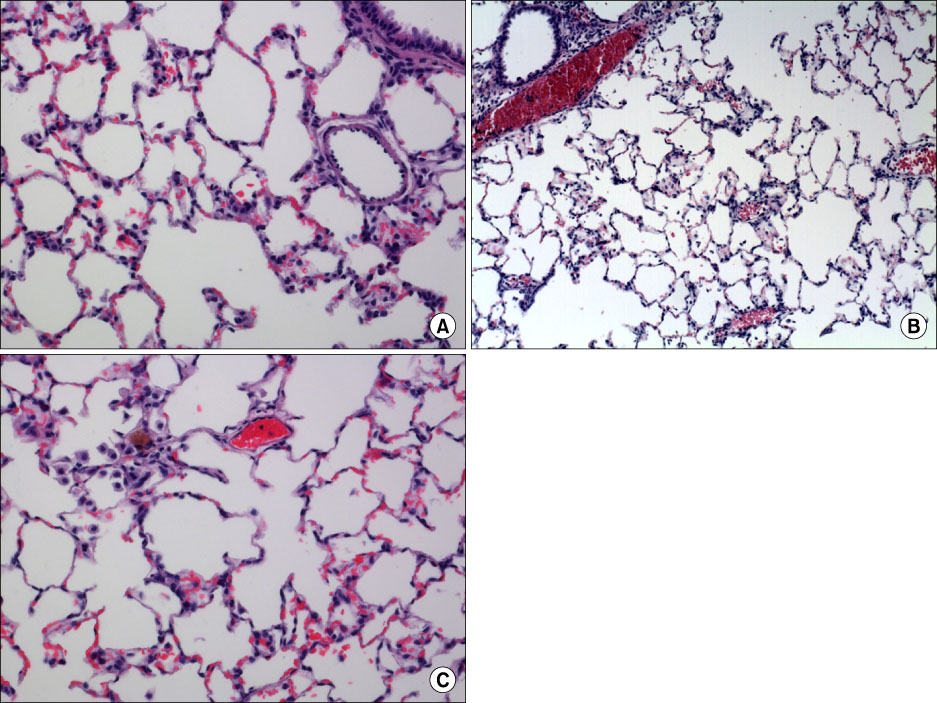
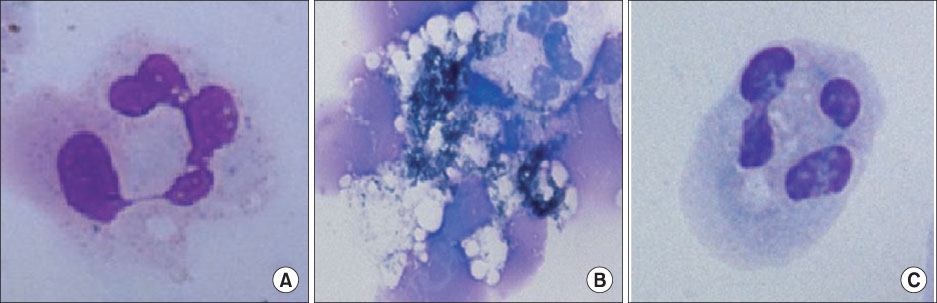
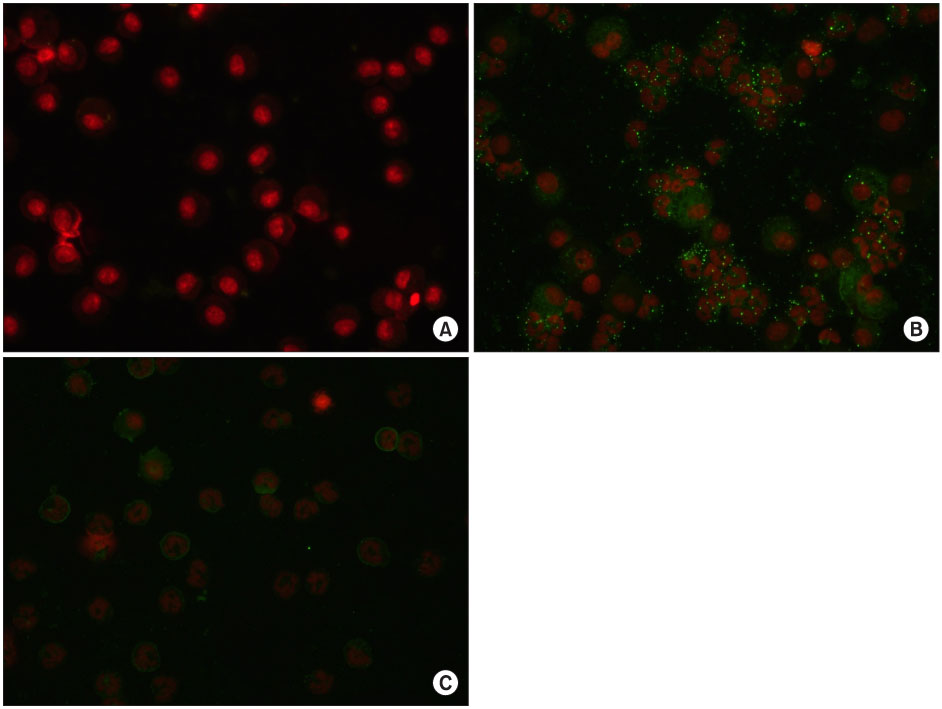
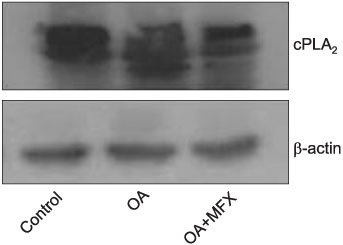
In the OA-induced acutely-injured lungs, neutrophils were accumulated, which was attenuated by MFX. The parameters denoting a neutrophilic respiratory burst, such as nitro blue tetrazolium reaction, cytochrome-c reduction, neutrophil aggregation, H2O2 production in neutrophils revealed increased neutrophilic respiratory burst by OA, and MFX decreased all of these parameters. In addition, the enhanced expression of cPLA2 in the lung and isolated murine neutrophils by OA were decreased by MFX.
CONCLUSION
MFX suppresses the OA-induced neutrophilic respiratory burst by the suppression of cPLA2 in neutrophils.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ware LB. Advances in the pathogenesis and treatment of the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Clin Pul Med. 2003. 10:208–218.2. Kitsiouli E, Nakos G, Lekka ME. Phospholipase A2 subclasses in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009. 1792:941–953.3. Nakos G, Kitsiouli E, Hatzidaki E, Koulouras V, Touqui L, Lekka ME. Phospholipases A2 and platelet-activating-factor acetylhydrolase in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit Care Med. 2005. 33:772–779.4. Stommer P, Steinmann U. Phospholipase A2 induced diffuse alveolar damage: effect of indomethacin and dexamethasone upon morphology and plasma-histamine level. Klin Wochenschr. 1989. 67:171–176.5. Schaloske RH, Dennis EA. The phospholipase A2 superfamily and its group numbering system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006. 1761:1246–1259.6. Wheeler DS. Phospholipase A2 and acute lung injury: it's just not that simple. Crit Care Med. 2005. 33:904–905.7. Pruzanski W, Vadas P. Phospholipase A2: a mediator between proximal and distal effectors of inflammation. Immunol Today. 1991. 12:143–146.8. Arbibe L, Vial D, Touqui L. Phospholipase A2 and acute respiratory distress syndrome. Prog Surg. 1997. 24:79–87.9. Kramer RM, Sharp JD. Structure, function and regulation of Ca2+-sensitive cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2). FEBS Lett. 1997. 410:49–53.10. Dana R, Malech HL, Levy R. The requirement for phospholipase A2 for activation of the assembled NADPH oxidase in human neutrophils. Biochem J. 1994. 297:217–223.11. Lucas KK, Dennis EA. The ABC's of Group IV cytosolic phospholipase A2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004. 1636:213–218.12. Huang HC, Shieh CC, Yu WL, Cheng KC, Chen CC, Chang ST, et al. Comparing the protective effects of ciprofloxacin, moxifloxacin and levofloxacin in mice with lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injuries. Respirology. 2008. 13:47–52.13. Wang JP, Raung SL, Huang LJ, Kuo SC. Involvement of cyclic AMP generation in the inhibition of respiratory burst by 2-phenyl-4-quinolone (YT-1) in rat neutrophils. Biochem Pharmacol. 1998. 56:1505–1514.14. Weiner RE, Sasso DE, Gionfriddo MA, Syrbu SI, Smilowitz HM, Vento J, et al. Early detection of bleomycin-induced lung injury in rat using indium-111-labeled antibody directed against intercellular adhesion molecule-1. J Nucl Med. 1998. 39:723–728.15. Goldblum SE, Wu KM, Jay M. Lung myeloperoxidase as a measure of pulmonary leukostasis in rabbits. J Appl Physiol. 1985. 59:1978–1985.16. Hobson J, Wright J, Churg A. Histochemical evidence for generation of active oxygen species on the apical surface of cigarette-smoke-exposed tracheal explants. Am J Pathol. 1991. 139:573–580.17. Haslett C, Guthrie LA, Kopaniak MM, Johnston RB Jr, Henson PM. Modulation of multiple neutrophil functions by preparative methods or trace concentrations of bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Am J Pathol. 1985. 119:101–110.18. Botha AJ, Moore FA, Moore EE, Fontes B, Banerjee A, Peterson VM. Postinjury neutrophil priming and activation states: therapeutic challenges. Shock. 1995. 3:157–166.19. Dalhoff A, Shalit I. Immunomodulatory effects of quinolones. Lancet Infect Dis. 2003. 3:359–371.20. Koksel O, Cinel I, Tamer L, Cinel L, Ozdulger A, Kanik A, et al. N-acetylcysteine inhibits peroxynitrite-mediated damage in oleic acid-induced lung injury. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2004. 17:263–270.21. Karagiorga G, Nakos G, Galiatsou E, Lekka ME. Biochemical parameters of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in fat embolism. Intensive Care Med. 2006. 32:116–123.22. Julien M, Hoeffel JM, Flick MR. Oleic acid lung injury in sheep. J Appl Physiol. 1986. 60:433–440.23. Lee YM, Kim BY, Park YY. Role of the PLA2-activated neutrophilic oxidative stress in oleic acid-induced acute lung injury. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2010. 68:55–61.24. Shmelzer Z, Haddad N, Admon E, Pessach I, Leto TL, Eitan-Hazan Z, et al. Unique targeting of cytosolic phospholipase A2 to plasma membranes mediated by the NADPH oxidase in phagocytes. J Cell Biol. 2003. 162:683–692.25. Leslie CC. Properties and regulation of cytosolic phospholipase A2. J Biol Chem. 1997. 272:16709–16712.26. Ghosh M, Tucker DE, Burchett SA, Leslie CC. Properties of the Group IV phospholipase A2 family. Prog Lipid Res. 2006. 45:487–510.27. Nagase T, Uozumi N, Ishii S, Kume K, Izumi T, Ouchi Y, et al. Acute lung injury by sepsis and acid aspiration: a key role for cytosolic phospholipase A2. Nat Immunol. 2000. 1:42–46.28. Magrioti V, Kokotos G. Phospholipase A2 inhibitors as potential therapeutic agents for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2010. 20:1–18.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Role of the PLA2-Activated Neutrophilic Oxidative Stress in Oleic Acid-Induced Acute Lung Injury
- Moxifloxacin Ameliorates Oleic Acid-induced Acute Lung Injury by Modulation of Neutrophilic Oxidative Stress in Rats
- A Study on the Mechanism of Immunomodulating Effects of Moxifloxacin in Oleic Acid-Induced Acute Lung Injury
- Cytosolic Phospholipase A2 Activity in Neutrophilic Oxidative Stress of Platelet-activating Factor-induced Acute Lung Injury
- Phospholipase A2 Contributes to Hemorrhage-induced Acute Lung Injury Through Neutrophilic Respiratory Burst