J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2008 Feb;43(1):30-35. 10.4055/jkoa.2008.43.1.30.
Comparison of Flexible Intramedullary Nailing with External Fixation in Pediatric Femoral Shaft Fractures
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Chuncheon Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea. ssros91@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2106413
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2008.43.1.30
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: This study compared the results of external fixation with those of flexible intramedullary nailing using Ender nails in pediatric femoral shaft fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
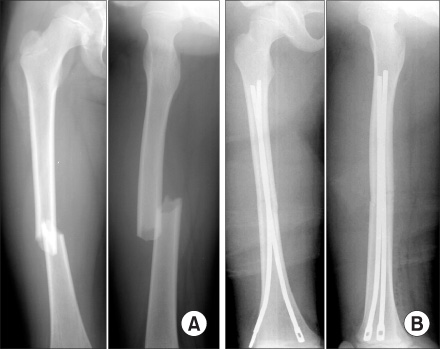
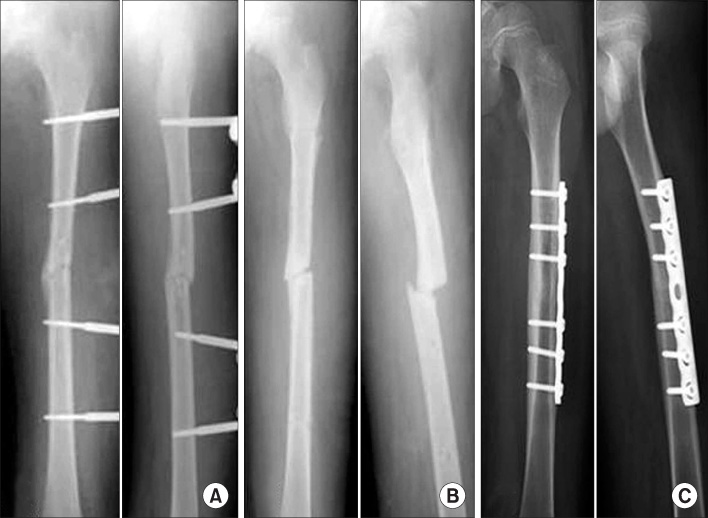
Twenty-eight children with pediatric femoral shaft fractures were enrolled in the study. The children's ages ranged from 6 to 11 years, and the average period of follow-up was 27.2 months. Fifteen patients underwent flexible intramedullary nailing (FIN) using Ender nails and thirteen patients underwent external fixation (EF). The outcomes were assessed based on the clinical and radiology findings.
RESULTS
The healing time averaged 9.8 weeks in the FIN group and 11.2 weeks in the EF group. In the FIN group, one patient suffered pin migration. In the EF group, three patients had a pin site infection, one patient had refracture after removing the external fixator and one patient had pin breakage 8 weeks after surgery. The broken pin was removed and the condition was stabilized with internal fixation using a plate.
CONCLUSION
Flexible intramedullary nailing with Ender nails is an effective treatment option for treating femoral shaft fractures in children because it has fewer complications than external fixation does.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Aronson J, Tursky EA. External fixation of femur fracture in children. J Pediatr Orthop. 1992. 12:157–163.2. Bar-On E, Sagiv S, Porat S. External fixation or flexible intramedullary nailing for femoral shaft fractures in children. A prospective, randomised study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1997. 79:975–978.3. Carey TP, Galpin RD. Flexible intramedullary nail fixation of paediatric femoral fracture. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996. 332:110–118.4. Corry IS, Nicol RO. Limb length after fracture of the femoral shaft in children. J Pediatr Orthop. 1995. 15:217–219.
Article5. Gregory RJ, Cubison TC, Pinder IM, Smith SR. External fixation of lower limb fractures in children. J Trauma. 1992. 33:691–693.
Article6. Evanoff M, Strong ML, MacIntosh R. External fixation mainiained until fracture consolidation in the skeletally immature. J Pediatr Orthop. 1993. 13:98–101.7. Flynn JM, Hresko T, Reynolds RA, Blasier RD, Davidson R, Kasser J. Titanium elastic nails for pediatric femur fractures: a multicerter study of early results with analysis of complications. J Pediatr Orthop. 2001. 21:4–8.8. Flynn JM, Luedtke LM, Ganley TJ, et al. Comparison of titanium elastic nails with traction and a spica cast to treat femoral fractures in children. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004. 86:770–777.
Article9. Hansen TB. Fractures of the femoral shaft in children treated with an AO-compression plate: Report of 12 cases followed until adulthood. Acta Orthop Scand. 1992. 63:50–52.10. Heinrich SD, Drvaric DM, Darr K, MacEwen GD. The operative stabilization of pediatric diaphyseal femur fractures with flexible intramedullary nails: a prospective analysis. J Pediatr Orthop. 1994. 14:501–507.
Article11. Hong KD, Ha SS, Chung NS, Sim JC, Kim JY. Nancy nail fixation for femur shaft fracture in children. J Korean Fracture Soc. 2003. 16:592–599.
Article12. Kim HY, Park JH, Lee SH, et al. Treatment of femoral shaft fractures with external fixators in children. J Korean Fracture Soc. 2002. 15:36–44.
Article13. Ligier JN, Metaizeau JP, Prevot J, Lascombes P. Elastic stable intramedullary nailing of femoral shaft fractures in children. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1988. 70:74–77.
Article14. McCartney D, Hinton A, Heinrich SD. Operative stabilization of pediatric femur fractures. Orthop Clin North Am. 1994. 25:635–650.
Article15. Yun YH, Choi CH, Jung JH. Flexible intramedullary nailing in children's femoral shaft fractures. J Korean Fracture Soc. 2003. 16:385–391.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Flexible Intramedullary Nailing with External Fixation for Treating Pediatric Femoral Shaft Fractures
- A Comparison of Overgrowth after Treatment for Pediatric Femoral Shaft Fractures: Flexible Intramedullary Nailing versus External Fixation
- Treatment of Open Type-III Tibial Shaft Fractures -Comparison Between Ilizarov External Fixation and Secondary Intramedullary Nailing-
- Flexible Intramedullary Nail Fixation of Pediatric Femoral Shaft Fracture
- Interlocking Intramedullary Nailing for the Femoral Shaft Fractures