Korean J Pain.
2013 Oct;26(4):392-395. 10.3344/kjp.2013.26.4.392.
Approach for Epiduroscopic Laser Neural Decompression in Case of the Sacral Canal Stenosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Konyang University Hospital, Daejeon, Korea. yusyuni@daum.net
- KMID: 2074049
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2013.26.4.392
Abstract
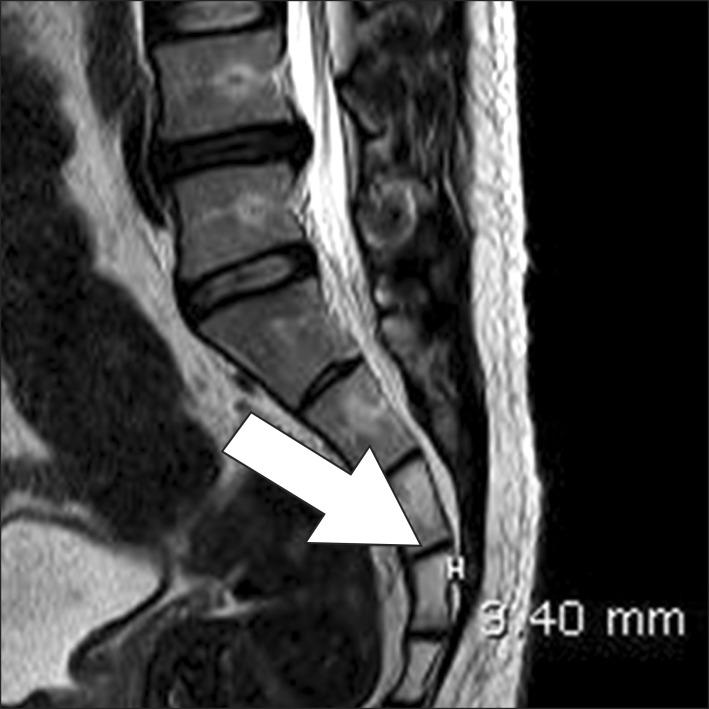
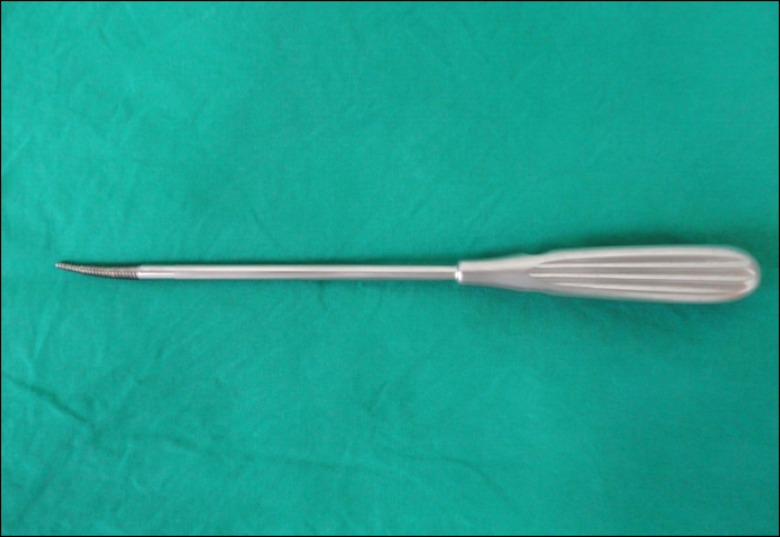
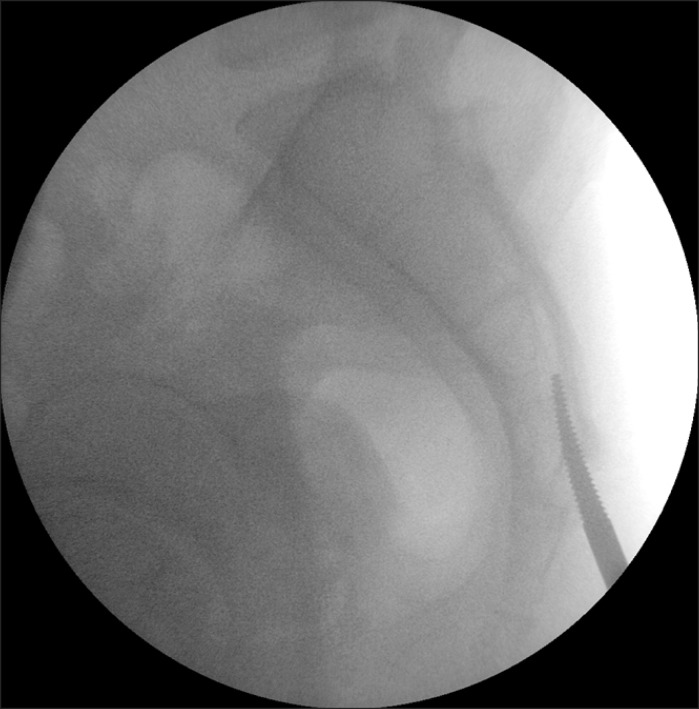
- Epiduroscopy is very useful in the treatment of not only low back pain caused by failed back surgery syndrome, epidural scar or herniated disc but also by chronic refractory low back pain which does not respond to interventional conservative treatment including fluoroscopically-directed epidural steroid injections and percutaneous adhesiolysis. Because cauterization using a laser fiber has become recently available, a wider opening is required to enter into the sacral canal in the case of epiduroscopic laser neural decompression (ELND). However, in a few patients, it is difficult to insert a device into the epidural space due to stenosis around the opening, and there is no alternative method. Herein, we report a case where a hiatus rasp specially designed for such patients was used to perform the operation.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Percutaneous Epidural Neuroplasty
Sang Ho Moon, Han Sik Kim
J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2015;50(3):215-224. doi: 10.4055/jkoa.2015.50.3.215.The Comparison of the Result of Epiduroscopic Laser Neural Decompression between FBSS or Not
Dae Hyun Jo, Eung Don Kim, Hyun Jin Oh
Korean J Pain. 2014;27(1):63-67. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2014.27.1.63.
Reference
-
1. Jo DH, Yang HJ. The survey of the patient received the epiduroscopic laser neural decompression. Korean J Pain. 2013; 26:27–31. PMID: 23342204.
Article2. Richter EO, Abramova MV, Cantu F, De Andres J, Lierz P, Manchiaro PL, et al. Anterior epiduroscopic neural decompression: eight-center experience in 154 patients. Eur J Pain Suppl. 2011; 5:401–407.
Article3. Helm S 2nd, Gross JD, Varley KG. Mini-surgical approach for spinal endoscopy in the presence of stenosis of the sacral hiatus. Pain Physician. 2004; 7:323–325. PMID: 16858469.4. Senoglu N, Senoglu M, Oksuz H, Gumusalan Y, Yuksel KZ, Zencirci B, et al. Landmarks of the sacral hiatus for caudal epidural block: an anatomical study. Br J Anaesth. 2005; 95:692–695. PMID: 16155035.
Article5. Aggarwal A, Kaur H, Batra YK, Aggarwal AK, Rajeev S, Sahni D. Anatomic consideration of caudal epidural space: a cadaver study. Clin Anat. 2009; 22:730–737. PMID: 19637298.
Article6. Sekiguchi M, Yabuki S, Satoh K, Kikuchi S. An anatomic study of the sacral hiatus: a basis for successful caudal epidural block. Clin J Pain. 2004; 20:51–54. PMID: 14668657.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Occurrence of Trochlear Nerve Palsy after Epiduroscopic Laser Discectomy and Neural Decompression
- The Survey of the Patient Received the Epiduroscopic Laser Neural Decompression
- Minimally Invasive Irrigation for Lumbar Spinal Epidural Abscess using a Trans-Sacral Epiduroscopic Laser Decompression Catheter
- The Comparison of the Result of Epiduroscopic Laser Neural Decompression between FBSS or Not
- Trans-Sacral Epiduroscopic-Assisted 1,414-nm Nd:YAG Laser Decompression for Lumbar Discal Cyst: A Report of 9 Cases