J Korean Soc Radiol.
2012 Dec;67(6):417-423. 10.3348/jksr.2012.67.6.417.
Diagnostic Accuracy of Detecting Hashimoto's Thyroiditis in Thyroid Cancer Patients Who Underwent Thyroid Surgery: Comparison of Ultrasonography, Positron Emission Tomography/CT, Contrast Enhanced CT, and Anti-Thyroid Antibody
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Korea Cancer Center Hospital, Seoul, Korea. elfland0304@naver.com
- KMID: 2097976
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2012.67.6.417
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To compare the diagnostic accuracy of ultrasonography (US), F18-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/CT (PET/CT), contrast enhanced CT (CECT), serum anti-thyroid antibody for detecting Hashimoto's thyroiditis in thyroid cancer patients who underwent neck surgery.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A total of 150 patients with suspicious for thyroid cancer, who had previously undergone US guided needle aspiration of thyroid, were evaluated with the use of US, PET/CT, CECT and serum anti-thyroid antibody. The four studies were performed within two months before neck surgery. Hashimoto's thyroiditis was confirmed by histopathological results. The diagnostic accuracy of US, PET/CT, CECT and serum anti-thyroid antibody were calculated statistically.
RESULTS
Hashimoto's thyroiditis was diagnosed in 51 out of the 150 patients, following neck surgery. The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value and accuracy of US were 76.5%, 92.9%, 84.8%, 88.5%, and 87.3%, respectively. The corresponding values of PET/CT were 37.3%, 96.0%, 82.6%, 74.8%, and 76.0%, and CECT were 62.7%, 89.9%, 76.2%, 82.4%, and 80.7%, and serum anti-thyroid antibody level were 90.2%, 93.9%, 88.5%, 94.9%, and 92.7%, respectively. McNemar test revealed significant difference among PET/CT and others, but no significant differences among US, CECT and serum anti-thyroid antibody. Overall, serum anti-thyroid antibody showed most accurate diagnostic performance.
CONCLUSION
In detecting Hashimoto's thyroiditis, serum anti-thyroid antibody showed higher diagnostic accuracy than others. US also showed relatively high diagnostic accuracy.
MeSH Terms
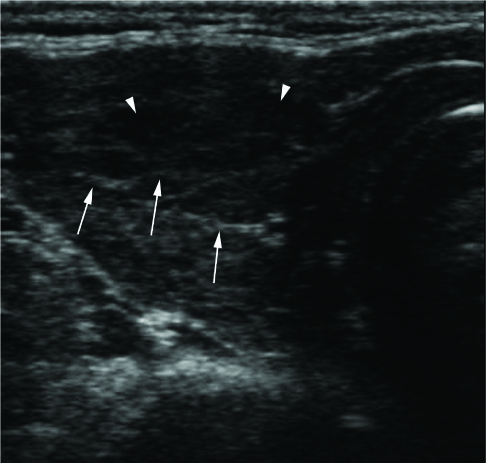
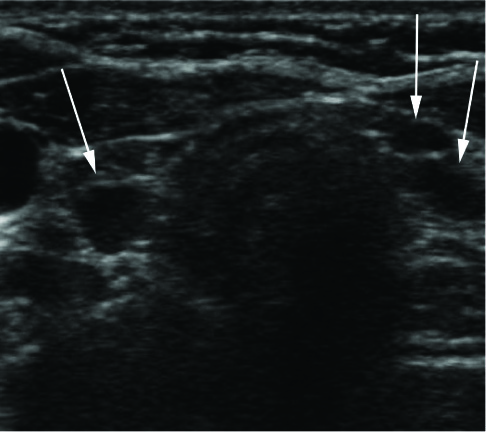
Figure
Reference
-
1. Moshynska OV, Saxena A. Clonal relationship between Hashimoto thyroiditis and thyroid lymphoma. J Clin Pathol. 2008. 61:438–444.2. Tamimi DM. The association between chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis and thyroid tumors. Int J Surg Pathol. 2002. 10:141–146.3. Yeh HC, Futterweit W, Gilbert P. Micronodulation: ultrasonographic sign of Hashimoto thyroiditis. J Ultrasound Med. 1996. 15:813–819.4. Toldy E, Lócsei Z, Kalmár I, Varga L, Kovács LG. [Diagnostic value of thyroid antibodies]. Orv Hetil. 1996. 137:2075–2080.5. Pedersen OM, Aardal NP, Larssen TB, Varhaug JE, Myking O, Vik-Mo H. The value of ultrasonography in predicting autoimmune thyroid disease. Thyroid. 2000. 10:251–259.6. Kurukahvecioglu O, Taneri F, Yüksel O, Aydin A, Tezel E, Onuk E. Total thyroidectomy for the treatment of Hashimoto's thyroiditis coexisting with papillary thyroid carcinoma. Adv Ther. 2007. 24:510–516.7. Erdogan M, Erdem N, Cetinkalp S, Ozgen AG, Saygılı F, Yilmaz C, et al. Demographic, clinical, laboratory, ultrasonographic, and cytological features of patients with Hashimoto's thyroiditis: results of a university hospital of 769 patients in Turkey. Endocrine. 2009. 36:486–490.8. Takashima S, Matsuzuka F, Nagareda T, Tomiyama N, Kozuka T. Thyroid nodules associated with Hashimoto thyroiditis: assessment with US. Radiology. 1992. 185:125–130.9. Ohmori N, Miyakawa M, Ohmori K, Takano K. Ultrasonographic findings of papillary thyroid carcinoma with Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Intern Med. 2007. 46:547–550.10. Kim DW, Eun CK, In HS, Kim MH, Jung SJ, Bae SK. Sonographic differentiation of asymptomatic diffuse thyroid disease from normal thyroid: a prospective study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010. 31:1956–1960.11. Liu Y. Clinical significance of thyroid uptake on F18-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography. Ann Nucl Med. 2009. 23:17–23.12. Lewis PJ, Salama A. Uptake of fluorine-18-fluorodeoxyglucose in sarcoidosis. J Nucl Med. 1994. 35:1647–1649.13. Keyes JW Jr, Harkness BA, Greven KM, Williams DW 3rd, Watson NE Jr, McGuirt WF. Salivary gland tumors: pretherapy evaluation with PET. Radiology. 1994. 192:99–102.14. Braams JW, Pruim J, Freling NJ, Nikkels PG, Roodenburg JL, Boering G, et al. Detection of lymph node metastases of squamous-cell cancer of the head and neck with FDG-PET and MRI. J Nucl Med. 1995. 36:211–216.15. Kim HK, Yoon JH, Kim SJ, Kang HC. Clinical meaning of diffuse 18F-FDG PET thyroid uptake. Korean J Med. 2011. 81:595–601.16. Kang KW, Kim SK, Kang HS, Lee ES, Sim JS, Lee IG, et al. Prevalence and risk of cancer of focal thyroid incidentaloma identified by 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography for metastasis evaluation and cancer screening in healthy subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003. 88:4100–4104.17. Yasuda S, Shohtsu A, Ide M, Takagi S, Takahashi W, Suzuki Y, et al. Chronic thyroiditis: diffuse uptake of FDG at PET. Radiology. 1998. 207:775–778.18. Silverman PM, Newman GE, Korobkin M, Workman JB, Moore AV, Coleman RE. Computed tomography in the evaluation of thyroid disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1984. 142:897–902.19. Iida Y, Konishi J, Harioka T, Misaki T, Endo K, Torizuka K. Thyroid CT number and its relationship to iodine concentration. Radiology. 1983. 147:793–795.20. Radecki PD, Arger PH, Arenson RL, Jennings AS, Coleman BG, Mintz MC, et al. Thyroid imaging: comparison of high-resolution real-time ultrasound and computed tomography. Radiology. 1984. 153:145–147.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ultrasonographic Findings of Papillary Thyroid Cancer with or without Hashimoto's Thyroiditis
- Thyroid MALT Lymphoma Associated with Thyroid Papillary Cancer
- The Diagnostic Utility of Ultrasonography, CT and PET/CT for the Preoperative Evaluation of Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis in Papillary Thyroid Cancer Patients
- Clinical Meaning of Incidental Thyroid Uptake on F-18 FDG PET-CT
- A case of Hashimoto's thyroiditis coexisting with thyroid papillary and follicular carcinoma