J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2007 Feb;42(1):1-7. 10.4055/jkoa.2007.42.1.1.
The "Four-in-One" Procedure for Habitual Patellar Dislocation in Children with Formation Failure of Femoral Trochlea and Generalized Ligamentous Laxity : A Preliminary Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. pedhkim@yumc.yonsei.ac.kr
- 2Hallym University College of Medicine, Anyang, Korea.
- KMID: 2106368
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2007.42.1.1
Abstract
-
Purpose: To evaluate the clinical results of a "Four-in-One" procedure for a habitual dislocation of the patella in children with generalized ligamentous laxity and formation failure of the femoral trochlea.
Materials and Methods
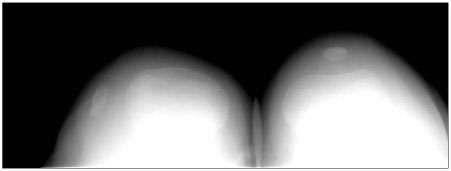
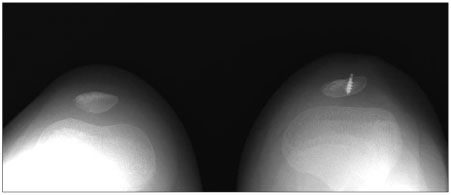
Five knees in 4 patients were included in this study. The average age of the patients at the time of surgery was 5.9 years and the subjects were followed up for an average of 41.6 months postoperatively. The clinical results were evaluated using the criteria of the Kujala's scoring system as well as a physical examination and radiological findings.
Results
During the follow-up period, there were no recurrent dislocations, knee joint pain, limitations of motion or gait disturbances in any of the cases. The mean Kujala score was 96.8. Two cases had complications related to wound healing but they healed eventually.
Conclusion
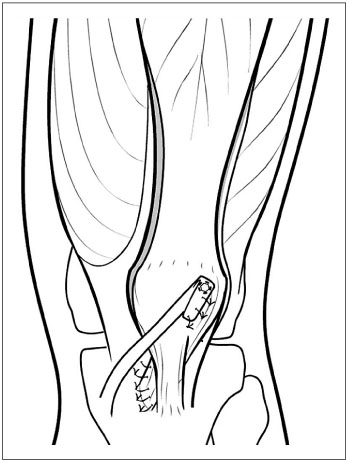
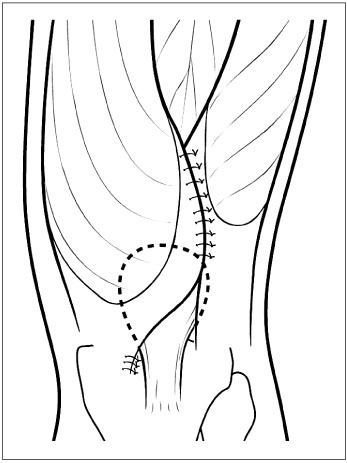
The "Four-in-One" procedure, which include the lateral retinacular release, medial vector augmentation, semitendinosus tenodesis, and patellar tendon transfer is recommended for a habitual dislocation of the patella in children with generalized ligament laxity and formation failure of the femoral trochlea.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Baker RH, Carroll N, Dewar FP, Hall JE. The semitendinosus tenodesis for recurrent dislocation of the patella. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1972. 54:103–109.
Article2. Baksi DP. Restoration of dynamic stability of the patella by pes anserinus transposition. A new approach. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1981. 63:399–403.
Article3. Beighton P, Solomon L, Soskolne CL. Articular mobility in an African population. Ann Rheum Dis. 1973. 32:413–418.
Article4. Chen SC, Ramanathan EB. The treatment of patella instability by lateral release. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1984. 66:344–348.5. Crosby EB, Insall J. Recurrent dislocation of the patella. Relation of treatment to osteo-arthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1976. 58:9–13.
Article6. Deie M, Ochi M, Sumen Y, Yasumoto M, Kobayashi K, Kimura H. Reconstruction of the medial patellofemoral ligament for the treatment of habitual or recurrent dislocation of the patella in children. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2003. 85:887–890.
Article7. Dejour H, Walch G, Neyret P, Adeleine P. Dysplasia of the femoral trochlea. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 1990. 76:45–54.8. Dougherty J, Wirth CR, Akbarnia BA. Management of patella subluxation. A modification of Hauser's technique. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976. 115:204–208.9. Fondren FB, Goldner JL, Bassett FH 3rd. Recurrent dislocation of the patella treated by the modified Roux-Goldthwait procedure. A prospective study of fourty-seven knees. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1985. 67:993–1005.10. Hall JE, Micheli LJ, McManama GB Jr. Semitendinosus tenodesis for recurrent subluxation or dislocation of the patella. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1979. 14:31–35.
Article11. Insall J, Bullough PG, Burstein AH. Proximal "tube" realignment of the patella for chondromalacia patellae. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1979. 144:63–69.
Article12. Letts RM, Davidson D, Beaule P. Semitendinosus tenodesis for repair of recurrent dislocation of the patella in children. J Pediatr Orthop. 1999. 19:742–747.
Article13. Madigan R, Wissinger HA, Donaldson WF. Preliminary experience with a method of quadricepsplasty in recurrent subluxation of the patella. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1975. 57:600–607.
Article14. Schottle PB, Fucentese SF, Pfirrmann C, Bereiter H, Romero J. Trochlearplasty for patellar instability due to trochlear dysplasia: a minimum 2-year clinical and radiological follow-up of 19 knees. Acta Orthop. 2005. 76:693–698.15. Smith H. Recurrent dislocation of the patella, principal lecture. 1971. 19. Boston: N Engl Orthop Soc;283–294.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical results of surgical treatment for recurrent and habitual patellar dislocation
- Surgical Treatment of Patellar Instability in Children and Adolescents
- Surgical Treatment of Habitual Patella Dislocation with Genu Valgum
- Surgical Treatment for Planovalgus Foot in Children with Generalized Ligamentous Laxity
- Habitual Dislocation of the Patella: 4 Patients Report