J Korean Soc Magn Reson Med.
2012 Aug;16(2):169-172. 10.13104/jksmrm.2012.16.2.169.
Simultaneous Bilateral Quadriceps Tendon Rupture in Patient with Secondary Hyperparathyroidism due to Chronic Renal Failure: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Seoul Paik Hospital, InJe University College of Medicine, Korea. jcshim@unitel.co.kr
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Seoul Paik Hospital, InJe University College of Medicine, Korea.
- KMID: 2099851
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13104/jksmrm.2012.16.2.169
Abstract
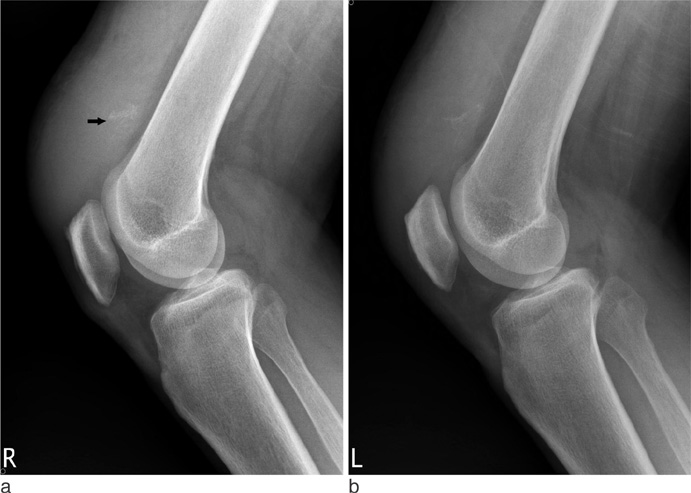
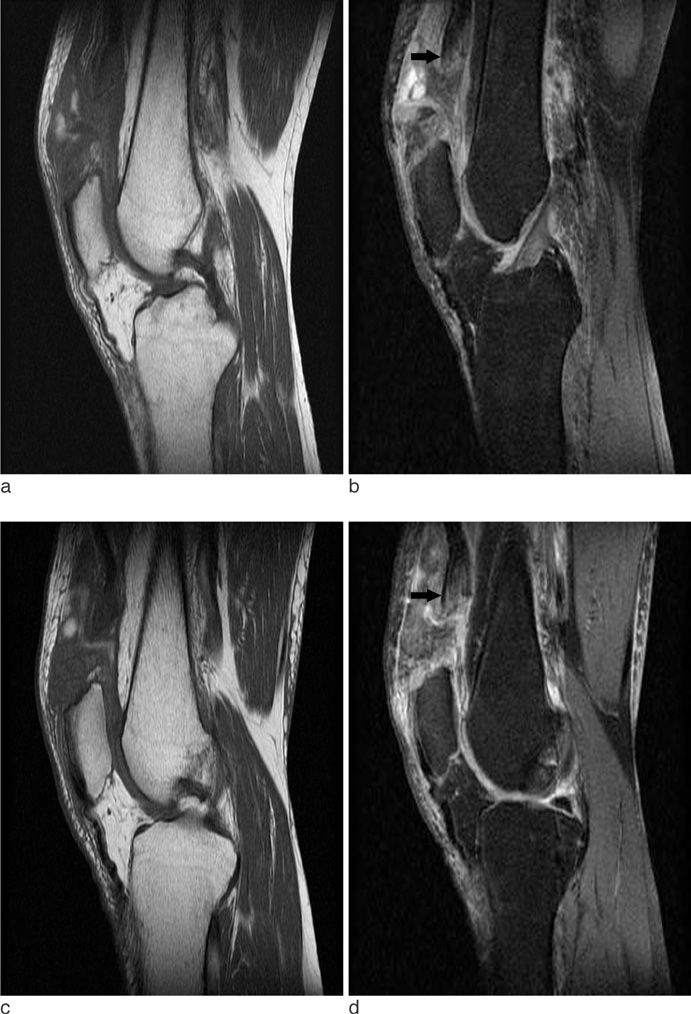
- Simultaneous bilateral spontaneous rupture of the quadriceps tendon is a very rare condition and only a few cases have been reported in the literature. The etiology is not clear yet. But it occurs infrequently in patients with chronic metabolic disorders, such as secondary hyperparathyroidism due to chronic renal failure. We describe a case of simultaneous spontaneous bilateral quadriceps tendon tupture in a 36-year-old male patient with secondary hyperaprathyroidism due to chronic renal failure.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Dunnick NR. Image interpretation session: 1999. Bilateral quadriceps tendon rupture and multiple brown tumors in a patient with secondary hyperparathyroidism. Radiographics. 2000. 20:262–263.2. Calvo E, Ferrer A, Robledo AG, Alvarez L, Castillo F, Vallejo C. Bilateral simultaneous spontaneous quadriceps tendons rupture. A case report studied by magnetic resonance imaging. Clin Imaging. 1997. 21:73–76.3. Lee YS, Son SB, Han CW, Kang SW. Bilateral simultaneous quadriceps tendon rupture in a patient with secondary hyperparathyroidism: a case report. J Korean Radiol Soc. 2001. 45:507–511.4. Lombardi LJ, Cleri DJ, Epstein E. Bilateral spontaneous quadriceps tendon rupture in a patient with renal failure. Orthopedics. 1995. 18:187–191.5. Shah MK. Simultaneous bilateral rupture of quadriceps tendons: analysis of risk factors and associations. South Med J. 2002. 95:860–866.6. Anderson WE 3rd, Habermann ET. Spontaneous bilateral quadriceps tendon rupture in a patient on hemodialysis. Orthop Rev. 1988. 17:411–414.7. Bhole R, Flynn JC, Marbury TC. Quadriceps tendon ruptures in uremia. Clin Orthop. 1985. 195:200–206.8. Newberg A, Wales L. Radiographic diagnosis of quadriceps tendon rupture. Radiology. 1977. 125:367–371.9. De Franco P, Varghese J, Brown WW, Bastani B. Secondary hyperparathyroidism, and not beta 2-microglobulin amyloid, as a cause of spontaneous tendon rupture in patients on chronic homodialysis. Am J kidney Dis. 1994. 24:951–955.10. Meneghello A, Bertoli M. Tendon disease and adjacent bone erosion in dialysis patients. Br J Radiol. 1983. 56:915–920.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Bilateral Simultaneous Quadriceps Tendon Rupture in a Patient with Secondary Hyperparathyroidism: A Case Report
- Simultaneous Bilateral Quadriceps Tendon Rupture in Patient with Chronic Renal Failure
- Modified Transosseous Suture Technique for the Quadriceps Avulsion Fracture in Chronic Renal Failure: A Case Report
- Pathologic Quadriceps Tendon Rupture in Patients with Chronic Renal Failure: Case Report
- Simultaneous Bilateral Quadriceps Tendon Rupture in a Patient with Chronic Renal Failure