Korean J Hematol.
2012 Jun;47(2):85-86. 10.5045/kjh.2012.47.2.85.
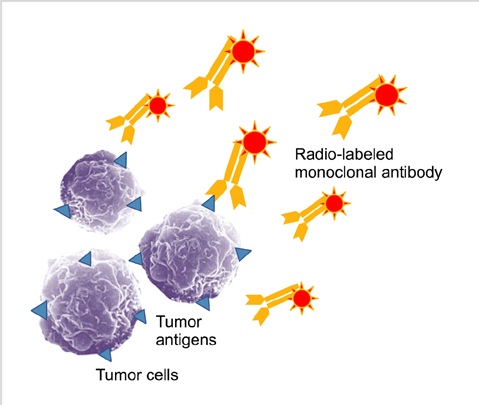
Is radioimmunotherapy a 'magic bullet'?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Hematology-Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2083598
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/kjh.2012.47.2.85
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chamarthy MR, Williams SC, Moadel RM. Radioimmunotherapy of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: from the 'magic bullets' to 'radioactive magic bullets'. Yale J Biol Med. 2011. 84:391–407.2. Gisselbrecht C, Vose J, Nademanee A, Gianni AM, Nagler A. Radioimmunotherapy for stem cell transplantation in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: in pursuit of a complete response. Oncologist. 2009. 14:Suppl 2. 41–51.
Article3. Jo JC, Yoon DH, Kim S, et al. Yttrium-90 ibritumomab tiuxetan plus busulfan, cyclophosphamide, and etoposide (BuCyE) versus BuCyE alone as a conditioning regimen for non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Korean J Hematol. 2012. 47:119–125.
Article4. Han EJ, Lee SE, Kim SH, et al. Clinical outcomes of post-remission therapy using (90)yttrium ibritumomab tiuxetan (Zevalin®) for high-risk patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Ann Hematol. 2011. 90:1075–1082.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Sodium-Glucose Co-transporter 2 Inhibitor: The Magic Bullet for Obesity in Diabetes?
- Forensic Review of Bullet Embolism
- The anesthetic management of a venous bullet embolism to the right ventricle: A case report
- Intracranial Bullet Migration in Penetrating Missile Injury
- Radiculopathy as Delayed Presentations of Retained Spinal Bullet