J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2015 Feb;50(1):18-24. 10.4055/jkoa.2015.50.1.18.
Treatment of Femur Subtrochanteric Fracture Using the Intramedullary Long Nail; Comparison of Closed Reduction and Minimal Open Reduction
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Chosun University School of Medicine, Gwangju, Korea. shalee@chosun.ac.kr
- KMID: 2106733
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2015.50.1.18
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of the study was to evaluate methods for treatment of femur subtrochanteric fractures using the intramedullary long nail.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
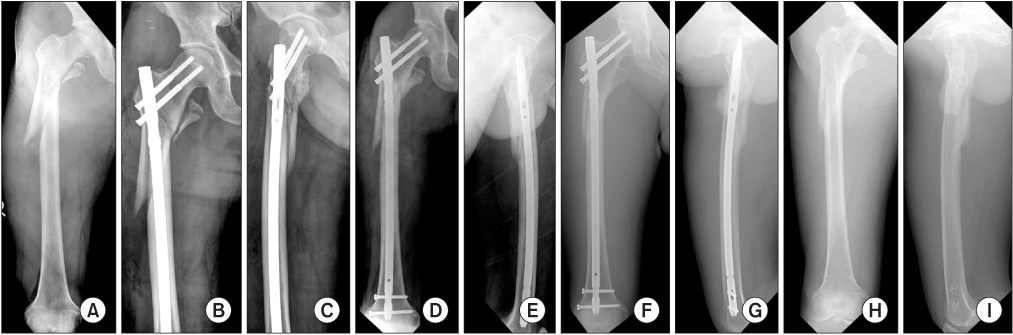
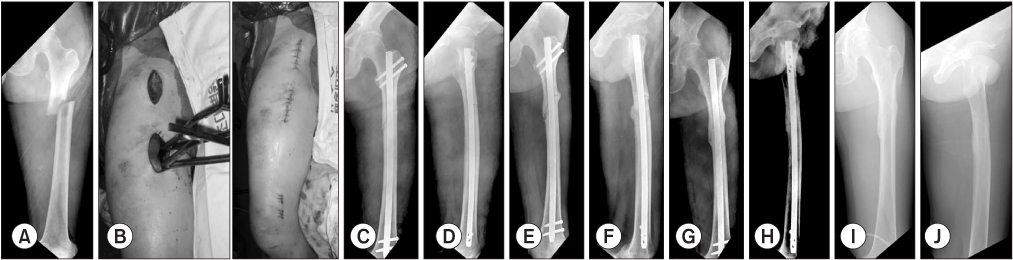
This retrospective study included 44 patients (44 cases) who were available for follow-up for at least one year. The patients had undergone intramedullary fixation specifically with a long nail for traumatic femur subtrochanteric fractures during the period from June 2005 to May 2012 in Chosun University Hospital. The study compares two groups. For group 1, closed reduction was attempted, and group 2 underwent minimal open reduction. Group 1 included 27 cases, and group 2 included 17 cases. Study parameters included injury mechanism, fracture classification according to the Seinsheimer type, nail design, size of skin incision, alignment, bony union time, malunion or nonunion, and complications.
RESULTS
Bony union times were 19.4 weeks (group 1) versus 21.4 weeks (group 2), but there were no statistical differences between the two groups with respect to gender, injury mechanism, fracture classification, or nail design. However, there were significant differences between the two groups with respect to skin incision, malalignment, and complications. Gender, injury mechanism, fracture classification, nail design, size of skin incision, minimal open reduction or close reduction, did not show a significant relationship with bony union. However, in cases of malalignment, the possibility of malunion increased 1.5 times per 1degrees increase in malaligment.
CONCLUSION
In treatment of femur subtrochanteric fracture using intramedullary nail, nonunion rate increases when malalignment occurs. Therefore, anatomical reduction with minimal open reduction is necessary if closed reduction is not satisfactory.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Giannoudis PV, Ahmad MA, Mineo GV, Tosounidis TI, Calori GM, Kanakaris NK. Subtrochanteric fracture non-unions with implant failure managed with the "Diamond" concept. Injury. 2013; 44:Suppl 1. S76–S81.
Article2. Forward DP, Doro CJ, OToole RV, et al. A biomechanical comparison of a locking plate, a nail, and a 95° angled blade plate for fixation of subtrochanteric femoral fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2012; 26:334–340.
Article3. Kim JJ, Kim JW. Subtrochanteric fracture: intramedullary nailing. J Korean Fract Soc. 2009; 22:114–122.
Article4. Kinast C, Bolhofner BR, Mast JW, Ganz R. Subtrochanteric fractures of the femur. Results of treatment with the 95 degrees condylar blade-plate. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989; 238:122–130.5. Craig NJ, Sivaji C, Maffulli N. Subtrochanteric fractures. A review of treatment options. Bull Hosp Jt Dis. 2001; 60:35–46.6. Perren SM. Evolution of the internal fixation of long bone fractures. The scientific basis of biological internal fixation: choosing a new balance between stability and biology. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002; 84:1093–1110.7. Kim JW, Chang JS, Lee H, Bae JY, Kim JJ. Clinical results of femoral subtrochanteric fractures. J Korean Hip Soc. 2010; 22:222–226.
Article8. Seinsheimer F. Subtrochanteric fractures of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1978; 60:300–306.
Article9. Seyhan M, Unay K, Sener N. Comparison of reduction methods in intramedullary nailing of subtrochanteric femoral fractures. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2012; 46:113–119.
Article10. Ha SH, Kim WH, Lee GC. Results of intramedullary nailing of femoral shaft fracture: trochanteric entry portal (Sirus Nail) versus piriformis entry portal (M/DN Nail). J Korean Fract Soc. 2014; 27:50–57.11. Kempf I, Grosse A, Beck G. Closed locked intramedullary nailing. Its application to comminuted fractures of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1985; 67:709–720.
Article12. Barquet A, Mayora G, Fregeiro J, López L, Rienzi D, Francescoli L. The treatment of subtrochanteric nonunions with the long gamma nail: twenty-six patients with a minimum 2-year follow-up. J Orthop Trauma. 2004; 18:346–353.13. Haidukewych GJ, Berry DJ. Nonunion of fractures of the subtrochanteric region of the femur. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004; 419:185–188.
Article14. Kim JO, Kim TH. Surgical treatment of femur intertrochanteric and subtrochanteric fracture. J Korean Hip Soc. 2010; 22:1–12.
Article15. Pelet S, Arlettaz Y, Chevalley F. Osteosynthesis of per- and subtrochanteric fractures by blade plate versus gamma nail. A randomized prospective study. Swiss Surg. 2001; 7:126–133.16. Robinson CM, Houshian S, Khan LA. Trochanteric-entry long cephalomedullary nailing of subtrochanteric fractures caused by low-energy trauma. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005; 87:2217–2226.
Article17. Shukla S, Johnston P, Ahmad MA, Wynn-Jones H, Patel AD, Walton NP. Outcome of traumatic subtrochanteric femoral fractures fixed using cephalo-medullary nails. Injury. 2007; 38:1286–1293.
Article18. Park SY, Yang KH, Yoo JH, Yoon HK, Park HW. The treatment of reverse obliquity intertrochanteric fractures with the intramedullary hip nail. J Trauma. 2008; 65:852–857.
Article19. Yang KH. Correction of malalignment during subtrochanteric nailing. J Korean Fract Soc. 2009; 22:66–70.
Article20. Afsari A, Liporace F, Lindvall E, Infante A Jr, Sagi HC, Haidukewych GJ. Clamp-assisted reduction of high subtrochanteric fractures of the femur: surgical technique. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010; 92:Suppl 1. (Pt 2):217–225.21. Müller T, Topp T, Kühne CA, Gebhart G, Ruchholtz S, Zettl R. The benefit of wire cerclage stabilisation of the medial hinge in intramedullary nailing for the treatment of subtrochanteric femoral fractures: a biomechanical study. Int Orthop. 2011; 35:1237–1243.
Article22. Kennedy MT, Mitra A, Hierlihy TG, Harty JA, Reidy D, Dolan M. Subtrochanteric hip fractures treated with cerclage cables and long cephalomedullary nails: a review of 17 consecutive cases over 2 years. Injury. 2011; 42:1317–1321.
Article23. Tomás J, Teixidor J, Batalla L, Pacha D, Cortina J. Subtrochanteric fractures: treatment with cerclage wire and long intramedullary nail. J Orthop Trauma. 2013; 27:e157–e160.24. Ansari Moein CM, Verhofstad MH, Bleys RL, van der Werken C. Soft tissue injury related to choice of entry point in antegrade femoral nailing: piriform fossa or greater trochanter tip. Injury. 2005; 36:1337–1342.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Treatment of Subtrochanteric Femur Fractures Using Intramedullary Devices
- Subtrochanteric Fracture Reduction during Intramedullary Nailing: Technical Note
- Surgical Treatment of Subtrochanteric Fracture of Femur with Spiral Blade Unreamed Intramedullary Femoral Nail
- Efficacy of Percutaneous Cerclage Wiring in Intramedullary Nailing of Subtrochanteric Femur Fracture: Technical Note
- Steinmann Pin Assisted Reduction of Subtrochanteric Femoral Fracture