J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2009 Mar;50(3):336-339. 10.3341/jkos.2009.50.3.336.
Exophthalmometric Values With Hertel Exophthalmometers in Children
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Pochun CHA University College of Medicine, Pundang CHA Hospital, Sungnam, Korea. eye@cha.ac.kr
- KMID: 2111241
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2009.50.3.336
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: To investigate the normal exophthalmometric values in children and facilitate the exophthalmic evaluation in pediatric patients with orbital disease.
METHODS
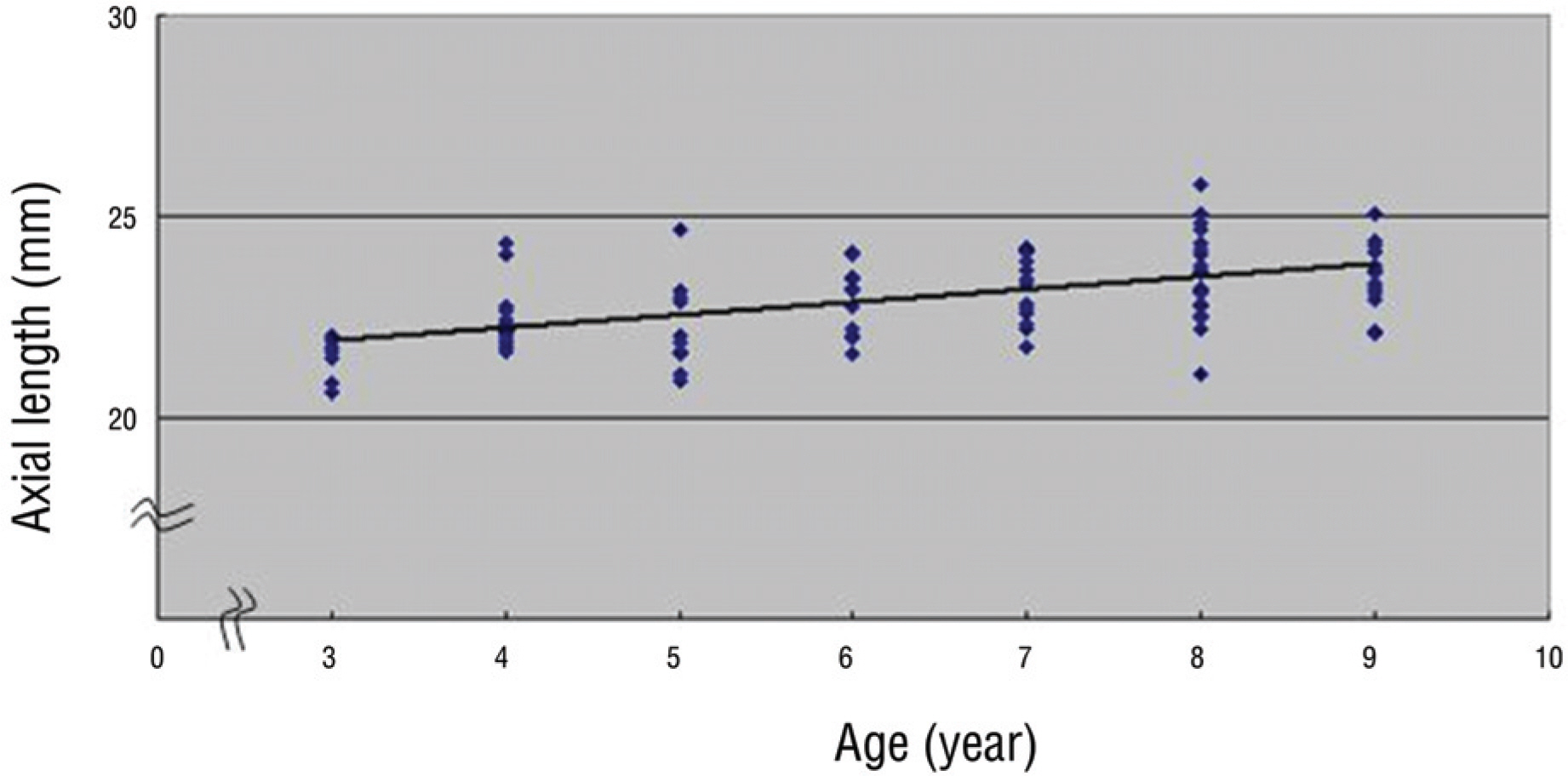
We measured 516 eyes in 258 children aged 3 to 9 years without any orbital disease such as thyroid ophthamopathy, orbital pseudotumor and orbital wall fracture. We considered the association of age, sex, binocular variance, inter rim distance and axial length with the exophthalmometric values. Axial length was measured in only 120 eyes of60 patients who underwent operation for strabismus.
RESULTS
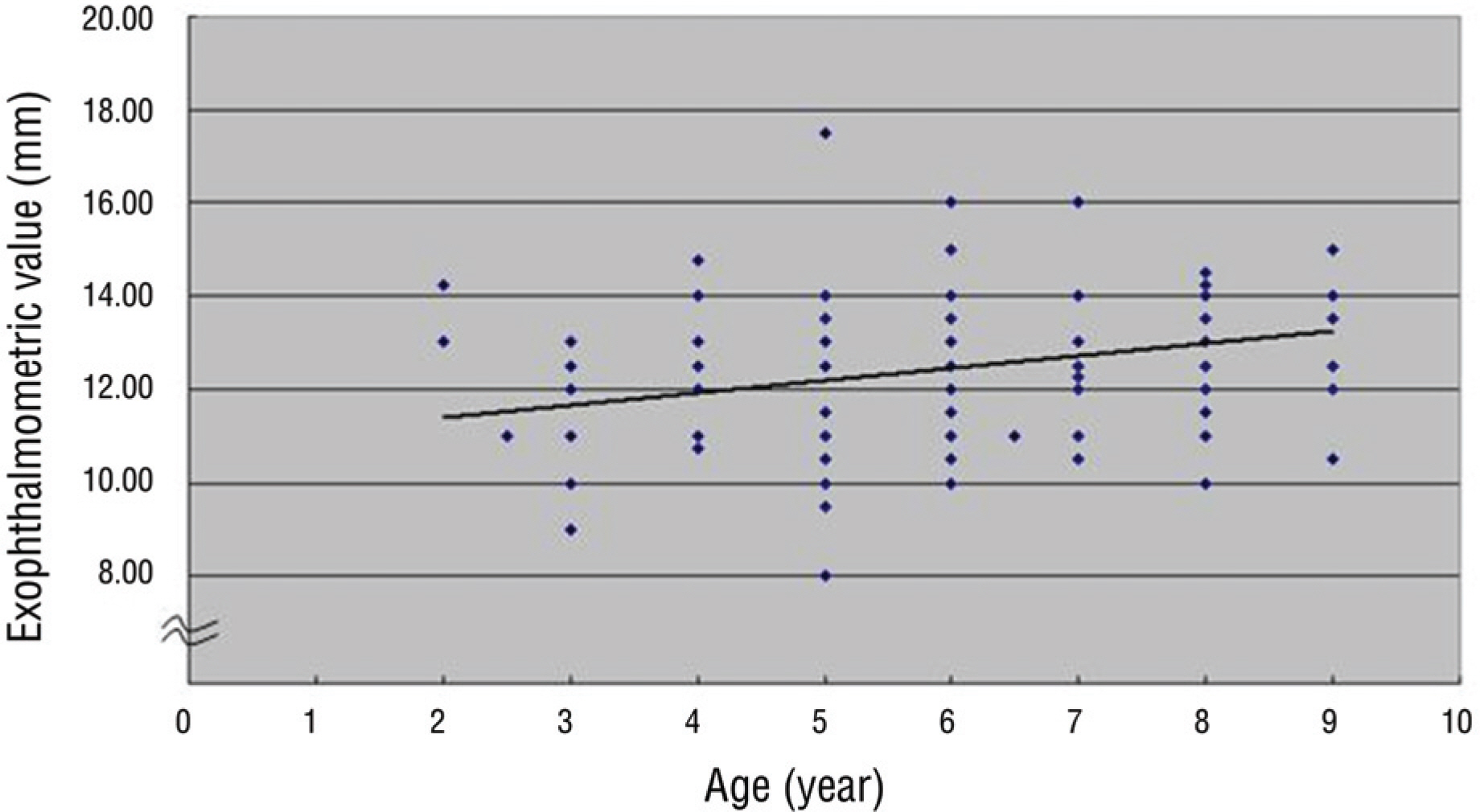
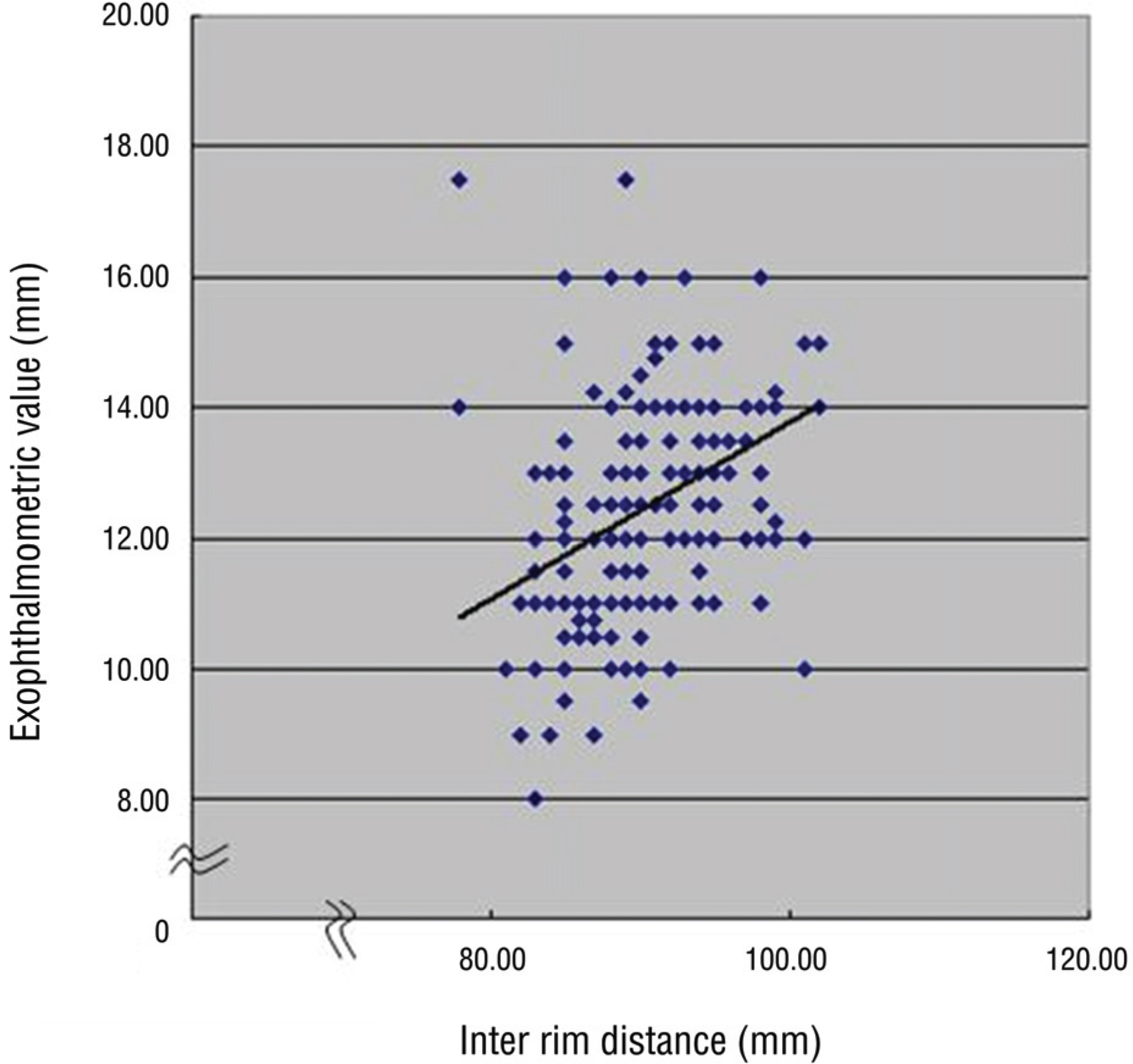
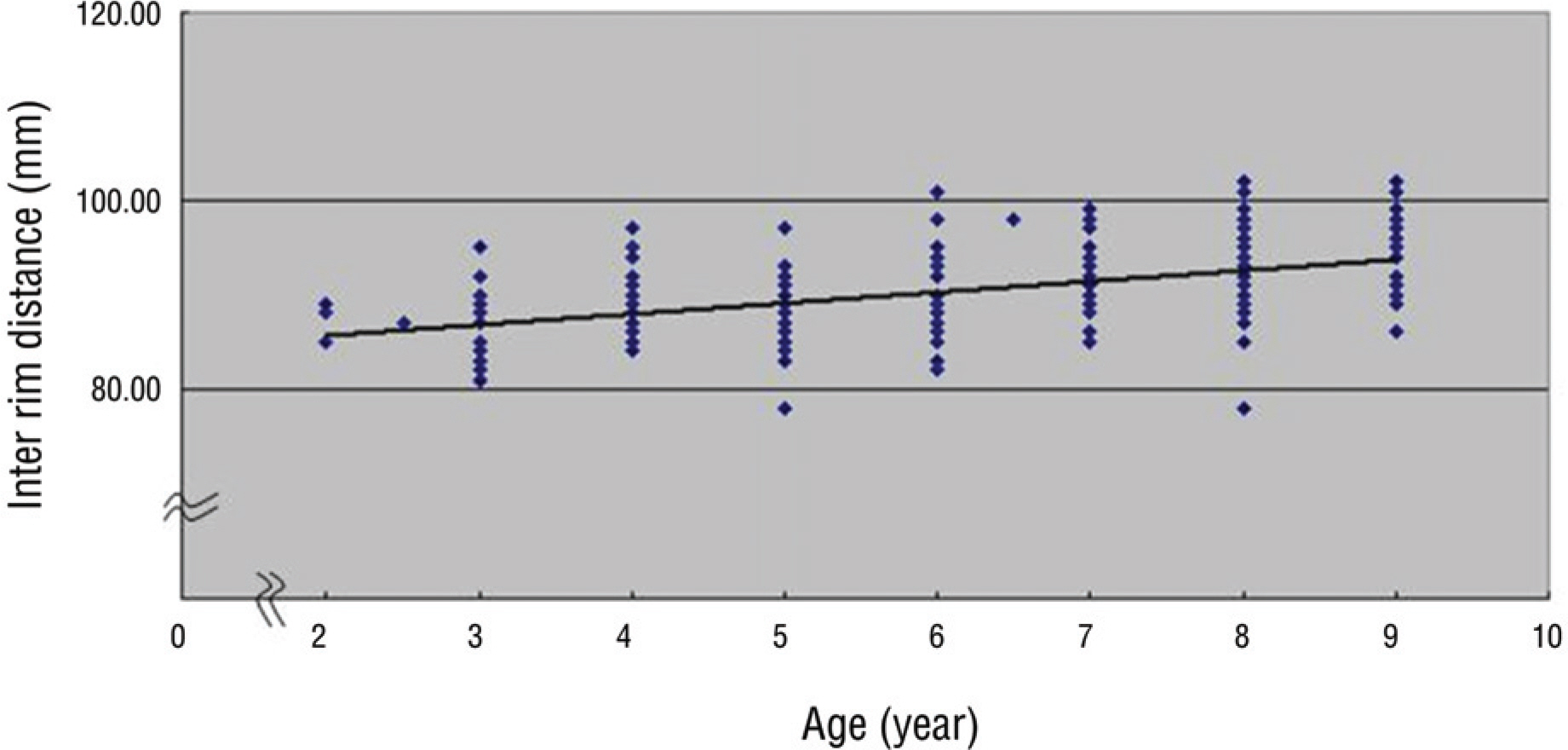
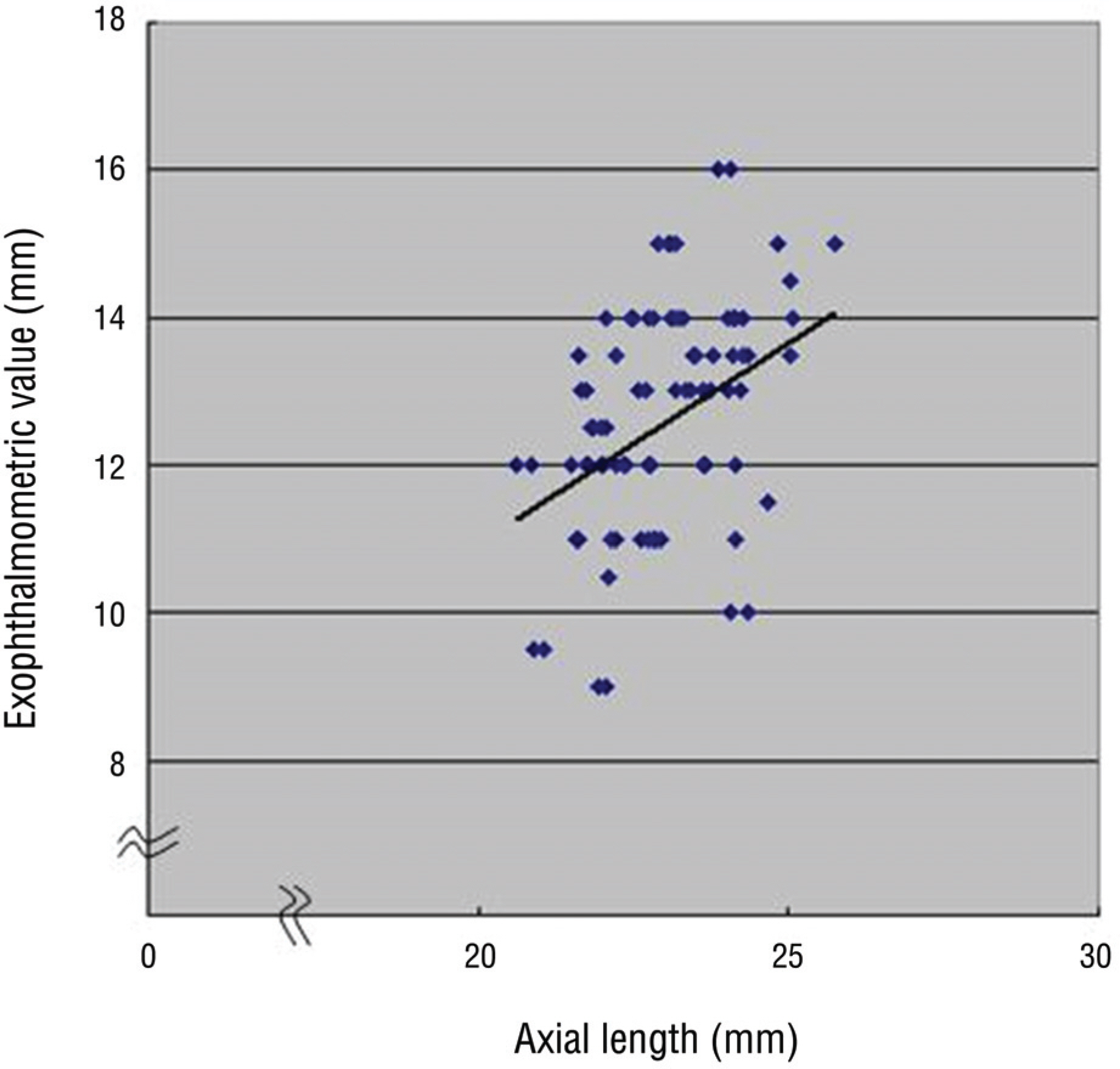
The mean exophthalmometric values in the patients was 12.43+/-1.55 mm. The exophthalmos had a significant positive correlation with the age, axial length and inter rim distance. There were significant differences in exophthalmometric values by sex in children aged from 8 to 9 years but no significant difference by binocular variance. There were significant differences in the inter-rim distance related to sex.
CONCLUSIONS
The exophthalmometric values in children had significant correlation with age, sex, axial length, and inter-rim distance. There was a significant increase of inter-rim distance in males compared to females. Knowing the mean exophthalmometric values in children would be useful with the exophthalmometric reference in pediatric patients with orbital disease.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Wiersinga WM. Thyroid associatedophthalmopathy: pediatric and endocrine aspects. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2004; 3:513–7.2. Yan J, Qiu H, Wu Z, Li Y. Idiopathic orbital inflammatory pseudotumor in Chinese children. Orbit. 2006; 25:1–4.
Article3. Homziuk M. An analysis of orbital fracture in open-clinic practice of Department of Ophthalmology Medical University of Gdansk 1990-1991 and 2000-2001 years. Klin Oczna. 2005; 107:266–8.4. Kook KH, Kim YK, Lee SY. Exophthalmometric values of Korean using Hertel and Naugle exophthalmometers. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2003; 47:10–5.5. Chung TM. The exophthalmometry, extraorbital width and height of lid fissure of Koreans. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1974; 15:305–11.6. Kwak YJ. Normal Range of Exophthalmos in Korea. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1974; 15:312–5.7. Nucci P, Brancato R, Bandello F, et al. Normal Exophthal-mometric Values in Children. Am J Ophthalmol. 1989; 108:582–4.
Article8. Zhang M, Hong R, Fu Z, et al. The measurement of normal values of exophthalmos, interpupillary distance and interorbital distance of children and alolescence in Xiamen and the rule of their development. Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2000; 36:462–6.9. Kikkawa DO, Lemke BN. Orbital and Eyelid Anatomy. Dortzbach RK, editor. Ophthalmic Plastic Surgery. 1st ed.New York: Raven Press;1994. chap. 1.10. Migliori ME, Gladstone CJ. Determination of the normal range of exophthalmometric values for black and white adults. Am J Ophthalmol. 1984; 98:438–42.
Article11. Youn DH, Park IW, You YS. Intraocular pressure and axial length in children. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1990; 31:397–401.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Exophthalmometric values of Korean using Hertel and Naugle exophthalmometers
- Comparison of Reproducibility between Exophthalmometer Readings Measured with Hertel and Naugle Exophthalmometer
- The Effect of Intraoperative Exophthalmometric Values on Enophthalmos Correction in Inferior Orbital Wall Reconstruction
- A Comparison of Hertel Exophthalmometer Measurements Between Various Manufacturer`s Models
- Three Cases of Orbitofrontal Cholesterol Granuloma