Korean J Urol.
2015 Jan;56(1):12-18. 10.4111/kju.2015.56.1.12.
Metabolic effects of androgen deprivation therapy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea. kamsungchul@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2070264
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/kju.2015.56.1.12
Abstract
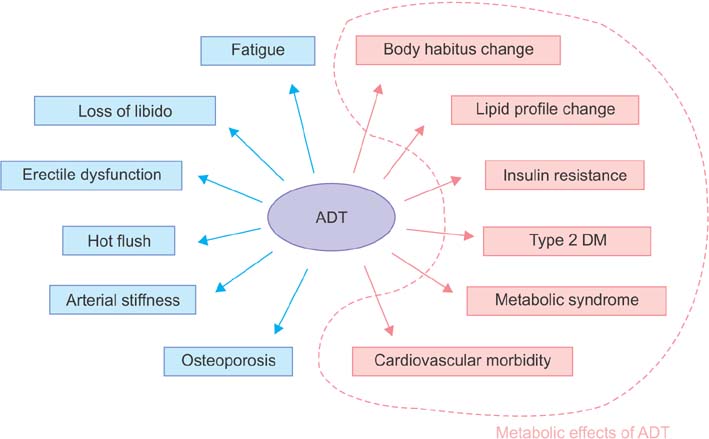
- The therapeutic effects and side effects of androgen deprivation therapy (ADT), which is a main treatment method for metastatic prostate cancer, are well known, but the metabolic effects have only recently been studied. This review describes the effects of ADT on body habitus, insulin resistance, lipid profiles, diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. The review was done by using KoreaMed and PubMed to search the medical literature related to prostate cancer, ADT, body habitus, lipid profile, diabetes, insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome, and cardiovascular disease. ADT increases fat mass and decreases lean body mass. Fat mostly accumulates in the subcutaneous area. ADT increases total cholesterol, triglycerides, and high-density lipoprotein, as well as the risk for insulin resistance and diabetes. ADT also increases the risk for cardiovascular events, but insufficient evidence is available for a correlation with mortality. ADT changes body habitus and lipid profiles and has different characteristics than those of classic metabolic syndrome, but it is related to insulin resistance and diabetes. ADT increases the risk for cardiovascular events. No consistent guidelines have been proposed for treating the metabolic effects of ADT, but the generally recommended treatment methods for lowering the risk of diabetes and cardiovascular disease should be fully understood. Additional studies are necessary.
MeSH Terms
-
Androgen Antagonists/*adverse effects/therapeutic use
Body Composition/drug effects
Cardiovascular Diseases/metabolism/mortality
Cholesterol/chemistry
Diabetes Mellitus/epidemiology/metabolism
Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone/*agonists
Humans
Insulin Resistance
Lipids/blood
Lipoproteins, HDL/blood
Male
Metabolic Syndrome X/epidemiology/metabolism
Prostatic Neoplasms/*drug therapy
Risk Factors
Triglycerides/chemistry
Androgen Antagonists
Cholesterol
Lipids
Lipoproteins, HDL
Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone
Triglycerides
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Correlation of Androgen Deprivation Therapy with Cognitive Dysfunction in Patients with Prostate Cancer: A Nationwide Population-Based Study Using the National Health Insurance Service Database
Bum Sik Tae, Byung Jo Jeon, Seung Hun Shin, Hoon Choi, Jae Hyun Bae, Jae Young Park
Cancer Res Treat. 2019;51(2):593-602. doi: 10.4143/crt.2018.119.
Reference
-
1. Siegel R, Ward E, Brawley O, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2011: the impact of eliminating socioeconomic and racial disparities on premature cancer deaths. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011; 61:212–236.2. Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010; 127:2893–2917.3. Baade PD, Youlden DR, Krnjacki LJ. International epidemiology of prostate cancer: geographical distribution and secular trends. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2009; 53:171–184.4. Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011; 61:69–90.5. Mottet N, Bellmunt J, Bolla M, Joniau S, Mason M, Matveev V, et al. EAU guidelines on prostate cancer. Part II: Treatment of advanced, relapsing, and castration-resistant prostate cancer. Eur Urol. 2011; 59:572–583.6. Jeong SJ, Kwak C, Lee SE. Therapeutic effect of maximal androgen blockade in metastatic prostate cancer. Korean J Urol. 2001; 42:642–649.7. Flaig TW, Glode LM. Management of the side effects of androgen deprivation therapy in men with prostate cancer. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2008; 9:2829–2841.8. Saylor PJ, Smith MR. Metabolic complications of androgen deprivation therapy for prostate cancer. J Urol. 2013; 189:1 Suppl. S34–S42.9. Nobes JP, Langley SE, Laing RW. Metabolic syndrome and prostate cancer: a review. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2009; 21:183–191.10. Leahy Y. Risk of metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes in androgen deprivation therapy. Clin J Oncol Nurs. 2008; 12:771–776.11. Saigal CS, Gore JL, Krupski TL, Hanley J, Schonlau M, Litwin MS, et al. Androgen deprivation therapy increases cardiovascular morbidity in men with prostate cancer. Cancer. 2007; 110:1493–1500.12. Efstathiou JA, Bae K, Shipley WU, Hanks GE, Pilepich MV, Sandler HM, et al. Cardiovascular mortality after androgen deprivation therapy for locally advanced prostate cancer: RTOG 85-31. J Clin Oncol. 2009; 27:92–99.13. Van Poppel H, Tombal B. Cardiovascular risk during hormonal treatment in patients with prostate cancer. Cancer Manag Res. 2011; 3:49–55.14. Roayaei M, Ghasemi S. Effect of androgen deprivation therapy on cardiovascular risk factors in prostate cancer. J Res Med Sci. 2013; 18:580–582.15. Vermeulen A, Goemaere S, Kaufman JM. Testosterone, body composition and aging. J Endocrinol Invest. 1999; 22:5 Suppl. 110–116.16. Berruti A, Dogliotti L, Terrone C, Cerutti S, Isaia G, Tarabuzzi R, et al. Changes in bone mineral density, lean body mass and fat content as measured by dual energy x-ray absorptiometry in patients with prostate cancer without apparent bone metastases given androgen deprivation therapy. J Urol. 2002; 167:2361–2367.17. Smith MR, Finkelstein JS, McGovern FJ, Zietman AL, Fallon MA, Schoenfeld DA, et al. Changes in body composition during androgen deprivation therapy for prostate cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002; 87:599–603.18. Smith MR. Changes in fat and lean body mass during androgen-deprivation therapy for prostate cancer. Urology. 2004; 63:742–745.19. Smith JC, Bennett S, Evans LM, Kynaston HG, Parmar M, Mason MD, et al. The effects of induced hypogonadism on arterial stiffness, body composition, and metabolic parameters in males with prostate cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001; 86:4261–4267.20. Smith MR, Lee H, Nathan DM. Insulin sensitivity during combined androgen blockade for prostate cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006; 91:1305–1308.21. Lee H, McGovern K, Finkelstein JS, Smith MR. Changes in bone mineral density and body composition during initial and long-term gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist treatment for prostate carcinoma. Cancer. 2005; 104:1633–1637.22. Dockery F, Bulpitt CJ, Agarwal S, Donaldson M, Rajkumar C. Testosterone suppression in men with prostate cancer leads to an increase in arterial stiffness and hyperinsulinaemia. Clin Sci (Lond). 2003; 104:195–201.23. Eri LM, Urdal P, Bechensteen AG. Effects of the luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone agonist leuprolide on lipoproteins, fibrinogen and plasminogen activator inhibitor in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Urol. 1995; 154:100–104.24. Torimoto K, Samma S, Kagebayashi Y, Chihara Y, Tanaka N, Hirayama A, et al. The effects of androgen deprivation therapy on lipid metabolism and body composition in Japanese patients with prostate cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2011; 41:577–581.25. Salvador C, Planas J, Agreda F, Placer J, Trilla E, Lopez MA, et al. Analysis of the lipid profile and atherogenic risk during androgen deprivation therapy in prostate cancer patients. Urol Int. 2013; 90:41–44.26. Despres JP, Lamarche B, Mauriège P, Cantin B, Dagenais GR, Moorjani S, et al. Hyperinsulinemia as an independent risk factor for ischemic heart disease. N Engl J Med. 1996; 334:952–957.27. Pyorala M, Miettinen H, Laakso M, Pyorala K. Hyperinsulinemia predicts coronary heart disease risk in healthy middleaged men: the 22-year follow-up results of the Helsinki Policemen Study. Circulation. 1998; 98:398–404.28. Keating NL, O'Malley AJ, Smith MR. Diabetes and cardiovascular disease during androgen deprivation therapy for prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2006; 24:4448–4456.29. Smith MR, Lee H, Fallon MA, Nathan DM. Adipocytokines, obesity, and insulin resistance during combined androgen blockade for prostate cancer. Urology. 2008; 71:318–322.30. American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2014; 37:Suppl 1. S81–S90.31. Derweesh IH, Diblasio CJ, Kincade MC, Malcolm JB, Lamar KD, Patterson AL, et al. Risk of new-onset diabetes mellitus and worsening glycaemic variables for established diabetes in men undergoing androgen-deprivation therapy for prostate cancer. BJU Int. 2007; 100:1060–1065.32. Keating NL, OMalley AJ, Freedland SJ, Smith MR. Diabetes and cardiovascular disease during androgen deprivation therapy: observational study of veterans with prostate cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2010; 102:39–46.33. Alibhai SM, Duong-Hua M, Sutradhar R, Fleshner NE, Warde P, Cheung AM, et al. Impact of androgen deprivation therapy on cardiovascular disease and diabetes. J Clin Oncol. 2009; 27:3452–3458.34. Braga-Basaria M, Dobs AS, Muller DC, Carducci MA, John M, Egan J, et al. Metabolic syndrome in men with prostate cancer undergoing long-term androgen-deprivation therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2006; 24:3979–3983.35. Smith MR, Lee H, McGovern F, Fallon MA, Goode M, Zietman AL, et al. Metabolic changes during gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist therapy for prostate cancer: differences from the classic metabolic syndrome. Cancer. 2008; 112:2188–2194.36. Trujillo ME, Scherer PE. Adiponectin: journey from an adipocyte secretory protein to biomarker of the metabolic syndrome. J Intern Med. 2005; 257:167–175.37. Haffner SM. The metabolic syndrome: inflammation, diabetes mellitus, and cardiovascular disease. Am J Cardiol. 2006; 97(2A):3A–11A.38. Roach M 3rd, Bae K, Speight J, Wolkov HB, Rubin P, Lee RJ, et al. Short-term neoadjuvant androgen deprivation therapy and external-beam radiotherapy for locally advanced prostate cancer: long-term results of RTOG 8610. J Clin Oncol. 2008; 26:585–591.39. Pilepich MV, Winter K, Lawton CA, Krisch RE, Wolkov HB, Movsas B, et al. Androgen suppression adjuvant to definitive radiotherapy in prostate carcinoma: long-term results of phase III RTOG 85-31. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005; 61:1285–1290.40. Efstathiou JA, Bae K, Shipley WU, Hanks GE, Pilepich MV, Sandler HM, et al. Cardiovascular mortality and duration of androgen deprivation for locally advanced prostate cancer: analysis of RTOG 92-02. Eur Urol. 2008; 54:816–823.41. Studer UE, Whelan P, Albrecht W, Casselman J, de Reijke T, Hauri D, et al. Immediate or deferred androgen deprivation for patients with prostate cancer not suitable for local treatment with curative intent: European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) Trial 30891. J Clin Oncol. 2006; 24:1868–1876.42. Nguyen PL, Je Y, Schutz FA, Hoffman KE, Hu JC, Parekh A, et al. Association of androgen deprivation therapy with cardiovascular death in patients with prostate cancer: a meta-analysis of randomized trials. JAMA. 2011; 306:2359–2366.43. Grossmann M, Zajac JD. Management of side effects of androgen deprivation therapy. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2011; 40:655–671.44. American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes--2008. Diabetes Care. 2008; 31:Suppl 1. S12–S54.45. Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults. Executive Summary of The Third Report of The National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, And Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol In Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). JAMA. 2001; 285:2486–2497.46. National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) final report. Circulation. 2002; 106:3143–3421.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Current Concepts in Androgen Deprivation Therapy
- Chemotherapy With Androgen Deprivation for Hormone-Naïve Prostate Cancer
- Differentiation Related Gene (Drg-1) as a Molecular Marker during the Treatment of in vitro Intermittent Androgen Deprivation in prostate Cancer
- How Does Androgen Deprivation Therapy Affect Mental Health including Cognitive Dysfunction in Patients with Prostate Cancer?
- Long-Lasting Antiandrogen Withdrawal Syndrome in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: Three Cases With Complete Response