J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2008 Feb;43(1):50-56. 10.4055/jkoa.2008.43.1.50.
Functional Results of the TKA with Non-resurfaced Patella according to Articular Degeneration of the Patella
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kyungpook National University Hospital, Daegu, Korea. hskyung@knu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2106416
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2008.43.1.50
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: We evaluated the functional outcome as degeneration of articular surface of the patella after total knee arthroplasty without resurfacing the patella.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From 2002 to 2003, 63 cases of 52 osteoarthritis patients who underwent total knee arthroplasty without resurfacing the patella as randomized selection were evaluated. Average age was 67.2 years old. Female were 49 patients, and male 3 patients Average follow-up periods were 32 months. Used implant were all PFC-sigma. Clinical outcomes was analyzed as Feller's patella score (perfect score; 30 points), anterior knee pain, crepitation according to the extent of involvement of articular surface of the patella and patello-femoral tracking.
RESULTS
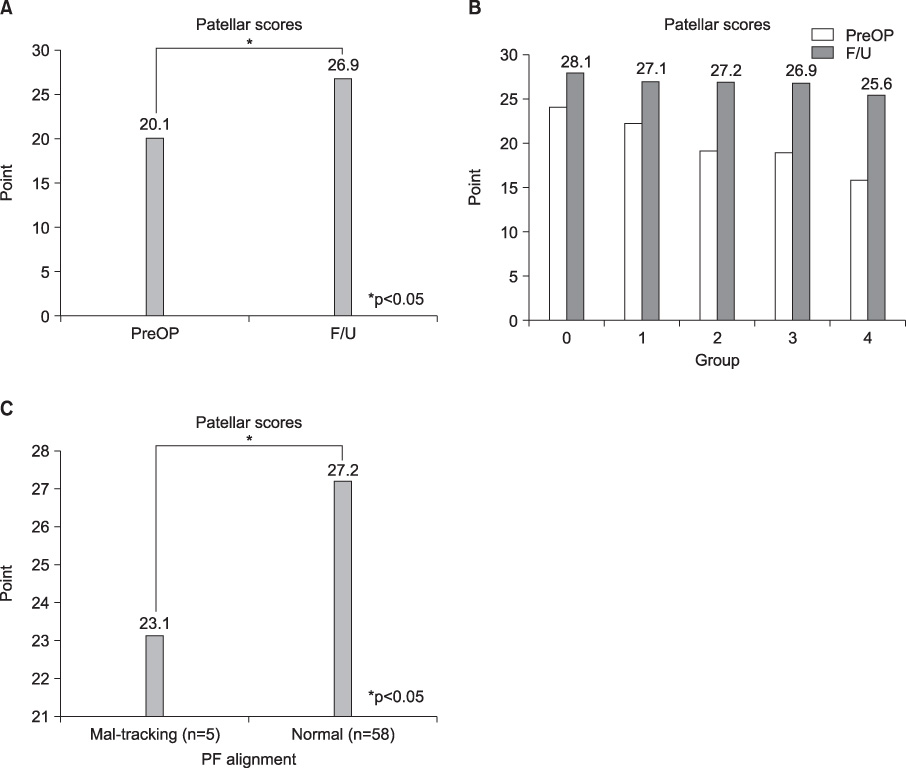
The Feller's patella score increased from mean 20.1 to 26.9 (p<0.05). However, there were no statistically significant differences as extent of involvement of patello-femoral joint (p>0.05). The patella score was low with patellar malalignment. Anterior knee pain after operation increased during postoperative 6 months according to the extent of degeneration of patellofemoral joint, but after 6 months there is no statistically significant differences except group 4 and all groups gradually decreased. Crepitation was increased during postoperative 1 year according to the extent of cartilage degeneration and after that its incidence decreased with time.
CONCLUSION
The clinical results of total knee arthroplasty without resurfacing the patella was not influenced by the extent of degeneration of patello-femoral joint, but by alignment of patellofemoral joint. Anterior knee pain and crepitation increased in proportion to the extent of degeneration of patello-femoral joint in early period, but it fade out with time.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Abraham W, Buchanan JR, Daubert H, Greer RB 3rd, Keefer J. Should the patella be resurfaced in total knee arthroplasty? Efficacy of patellar resurfacing. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988. 236:128–134.2. Barrack RL, Bertot AJ, Wolfe MW, Waldman DA, Milicic M, Myers L. Patellar resurfacing in total knee arthroplasty. A prospective, randomized, double-blind study with five to seven years of follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001. 83:1376–1381.3. Barrack RL. All patellae should be resurfaced during primary total knee arthroplasty, in opposition. J Arthroplasty. 2003. 18:Suppl 1. S35–S38.4. Bourne RB, Burnett RS. The consequences of not resurfacing the patella. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004. 428:166–169.
Article5. Bourne RB, Rorabeck CH, Vaz M, Kramer J, Hardie R, Robertson D. Resurfacing versus not resurfacing the patella during total knee replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995. 321:156–161.
Article6. Braakman M, Verburg AD, Bronsema G, van Leeuwen WM, Eeftinck MP. The outcome of three methods of patellar resurfacing in total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 1995. 19:7–11.
Article7. Brick GW, Scott RD. The patellofemoral component of total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988. 231:163–178.
Article8. Burnett RS, Bourne RB. Indications for patellar resurfacing in total knee arthroplasty. Instr Course Lect. 2004. 53:167–186.
Article9. Dennis DA. The role of patellar resurfacing in TKA. Point. Orthopedics. 2006. 29:832–835.10. Feller JA, Bartlett RJ, Lang DM. Patellar resurfacing versus retention in total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1996. 78:226–228.
Article11. Han I, Chang CB, Lee S, Lee MC, Seong SC, Kim TK. Correlation of the condition of the patellar articular cartilage and patellofemoral symptoms and function in osteoarthritic patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005. 87:1081–1084.
Article12. Kim BS, Reitman RD, Schai PA, Scott RD. Selective patellar non-resurfacing in total knee arthroplasty. 10 year results. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999. 367:81–88.
Article13. Levai JP, McLeod HC, Freeman MA. Why not resurface the patella? J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1983. 65:448–451.
Article14. Levitsky KA, Harris WJ, McManus J, Scott RD. Total knee arthroplasty without patellar resurfacing. Total knee arthroplasty without patellar resurfacing. Clinical outcomes and long-term follow-up evaluation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993. 286:116–121.15. Math KR, Ghelman B, Potter HG. Scuderi BR, editor. Imaging of the patellofemoral joint. The patella. 1995. 1st ed. New York: Springer-Verlag;83–125.
Article16. Mayman D, Bourne RB, Rorabeck CH, Vaz M, Kramer J. Resurfacing versus not resurfacing the patella in total knee arthroplasty: 8-to 10-year results. J Arthroplasty. 2003. 18:541–545.17. Nizard RS, Biau D, Porcher R, et al. A meta-analysis of patellar replacement in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005. 432:196–203.
Article18. Outerbridge RE. The etiology of chondromalacia patellae. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1961. 43:752–757.
Article19. Pakos EE, Ntzani EE, Trikalinos TA. Patellar resurfacing in total knee arthroplasty. A meta-analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005. 87:1438–1445.20. Rae PJ, Noble J, Hodgkinson JP. Patellar resurfacing in total condylar knee arthroplasty. Technique and results. J Arthroplasty. 1990. 5:259–265.21. Ranawat CS. The patellofemoral joint in total condylar knee arthroplasty: Pros and cons based on five to ten-year follow up observations. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986. 205:93–99.22. Smith SR, Stuart P, Pinder IM. Nonresurfaced patella in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1989. 4:Suppl. S81–S86.
Article23. Soudry M, Mestriner LA, Binazzi R, Insall JN. Total knee arthroplasty without patellar resurfacing. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986. 205:166–170.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparative Analysis of Resurfaced and Unresurfaced Patella in Bilateral Total Knee Arthroplasty: A 10 year, Prospective and Controlled Study of Clinical and Radiological Results
- Patella Resurfacing during Total Knee Arthroplasty: Have We Got the Issue Covered?
- Availability of Patella Resurfacing in Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty Through Evaluation and Analysis of the Patella in Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Intra-Articular Osteochondroma of the Patella
- Comparison of the Results of Resurfacing Versus Non Resurfacing the Patella after Total Knee Arthroplasties in the Same Patient