Korean J Pain.
2013 Jul;26(3):303-306. 10.3344/kjp.2013.26.3.303.
A Case of Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome Associated with Migraine and Fibromyalgia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Eulji University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. djy@eulji.ac.kr
- KMID: 2074034
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2013.26.3.303
Abstract
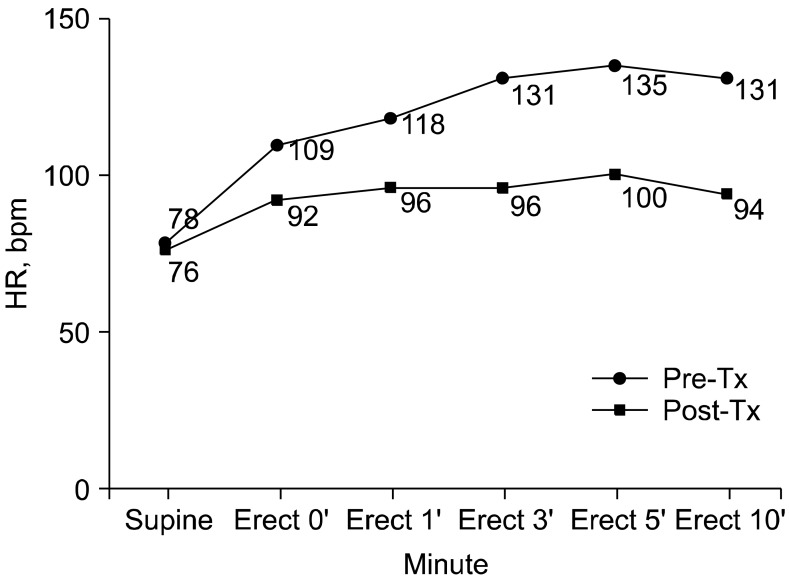
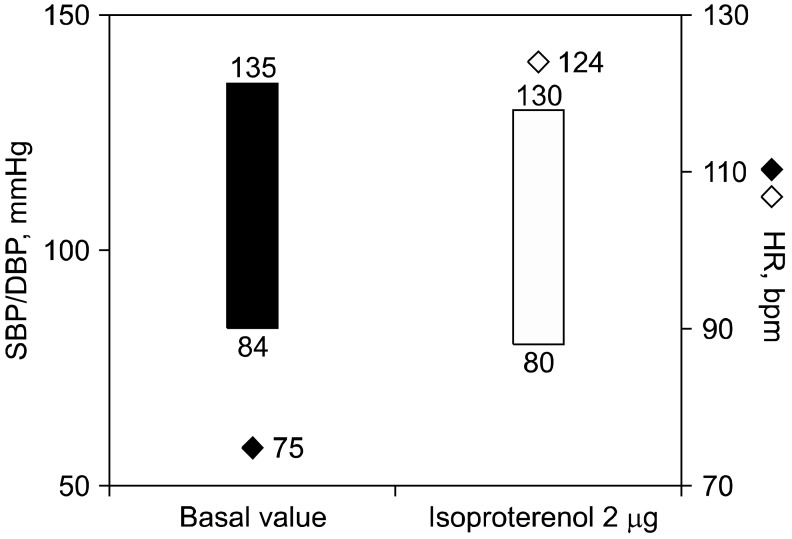
- Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS) refers to the presence of orthostatic intolerance with a heart rate (HR) increment of 30 beats per minute (bpm) or an absolute HR of 120 bpm or more. There are sporadic reports of the autonomic nervous system dysfunction in migraine and fibromyalgia. We report a case of POTS associated with migraine and fibromyalgia. The patient was managed with multidisciplinary therapies involving medication, education, and exercise which resulted in symptomatic improvement. We also review the literature on the association between POTS, migraine, and fibromyalgia.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Piovesan EJ, Sobreira CF, Scola RH, Lorenzoni PJ, Lange MC, Werneck LC, et al. Episodic migraine associated with postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome and vasovagal syncope: migraine triggers neuromediated syncope. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2008; 66:77–79. PMID: 18392420.
Article2. Staud R. Autonomic dysfunction in fibromyalgia syndrome: postural orthostatic tachycardia. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2008; 10:463–466. PMID: 19007537.
Article3. Low PA, Sandroni P, Joyner MJ, Shen WK. Postural tachycardia syndrom. In : Low PA, Benarroch EE, editors. Clinical autonomic disorders. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;2008. p. 515–533.4. Shim JC. Fibromyalgia syndrome. J Korean Pain Soc. 2004; 17:80–87.
Article5. Yunus MB. Towards a model of pathophysiology of fibromyalgia: aberrant central pain mechanisms with peripheral modulation. J Rheumatol. 1992; 19:846–850. PMID: 1404119.6. Wolfe F, Clauw DJ, Fitzcharles MA, Goldenberg DL, Katz RS, Mease P, et al. The American College of Rheumatology preliminary diagnostic criteria for fibromyalgia and measurement of symptom severity. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2010; 62:600–610. PMID: 20461783.
Article7. Kim SM, Lee SH, Kim HR. Applying the ACR preliminary diagnostic criteria in the diagnosis and assessment of fibromyalgia. Korean J Pain. 2012; 25:173–182. PMID: 22787548.
Article8. de Tommaso M, Sardaro M, Serpino C, Costantini F, Vecchio E, Prudenzano MP, et al. Fibromyalgia comorbidity in primary headaches. Cephalalgia. 2009; 29:453–464. PMID: 19170692.
Article9. Bou-Holaigah I, Calkins H, Flynn JA, Tunin C, Chang HC, Kan JS, et al. Provocation of hypotension and pain during upright tilt table testing in adults with fibromyalgia. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1997; 15:239–246. PMID: 9177917.10. Kosinski M, Bayliss MS, Bjorner JB, Ware JE Jr, Garber WH, Batenhorst A, et al. A six-item short-form survey for measuring headache impact: the HIT-6. Qual Life Res. 2003; 12:963–974. PMID: 14651415.11. Burckhardt CS, Clark SR, Bennett RM. The fibromyalgia impact questionnaire: development and validation. J Rheumatol. 1991; 18:728–733. PMID: 1865419.12. Beck AT, Ward CH, Mendelson M, Mock J, Erbaugh J. An inventory for measuring depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1961; 4:561–571. PMID: 13688369.
Article