J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2008 Jun;49(6):935-941. 10.3341/jkos.2008.49.6.935.
Analysis of the Optic Nerve Head and RNFL Thickness Using Optical Coherence Tomography in Diabetes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. LK1246@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2110874
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2008.49.6.935
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: Retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) thickness and optic nerve head (ONH) in diabetic patients with normal tension were analyzed using optical coherence tomography (OCT), which revealed that diabetes induce morphologic changes in optic disc and RNFL thickness.
METHODS
A total of 192 patients with type 2 diabetes were analyzed with fundus examination and classified as having normal retina, mild - moderate, severe nonproliferative retinopathy (NPDR), or proliferative retinopathy (PDR). These patients were evaluated with OCT and compared with normal control group.
RESULTS
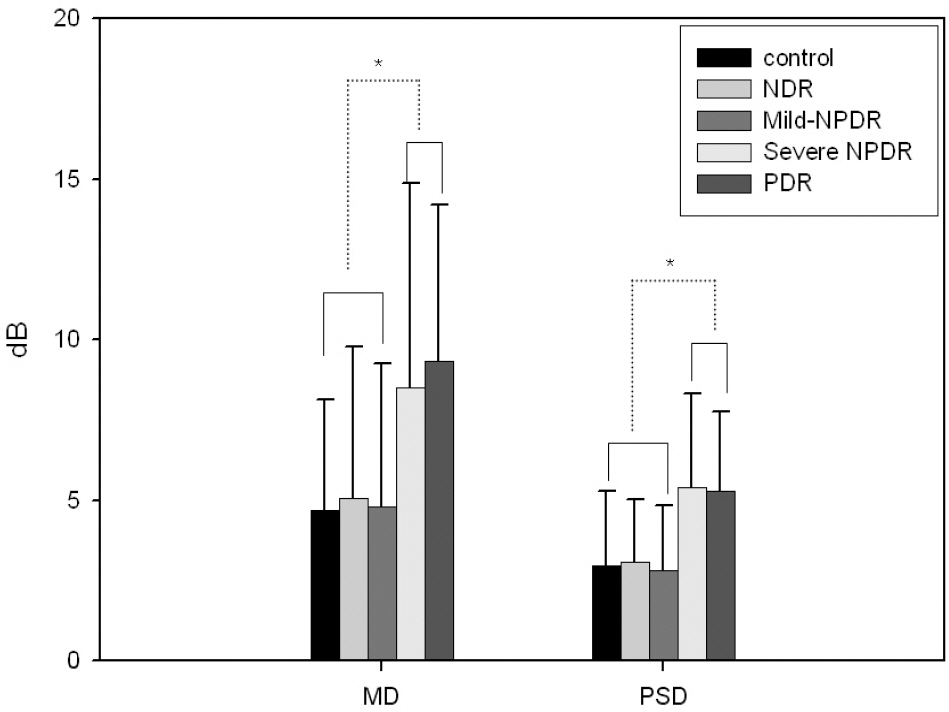
The mean average thickness and nasal average thickness of RNFL in mild-moderate, and severe NPDR groups decreased compared with those of the other groups. There was an increase in the temporal average thickness of RNFL in the PDR group. As the duration of diabetes increased, the mean average and nasal average of RNFL thickness also decreased. The severity of diabetic retinopathy didn't show statistically significant differences in a topographic analysis of the optic nerve head.
CONCLUSIONS
The mean average thickness and nasal average of RNFL decreased in NPDR groups. Diabetic changes should be considered when diabetes patients are diagnosed with glaucoma or glaucoma progression.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Long-term Changes in the Peripapillary RNFL and Macular GCIPL Thicknesses after Panretinal Photocoagulation in Diabetic Retinopathy Patients
Jung Hyun Yoon, Dong Ho Park, Dai Woo Kim
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2018;59(10):938-945. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2018.59.10.938.Correlation between Macular GCIPL Thickness and Visual Acuity after Resolution of Diabetic Macular Edema
Ji Man Park, Young Chang Lee, Seong Taeck Kim
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2015;56(9):1345-1352. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2015.56.9.1345.
Reference
-
References
1. Klein BE, Klein R, Jensen SC. Open angle glaucoma and older onset diabetes The Beaver Dam Eye Study. Ophthalmology. 1994; 101:1173–7.2. Mitchell P, Smith W, Chey T, Healey PR. Open angle glaucoma and diabetes: the Blue Mountains Eye study, Australia. Ophthalmology. 1997; 104:712–8.3. Dyck PJ, Lais A, Karnes JL. . Fiber loss is primary and multifocal in sural nerves in diabetic polyneuropathy. Ann Neurol. 1986; 19:425–39.
Article4. Takahashi H, Goto T, Shoji T. . Diabetes-associated Retinal Nerve Fiber Damage Evaluated With Scanning Laser Polarimetry. Am J Ophthalmol. 2006; 142:88–94.
Article5. Russ H, Costa VP. Retinal nerve fiber layer loss in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus without retinopathy. Br J Ophthalmol. 2002; 86:725–8.6. Ozdek S, Lonneville YH, Onol M. . Assessment of nerve fiber layer in diabetic patients with scanning laser polarimetry. Eye. 2002; 16:761–5.
Article7. Sugimoto M, Sasoh M, Ido M. . Detection of Early Diabetic Change with Optical Coherence Tomography in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients without Retinopathy. Ophthal mologica. 2005; 219:379–85.
Article8. Lonneville YH, Ozdek SC, Onol M. . The effect of blood glucose regulation on retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in diabetic patients. Ophthalmologica. 2003; 217:347–50.
Article9. Jaffe GJ, Caprioli J. Optical Coherence Tomography to Detect and Manage Retinal Disease and Glaucoma. Am J Ophthalmol. 2004; 137:156–69.
Article10. Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study Report Number 12. Fundus photographic risk factors for progression of diabetic retinopathy. Ophthalmology. 1991; 98:823–33.11. Greenfield DS, Knighton RW, Feuer WJ. . Correction of corneal polarization axis improves the discriminating power of scanning laser polarimetry. Am J Ophthalmol. 2002; 134:27–33.12. Weinreb RN. Evaluating the retinal nerve fiber layer in glaucoma with scanning laser polarimetry. Arch Ophthalmol. 1999; 117:1403–6.
Article13. Lee SY, Choi KR. Influence of diabetes mellitus on the retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measurement by nerve fiber analyzer. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2000; 41:1396–406.14. Lee SY, Choi KR. Influence of diabetes mellitus on the morphometric analysis of the optic nerve head. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2000; 41:1425–36.15. Shin YJ, Kyoung HS, Park KH, Yu HG. The analysis of retinal nerve fiber layer in the patients with nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2003; 44:2010–5.16. Gillies MC, Su T, Stayt J. . Effect of high glucose on permeability of retinal capillary endothelium in vitro. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1997; 38:635–42.17. Mizutani M, Gerhardinger C, Lorenzi M. Muller cell changes in human diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes. 1998; 47:445–9.18. Rungger-Brandle E, Dosso AA, Leuenberger PM. Glial reactivity, an early feature of diabetic retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2000; 41:1971–80.19. Dralands L, Missotten L. . Expression of apoptosis markers in the retinas of human subjects with diabetes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2004; 45:2760–6.20. Zhang L, Inoue M, Dong K, Yamamoto M. Retrograde axonal transport impairment of large- and medium-sized retinal ganglion cells in diabetic rat. Curr Eye Res. 2000; 20:131–6.
Article21. Chung HS, Harris A, Halter PJ. . Regional differences in retinal vascular reactivity. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1999; 40:2448–53.22. Kern TS, Engerman RL. Vascular lesion in diabetes is distributed non-uniformly within the retina. Exp Eye Res. 1995; 60:545–9.23. Kanamori A, Escano MF, Eno A. . Evaluation of the effect of aging on retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measured by optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmologica. 2003; 217:273–8.
Article24. Parikh RS, Parikh SR, Sekhar GC. . Normal age-related decay of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness. Ophthalmology. 2007; 114:921–6.
Article25. Klein BE, Moss SE, Klein R. Neuroretinal rim area in diabetes mellitus. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1990; 31:805–9.26. Amano S, Kaji Y, Oshika T. . Advanced glycation end products in human optic nerve head. Br J Ophthalmol. 2001; 85:52–55.
Article27. Zhang L, Naka H. . Polyol metabolism of retrograde axonal transport in diabetic rat large optic nerve fiber. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2000; 41:4055–8.28. Verrotti A, Lobefalo L, Trotta D. . Visual evoked potentials in young persons with newly diagnosed diabetes: a long-term follow-up. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2000; 42:240–4.
Article29. Konigsreuther KA, Jonas JB. Optic disc morphology in diabetes mellitus. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1995; 233:200–4.30. Henricsson M, Heijl A. Visual fields at different stages of diabetic retinopathy. Acta Ophthalmol. 1994; 72:560–9.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Correlation between Visual Acuity and Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness in Optic Neuropathies
- Changes in Optic Nerve Parameter Measurements on Spectral-Domain Optical Coherence Tomography, after Cataract Surgery
- Optical Coherence Tomography Parameters of Normal, Glaucoma Suspect, and Early Glaucoma Patients
- Comparison of Diagnostic Precision between Preprogramed Indicator and Newly Calculated Indicator in Optical Coherence Tomography
- The Analysis of Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer in Amblyopia Using Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography