J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2001 Jun;8(2):148-155. 10.4184/jkss.2001.8.2.148.
Changes of Kyphotic Angle Following Operative Treatment of Tuberculous Spondylitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, School of Medicine, Chungnam National University, Taejon, Korea. jsahn@cuvic.cnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2097755
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2001.8.2.148
Abstract
-
STUDY DESIGN: Thirty-seven patients with spinal tuberculosis were evaluated according to surgical method.
OBJECTIVES
To evaluate the effectiveness of posterior spinal instrumentation in the surgical treatment of patient with tuberculous spondylitis. SUMMARY OF LITERATURE REVIEWS: There are many debates about the effectiveness of posterior spinal instrumentation combined with anterior interbody fusion in tuberculous spondylitis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From January 1995 to June 2000, 37 patients were divided into two groups depending on their use of posterior spinal instrumentation. Group I consist of thirteen patients who were treated with conventional anterior corpectomy and anterior interbody fusion using autogenous strut bone graft. Group II was composed of twenty-four patients who were treated with conventional anterior corpectomy and anterior interbody fusion combined with posterior spinal instrumentation. Changes of corrected kyphotic angle and complication were measured using pre-, post-operative and follow-up radiographs and chart review.
RESULTS
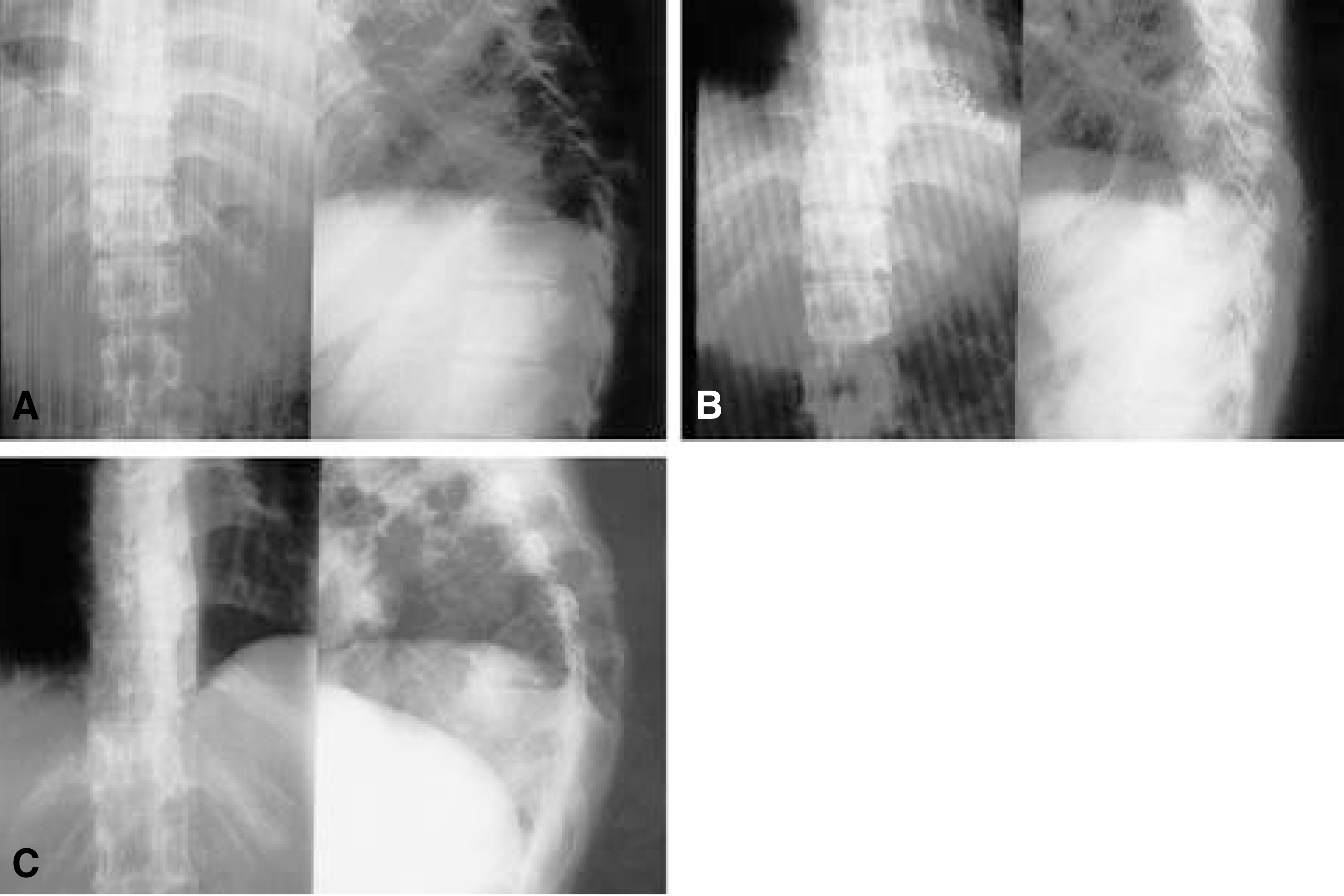
In group I, six cases (46.2%) showed loss of corrected kyphotic angle. Of these six cases, five cases had initial kyphotic angle of more than 20 dgree and three cases had involvement of two or more vertebrae. All six cases had thoracic or thoracolumbar involvement. Comparing two groups, maintaining corrected kyphotic angle and low complication rates were obtained in group II during follow-up period. The change of deformity as followed. In thoracic area, the mean kyphotic angle of 26.5 dgree was reduced to 18 dgree postoperatively, At the most recent follow-up, the mean kyphotic angle was 31.5 dgree in group I, a loss of correction of 13.5 dgree . In group II, the mean kyphotic angle was corrected from 27 dgrees to 13.5 dgree after surgery. At the most recent follow-up, the mean kyphotic angle was 17.5 dgrees, a loss of correction of 4 dgree .
CONCLUSION
Posterior spinal instrumentation combined with conventional anterior corpectomy and anterior interbody fusion were found to be effective for preventing loss of kyphotic angle and for maintaining stable bone fusion in patients with mean
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Multidrug-resistant Tuberculosis Spondylitis
Sung Chan Ki, Ki Soo Kim, Yoon Hong Kim, Yong Soo Choi
J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 2008;15(2):102-105. doi: 10.4184/jkss.2008.15.2.102.Tuberculosis Spondylitis T4-6 with Compression Fracture T5 - A Case Report -
Ho-yong Shim, Ha-lim Lee, Ki-deok Park, Ju-kang Lee, Oh-kyung Lim
J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 2012;19(1):25-30. doi: 10.4184/JKSS.2021.19.1.25.
Reference
-
1). Ahn B.H.Treatment for Pott's paraplegia. Acta orthop. Scand. 39:145–60. 1968.2). Bailey HL, Mary G, Hodgson AR, Shin JS. Tuberculosis of the spine. Operative findings and results in one hundred consecutive patients treated by removal of the lesion and anterior grafting. J Bone Joint Surg. 54-A:1633–1657. 1972.3). Chu J.B.Treatment of spinal tuberculosis in Korea using focal debridement and interbody fusion. Clin. Orthop. 50:235–53. 1968.4). Chung Y.K., Kim S.W., Han H.M., et al. .:. The results of the surgical treatment using posterior spinal instrumentation for tuberculous spondylitis. J of Korean Spine Surg. vol. 6:No.(1):pp. 81–88.5). Fountain SS, Hsu LCS, Yau ACMC, et al. .:. Progressive kyphosis following solid anterior spinal fusion in children with tuberculosis of the spine. J Bone Joint Surg. 57-A:1104–1107. 1975.6). Goel MK. Treatment of Potts paraplegia by operation. J Bone Joint Surg. 49-B:674–681. 1967.
Article7). Griffiths D.L.L.The treatment of spinal tuberculosis. Recent Advances in Orthopaedics. London: Churchill Liv ingston;1979.8). Griffith DL, Roaf R, Seddon HJ. Potts paraplegia and its operative treatment. J Bone Joint Surg. 35-B:487. 1953.9). Guven O, Kumano K, Yalcin S, et al. .:. A single stage posterior approach and rigid fixation for preventing kyphosis in the treatment of spinal tuberculosis. Spine. 19:1039–1043. 1994.
Article10). Hallock H, Jones JB. An end-result study of the effectives of the spine-fusion operation in a large number of patients. J Bone Joint Surg. 36-A:219–240. 1954.11). Hodgson AR, Stock FE. Anterior spinal fusion for the treatment of tuberculosis of the spine. The operative findings and results of treatment in the first one hundred cases. J Bone Joint Surg. 42-A:295–310. 1960.12). Kee J.I., Kang S.Y., Moon M.S., et al. .:. Treatment of the spinal tuberculosis with severe kyphosis and paraplegia. J. Korean Orthop. Assoc. 5-. 2:73–78. 1970.13). Kemp HBS, Jackson JW, Jeremiah JD, Cook J. Anterior fusion of the spine for infective lesions in adults. J Bone Joint Surg. 55-B:715–734. 1973.
Article14). Kohli SB. Radical surgical approach to spinal tuberculosis. J Bone Joint Surg. 49-B:668. 1967.
Article15). Konstam PG, Blesovsky A. The ambulant treatment of spinal tuberculosis. Br J Surg. 50:26–38. 1962.
Article16). Lifeso RM, Weaver P, Harder EH. Tubercu lous spondylitis in adults. J Bone Joint Surg. 67-A:1405–1413. 1985.17). Medical Research Council Working Party on Tuberculosis of the Spine. A controlled trial of ambulant outpatient treatment and inpatient rest in bed in the management of tuberculosis of the spine in young korean patients on standard chemotherapy. A study in Masan, Korea. J Bone Joint Surg. 55-B:678–697. 1973.18). Medical Research Council Working Party on Tuberculosis of the Spine. Five-year assessment of controlled tri -als of ambulatory treatment. Debridement and anterior spinal fusion in the management of tuberculosis of the spine. Studies in Bulawayo (Rhodesia) and in Hong Kong. J Bone Joint Surg. 60-B:163–177. 1978.19). Medical Research Council Working Party on Tuberculosis of the Spine. A 10-year assessment of a controlled trial comparting debridement and anterior spinal fusion in the management of tuberculosis of the spine in patients on standard chemotherapy in Hong Kong. J Bone Joint Surg. 64-B:393–398. 1982.20). Medical Research Council Working Party on tuberculosis of the spine. A 10 year assessment of controlled tri -als of inpatient and outpatient treatment and plaster of Paris jackets for tuberculosis of the spine in children on standard chemotherapy. Studies in Pusan and Masan, Korea. J Bone Joint Surg. 67-B:103–110. 1985.21). Moon M.S., Woo Y.K., Lee K.S., et al. .:. posterior instrumentation and anterior interbody fusion for tuberculous kyphosis of dorsal and lumbar spine. Spine. 20:1910–1916. 1995.22). Moon M.S., Woo Y.K., Ok I.Y., et al. .:. Posterior instrumentation for treatment of active dorsolumbar tuberculosis with kyphosis. J Korean Orthop. 24:660–665. 1989.
Article23). Moon MS, Rhee SK, Kang YK. Harrington rods in treatment of active spinal tuberculosis with kyphosis. J Western Pacif Orthop Assoc. 53-58:1986.24). Oga M, arizono T, Takasita M, et al. .:. Evaluation of the risk of instrumentation as a foreign body in spinal tuberculosis. Clinical and biologic study. Spine. 18:1890–1894. 1993.25). Rajasekaran S, Shanmugasundaram TK. Predilection of the angle of gibbus deformity in tuberculosis of the spine. J Bone Joint Surg. 69-A:503–509. 1987.26). Rajasekaran B, Soundarapandian S. Progression of kyphosis in tuberculosis of the spine treated by anterior arthrodesis. J Bone Joint Surg. 71-A:1314–1323. 1989.
Article27). Tuli SM, Srivastava TP, Varma BP, et al. .:. Tuberculosis of spine. Acta Orthop Scand. 38:445–458. 1967.
Article28). Tuli SM. Treatment of neurological complications in the tuberculosis of the spine. J Bone Joint Surg. 51-A:680–692. 1969.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Analysis on the Anterior Approach for Tuberculous Spondylitis of Thoraco-Lumbar Junction
- The Efficacy of Titanium Mesh Cage in Tuberculous Spondylitis Treated with Anterior Intervertebral Fusion
- The Results of the Surgical Treatment using Posterior Spinal instrumentation for Tuberculous Spondylitis
- Combined Anterior and Posterior Operation for Thoracic Tuberculous Spondylitis
- Vascularized Fibular Bone Graft for Tuberculous Spondylitis: Case Report