J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2013 Feb;48(1):33-37. 10.4055/jkoa.2013.48.1.33.
Laparoscopic Treatment for Psoas Abscess
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, College of Medicine, Soon Chun Hyang University, Cheonan, Korea. chhong@sch.ac.kr
- 2Department of General Surgery, College of Medicine, Soon Chun Hyang University, Cheonan, Korea.
- KMID: 2106661
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2013.48.1.33
Abstract
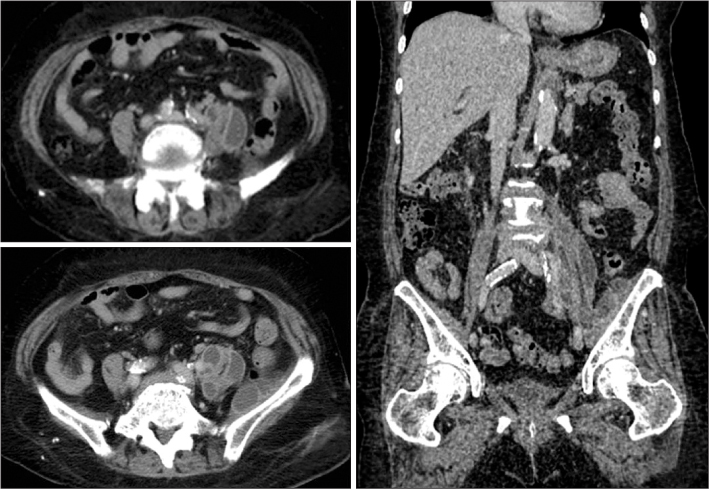
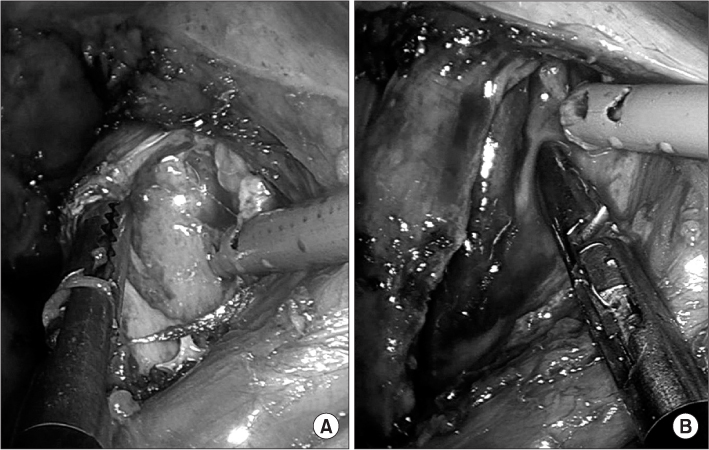
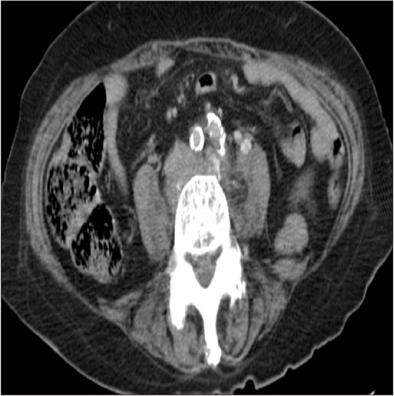
- Psoas abscess is a rare and high mortality disease if there is no appropriate treatment. The surgical approach of psoas abscess is very difficult because psoas muscle is anatomically located within retroperitoneum. Recently, computed tomography guided percutaneous catheter drainage with proper antibiotic therapy has shown good results. If this therapy fails to resolve the psoas abscess, surgical treatment may be necessary. We experienced two cases of psoas abscess resolved by surgical drainage using laparoscopy. We report two successful results with relevant literatures.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Santaella RO, Fishman EK, Lipsett PA. Primary vs secondary iliopsoas abscess. Presentation, microbiology, and treatment. Arch Surg. 1995. 130:1309–1313.2. Ricci MA, Rose FB, Meyer KK. Pyogenic psoas abscess: worldwide variations in etiology. World J Surg. 1986. 10:834–843.
Article3. Malhotra R, Singh KD, Bhan S, Dave PK. Primary pyogenic abscess of the psoas muscle. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1992. 74:278–284.
Article4. Gupta S, Suri S, Gulati M, Singh P. Ilio-psoas abscesses: percutaneous drainage under image guidance. Clin Radiol. 1997. 52:704–707.
Article5. Dinç H, Onder C, Turhan AU, et al. Percutaneous catheter drainage of tuberculous and nontuberculous psoas abscesses. Eur J Radiol. 1996. 23:130–134.
Article6. Dinç H, Sari A, Yuluğ G, Gümele HR. CT-guided drainage of multilocular pelvic and gluteal tuberculous abscesses. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1996. 167:667–668.
Article7. Cantasdemir M, Kara B, Cebi D, Selcuk ND, Numan F. Computed tomography-guided percutaneous catheter drainage of primary and secondary iliopsoas abscesses. Clin Radiol. 2003. 58:811–815.
Article8. Kao PF, Tsui KH, Leu HS, Tsai MF, Tzen KY. Diagnosis and treatment of pyogenic psoas abscess in diabetic patients: usefulness of computed tomography and gallium-67 scanning. Urology. 2001. 57:246–251.
Article9. Atkin G, Qurashi K, Isla A. Laparoscopic drainage of bilateral tuberculous psoas abscesses. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2005. 15:380–382.
Article10. Choi SB, Han HJ, Kim WB, Song TJ, Choi SY. A case of a recurrent iliopsoas abscess masking a complicated appendicitis successfully treated by a laparoscopic approach. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2010. 20:e69–e72.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Primary Pyogenic Psoas Abscess in Child
- Primary Psoas Abscess: A Case Report
- Psoas Abscess Secondary to Renal Tuberculosis in a Middle-aged Woman
- Ultrasonographic Findings of Psoas abscess and Hematoma
- Tuberculous Abscess of the Psoas Muscle in a Patient with Acute Lumbar Burst Fracture: A Missed Diagnosis