J Vet Sci.
2014 Dec;15(4):583-586. 10.4142/jvs.2014.15.4.583.
Detection of Corynebacterium bovis infection in athymic nude mice from a research animal facility in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Animal Medicine, College of Veterinary Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul 151-742, Korea. pjhak@snu.ac.kr
- 2BK21 PLUS Program for Creative Veterinary Science Research, Research Institute for Veterinary, College of Veterinary Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul 151-742, Korea.
- 3Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul 110-799, Korea.
- 4Department of Biochemistry, College of Medicine, Konyang University, Daejeon 302-832, Korea.
- KMID: 2070248
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2014.15.4.583
Abstract
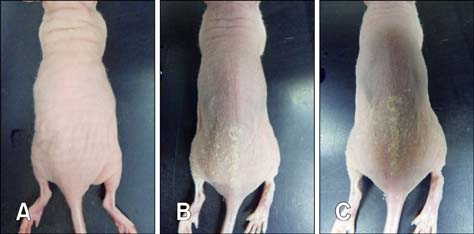
- Corynebacterium (C.) bovis infection in nude mice causes hyperkeratosis and weight loss and has been reported worldwide but not in Korea. In 2011, nude mice from an animal facility in Korea were found to have white flakes on their dorsal skin. Histopathological testing revealed that the mice had hyperkeratosis and Gram-positive bacteria were found in the skin. We identified isolated bacteria from the skin lesions as C. bovis using PCR and 16S rRNA sequencing. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of C. bovis infection in nude mice from Korea.
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Corynebacterium/*isolation & purification
Corynebacterium Infections/*microbiology/pathology
*Mice
Mice, Nude
Polymerase Chain Reaction/veterinary
RNA, Ribosomal, 16S/genetics
Republic of Korea
Rodent Diseases/*microbiology/pathology
Skin Diseases, Bacterial/*microbiology/pathology
RNA, Ribosomal, 16S
Figure
Reference
-
1. Burr HN, Lipman NS, White JR, Zheng J, Wolf FR. Strategies to prevent, treat, and provoke Corynebacterium-associated hyperkeratosis in athymic nude mice. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2011; 50:378–388.2. Burr HN, Wolf FR, Lipman NS. Corynebacterium bovis: epizootiologic features and environmental contamination in an enzootically infected rodent room. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2012; 51:189–198.3. Clifford CB, Walton BJ, Reed TH, Coyle MB, White WJ, Amyx HL. Hyperkeratosis in athymic nude mice caused by a coryneform bacterium: microbiology, transmission, clinical signs, and pathology. Lab Anim Sci. 1995; 45:131–139.4. Dalal A, Urban C, Ahluwalia M, Rubin D. Corynebacterium bovis line related septicemia: a case report and review of the literature. Scand J Infect Dis. 2008; 40:575–577.
Article5. Duga S, Gobbi A, Asselta R, Crippa L, Tenchini ML, Simonic T, Scanziani E. Analysis of the 16S rRNA gene sequence of the coryneform bacterium associated with hyperkeratotic dermatitis of athymic nude mice and development of a PCR-based detection assay. Mol Cell Probes. 1998; 12:191–199.
Article6. Gobbi A, Crippa L, Scanziani E. Corynebacterium bovis infection in immunocompetent hirsute mice. Lab Anim Sci. 1999; 49:209–211.7. Hanna N, Davis TW, Fidler IJ. Environmental and genetic factors determine the level of NK activity of nude mice and affect their suitability as models for experimental metastasis. Int J Cancer. 1982; 30:371–376.
Article8. Lipsky BA, Goldberger AC, Tompkins LS, Plorde JJ. Infections caused by nondiphtheria corynebacteria. Rev Infect Dis. 1982; 4:1220–1235.
Article9. Scanziani E, Gobbi A, Crippa L, Giusti AM, Giavazzi R, Cavalletti E, Luini M. Outbreaks of hyperkeratotic dermatitis of athymic nude mice in northern Italy. Lab Anim. 1997; 31:206–211.
Article10. Sharkey FE, Fogh J. Considerations in the use of nude mice for cancer research. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1984; 3:341–360.
Article11. Vale JA, Scott GW. Corynebacterium bovis as a cause of human disease. Lancet. 1977; 2:682–684.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Attempts to transfer immunity against Clonorchis sinensis in nude and DS mice
- Prominent IL-12 Production and Tumor Reduction in Athymic Nude Mice after Toxoplasma gondii Lysate Antigen Treatment
- Improved protocols for the purification and maintenance of Mycobacterium lepraestrains in athymic nude mice
- An Experimental Study for Establishment of Orthotopic Salivary Tumor Models in Mice
- Making In Vivo Model To Study About Human Oral Cancer (I)