Korean J Radiol.
2015 Feb;16(1):32-49. 10.3348/kjr.2015.16.1.32.
Integrated Whole Body MR/PET: Where Are We?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul 110-744, Korea. jmsh@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Nuclear Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul 110-744, Korea.
- 3Institute of Radiation Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul 110-744, Korea.
- KMID: 2069983
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2015.16.1.32
Abstract
- Whole body integrated magnetic resonance imaging (MR)/positron emission tomography (PET) imaging systems have recently become available for clinical use and are currently being used to explore whether the combined anatomic and functional capabilities of MR imaging and the metabolic information of PET provide new insight into disease phenotypes and biology, and provide a better assessment of oncologic diseases at a lower radiation dose than a CT. This review provides an overview of the technical background of combined MR/PET systems, a discussion of the potential advantages and technical challenges of hybrid MR/PET instrumentation, as well as collection of possible solutions. Various early clinical applications of integrated MR/PET are also addressed. Finally, the workflow issues of integrated MR/PET, including maximizing diagnostic information while minimizing acquisition time are discussed.
MeSH Terms
-
Coordination Complexes/chemistry/diagnostic use
Heart/radiography
Humans
*Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Neoplasm Metastasis
Neoplasm Staging
Neoplasms/pathology/radiography
*Positron-Emission Tomography
Radiopharmaceuticals/diagnostic use
Tomography, X-Ray Computed
Whole Body Imaging/*standards/*trends
Coordination Complexes
Radiopharmaceuticals
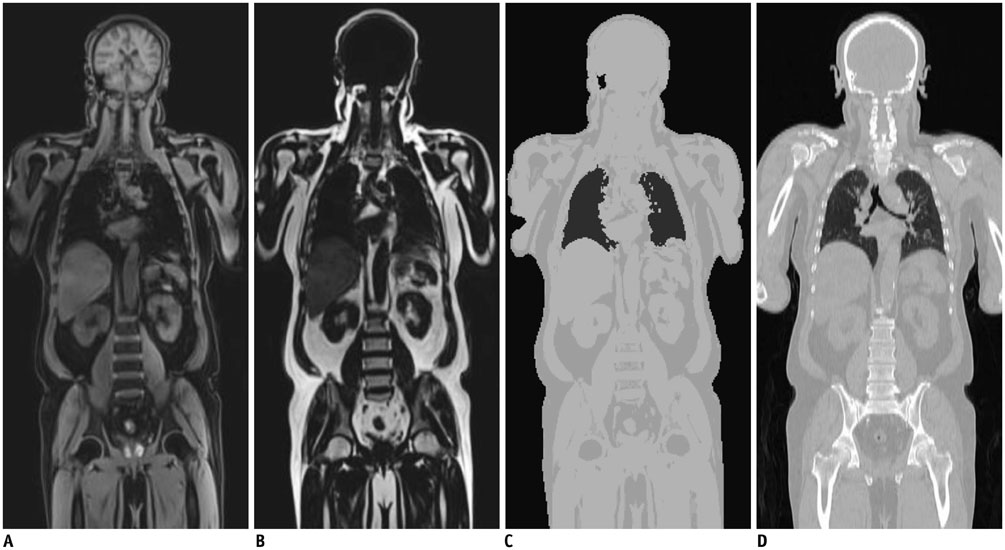
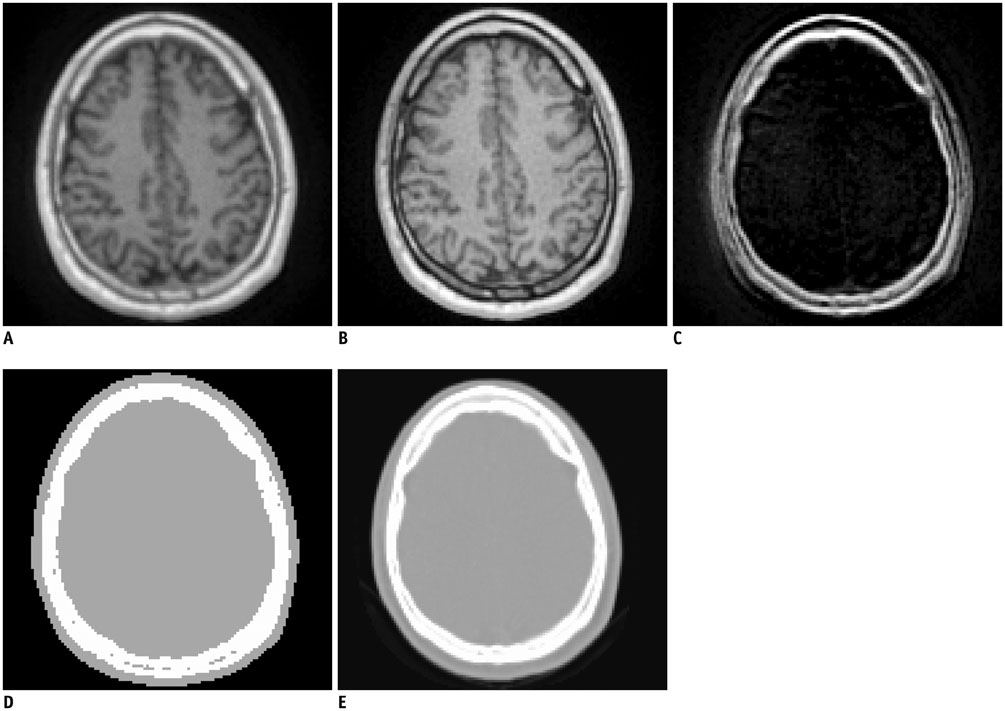
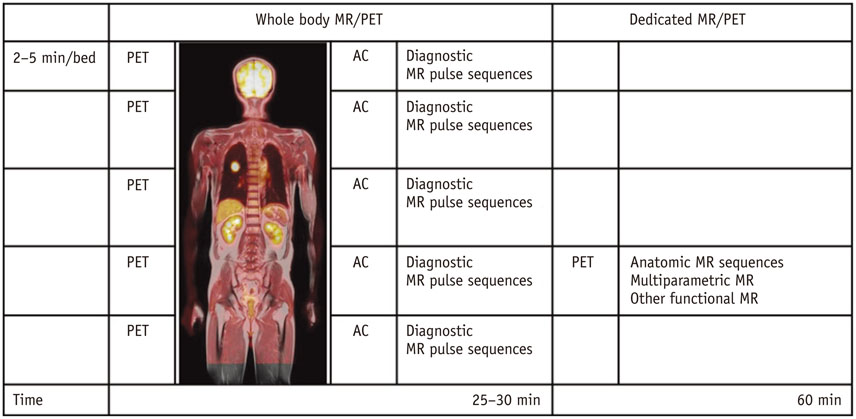
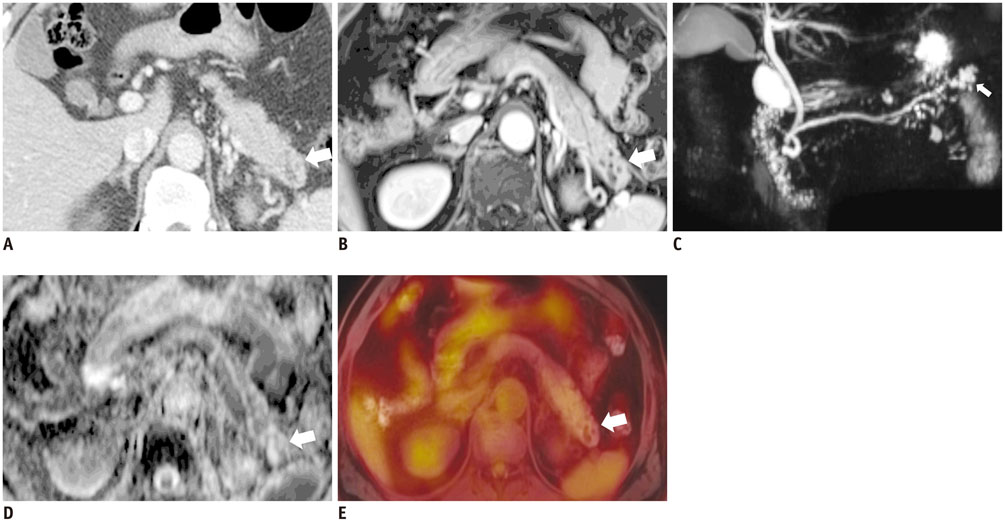
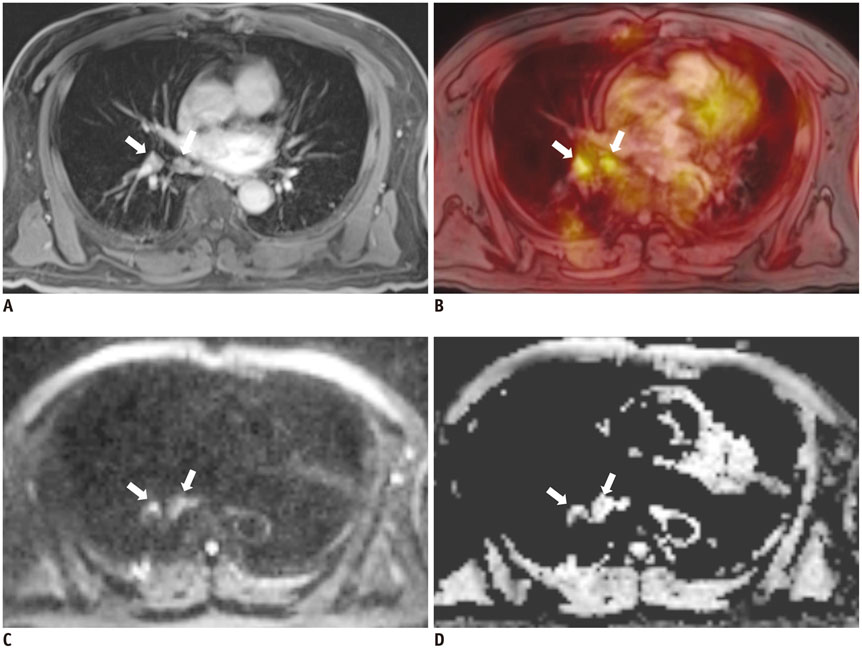
Figure
Reference
-
1. Antoch G, Bockisch A. Combined PET/MRI: a new dimension in whole-body oncology imaging? Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2009; 36:Suppl 1. S113–S120.2. Balyasnikova S, Löfgren J, de Nijs R, Zamogilnaya Y, Højgaard L, Fischer BM. PET/MR in oncology: an introduction with focus on MR and future perspectives for hybrid imaging. Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2012; 2:458–474.3. Catalano OA, Rosen BR, Sahani DV, Hahn PF, Guimaraes AR, Vangel MG, et al. Clinical impact of PET/MR imaging in patients with cancer undergoing same-day PET/CT: initial experience in 134 patients--a hypothesis-generating exploratory study. Radiology. 2013; 269:857–869.4. Catana C, Guimaraes AR, Rosen BR. PET and MR imaging: the odd couple or a match made in heaven? J Nucl Med. 2013; 54:815–824.5. Gaertner FC, Fürst S, Schwaiger M. PET/MR: a paradigm shift. Cancer Imaging. 2013; 13:36–52.6. Herzog H. PET/MRI: challenges, solutions and perspectives. Z Med Phys. 2012; 22:281–298.7. Jadvar H, Colletti PM. Competitive advantage of PET/MRI. Eur J Radiol. 2014; 83:84–94.8. Pichler BJ, Judenhofer MS, Pfannenberg C. Multimodal imaging approaches: PET/CT and PET/MRI. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2008; (185 Pt 1):109–132.9. von Schulthess GK, Schlemmer HP. A look ahead: PET/MR versus PET/CT. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2009; 36:Suppl 1. S3–S9.10. Wehrl HF, Sauter AW, Judenhofer MS, Pichler BJ. Combined PET/MR imaging--technology and applications. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2010; 9:5–20.11. Zaidi H, Montandon ML, Alavi A. The clinical role of fusion imaging using PET, CT, and MR imaging. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2010; 18:133–149.12. Al-Nabhani KZ, Syed R, Michopoulou S, Alkalbani J, Afaq A, Panagiotidis E, et al. Qualitative and quantitative comparison of PET/CT and PET/MR imaging in clinical practice. J Nucl Med. 2014; 55:88–94.13. Andersen FL, Ladefoged CN, Beyer T, Keller SH, Hansen AE, Højgaard L, et al. Combined PET/MR imaging in neurology: MR-based attenuation correction implies a strong spatial bias when ignoring bone. Neuroimage. 2014; 84:206–216.14. Bailey DL, Barthel H, Beuthin-Baumann B, Beyer T, Bisdas S, Boellaard R, et al. Combined PET/MR: Where are we now? Summary report of the second international workshop on PET/MR imaging April 8-12, 2013, Tubingen, Germany. Mol Imaging Biol. 2014; 16:295–310.15. Boss A, Stegger L, Bisdas S, Kolb A, Schwenzer N, Pfister M, et al. Feasibility of simultaneous PET/MR imaging in the head and upper neck area. Eur Radiol. 2011; 21:1439–1446.16. Buchbender C, Heusner TA, Lauenstein TC, Bockisch A, Antoch G. Oncologic PET/MRI, part 2: bone tumors, soft-tissue tumors, melanoma, and lymphoma. J Nucl Med. 2012; 53:1244–1252.17. Buchbender C, Heusner TA, Lauenstein TC, Bockisch A, Antoch G. Oncologic PET/MRI, part 1: tumors of the brain, head and neck, chest, abdomen, and pelvis. J Nucl Med. 2012; 53:928–938.18. Czernin J, Ta L, Herrmann K. Does PET/MR Imaging Improve Cancer Assessments? Literature Evidence from More Than 900 Patients. J Nucl Med. 2014; 55:Supplement 2. 59S–62S.19. Disselhorst JA, Bezrukov I, Kolb A, Parl C, Pichler BJ. Principles of PET/MR Imaging. J Nucl Med. 2014; 55:Supplement 2. 2S–10S.20. Drzezga A, Souvatzoglou M, Eiber M, Beer AJ, Fürst S, Martinez-Möller A, et al. First clinical experience with integrated whole-body PET/MR: comparison to PET/CT in patients with oncologic diagnoses. J Nucl Med. 2012; 53:845–855.21. Quick HH, von Gall C, Zeilinger M, Wiesmüller M, Braun H, Ziegler S, et al. Integrated whole-body PET/MR hybrid imaging: clinical experience. Invest Radiol. 2013; 48:280–289.22. von Schulthess GK, Veit-Haibach P. Workflow Considerations in PET/MR Imaging. J Nucl Med. 2014; 55:Supplement 2. 19S–24S.23. Torigian DA, Zaidi H, Kwee TC, Saboury B, Udupa JK, Cho ZH, et al. PET/MR imaging: technical aspects and potential clinical applications. Radiology. 2013; 267:26–44.24. Vaska P, Cao T. The state of instrumentation for combined positron emission tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. Semin Nucl Med. 2013; 43:11–18.25. von Schulthess GK, Kuhn FP, Kaufmann P, Veit-Haibach P. Clinical positron emission tomography/magnetic resonance imaging applications. Semin Nucl Med. 2013; 43:3–10.26. Bailey DL. Transmission scanning in emission tomography. Eur J Nucl Med. 1998; 25:774–787.27. Zaidi H, Hasegawa B. Determination of the attenuation map in emission tomography. J Nucl Med. 2003; 44:291–315.28. Ollinger JM. Model-based scatter correction for fully 3D PET. Phys Med Biol. 1996; 41:153–176.29. Burger C, Goerres G, Schoenes S, Buck A, Lonn AH, Von Schulthess GK. PET attenuation coefficients from CT images: experimental evaluation of the transformation of CT into PET 511-keV attenuation coefficients. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2002; 29:922–927.30. Kinahan PE, Hasegawa BH, Beyer T. X-ray-based attenuation correction for positron emission tomography/computed tomography scanners. Semin Nucl Med. 2003; 33:166–179.31. Townsend DW. Dual-modality imaging: combining anatomy and function. J Nucl Med. 2008; 49:938–955.32. Delso G, Martinez-Möller A, Bundschuh RA, Ladebeck R, Candidus Y, Faul D, et al. Evaluation of the attenuation properties of MR equipment for its use in a whole-body PET/MR scanner. Phys Med Biol. 2010; 55:4361–4374.33. Delso G, Martinez-Möller A, Bundschuh RA, Nekolla SG, Ziegler SI. The effect of limited MR field of view in MR/PET attenuation correction. Med Phys. 2010; 37:2804–2812.34. MacDonald LR, Kohlmyer S, Liu C, Lewellen TK, Kinahan PE. Effects of MR surface coils on PET quantification. Med Phys. 2011; 38:2948–2956.35. Montandon ML, Zaidi H. Atlas-guided non-uniform attenuation correction in cerebral 3D PET imaging. Neuroimage. 2005; 25:278–286.36. Kim JS, Lee JS, Park MH, Kim KM, Oh SH, Cheon GJ, et al. Feasibility of template-guided attenuation correction in cat brain PET imaging. Mol Imaging Biol. 2010; 12:250–258.37. Berker Y, Franke J, Salomon A, Palmowski M, Donker HC, Temur Y, et al. MRI-based attenuation correction for hybrid PET/MRI systems: a 4-class tissue segmentation technique using a combined ultrashort-echo-time/Dixon MRI sequence. J Nucl Med. 2012; 53:796–804.38. Hofmann M, Steinke F, Scheel V, Charpiat G, Farquhar J, Aschoff P, et al. MRI-based attenuation correction for PET/MRI: a novel approach combining pattern recognition and atlas registration. J Nucl Med. 2008; 49:1875–1883.39. Hofmann M, Bezrukov I, Mantlik F, Aschoff P, Steinke F, Beyer T, et al. MRI-based attenuation correction for whole-body PET/MRI: quantitative evaluation of segmentation- and atlas-based methods. J Nucl Med. 2011; 52:1392–1399.40. Martinez-Möller A, Souvatzoglou M, Delso G, Bundschuh RA, Chefd'hotel C, Ziegler SI, et al. Tissue classification as a potential approach for attenuation correction in whole-body PET/MRI: evaluation with PET/CT data. J Nucl Med. 2009; 50:520–526.41. Keereman V, Fierens Y, Broux T, De Deene Y, Lonneux M, Vandenberghe S. MRI-based attenuation correction for PET/MRI using ultrashort echo time sequences. J Nucl Med. 2010; 51:812–818.42. Schulz V, Torres-Espallardo I, Renisch S, Hu Z, Ojha N, Börnert P, et al. Automatic, three-segment, MR-based attenuation correction for whole-body PET/MR data. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2011; 38:138–152.43. Eiber M, Martinez-Möller A, Souvatzoglou M, Holzapfel K, Pickhard A, Löffelbein D, et al. Value of a Dixon-based MR/PET attenuation correction sequence for the localization and evaluation of PET-positive lesions. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2011; 38:1691–1701.44. Kim JH, Lee JS, Song IC, Lee DS. Comparison of segmentation-based attenuation correction methods for PET/MRI: evaluation of bone and liver standardized uptake value with oncologic PET/CT data. J Nucl Med. 2012; 53:1878–1882.45. Eiber M, Takei T, Souvatzoglou M, Mayerhoefer ME, Fürst S, Gaertner FC, et al. Performance of whole-body integrated 18F-FDG PET/MR in comparison to PET/CT for evaluation of malignant bone lesions. J Nucl Med. 2014; 55:191–197.46. Catana C, van der Kouwe A, Benner T, Michel CJ, Hamm M, Fenchel M, et al. Toward implementing an MRI-based PET attenuation-correction method for neurologic studies on the MR-PET brain prototype. J Nucl Med. 2010; 51:1431–1438.47. Aitken AP, Giese D, Tsoumpas C, Schleyer P, Kozerke S, Prieto C, et al. Improved UTE-based attenuation correction for cranial PET-MR using dynamic magnetic field monitoring. Med Phys. 2014; 41:012302.48. Dickson JC, O'Meara C, Barnes A. A comparison of CT- and MR-based attenuation correction in neurological PET. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2014; 41:1176–1189.49. Nuyts J, Dupont P, Stroobants S, Benninck R, Mortelmans L, Suetens P. Simultaneous maximum a posteriori reconstruction of attenuation and activity distributions from emission sinograms. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 1999; 18:393–403.50. Defrise M, Rezaei A, Nuyts J. Time-of-flight PET data determine the attenuation sinogram up to a constant. Phys Med Biol. 2012; 57:885–899.51. Conti M. Why is TOF PET reconstruction a more robust method in the presence of inconsistent data? Phys Med Biol. 2011; 56:155–168.52. Keereman V, Mollet P, Berker Y, Schulz V, Vandenberghe S. Challenges and current methods for attenuation correction in PET/MR. MAGMA. 2013; 26:81–98.53. Weber WA. PET/MR Imaging: A Critical Appraisal. J Nucl Med. 2014; 55:Supplement 2. 56S–58S.54. Rauscher I, Eiber M, Souvatzoglou M, Schwaiger M, Beer AJ. PET/MR in Oncology: Non-18F-FDG Tracers for Routine Applications. J Nucl Med. 2014; 55:Supplement 2. 25S–31S.55. Liu X, Yetik IS. Automated prostate cancer localization without the need for peripheral zone extraction using multiparametric MRI. Med Phys. 2011; 38:2986–2994.56. Wehrl HF, Wiehr S, Divine MR, Gatidis S, Gullberg GT, Maier FC, et al. Preclinical and Translational PET/MR Imaging. J Nucl Med. 2014; 55:Supplement 2. 11S–18S.57. Histed SN, Lindenberg ML, Mena E, Turkbey B, Choyke PL, Kurdziel KA. Review of functional/anatomical imaging in oncology. Nucl Med Commun. 2012; 33:349–361.58. Filss CP, Galldiks N, Stoffels G, Sabel M, Wittsack HJ, Turowski B, et al. Comparison of 18F-FET PET and perfusion-weighted MR imaging: a PET/MR imaging hybrid study in patients with brain tumors. J Nucl Med. 2014; 55:540–545.59. Kuhn FP, Hüllner M, Mader CE, Kastrinidis N, Huber GF, von Schulthess GK, et al. Contrast-enhanced PET/MR imaging versus contrast-enhanced PET/CT in head and neck cancer: how much MR information is needed? J Nucl Med. 2014; 55:551–558.60. Platzek I, Beuthien-Baumann B, Schneider M, Gudziol V, Kitzler HH, Maus J, et al. FDG PET/MR for lymph node staging in head and neck cancer. Eur J Radiol. 2014; 83:1163–1168.61. Platzek I, Beuthien-Baumann B, Schneider M, Gudziol V, Langner J, Schramm G, et al. PET/MRI in head and neck cancer: initial experience. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2013; 40:6–11.62. Donati OF, Hany TF, Reiner CS, von Schulthess GK, Marincek B, Seifert B, et al. Value of retrospective fusion of PET and MR images in detection of hepatic metastases: comparison with 18F-FDG PET/CT and Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI. J Nucl Med. 2010; 51:692–699.63. Sun H, Xin J, Zhang S, Guo Q, Lu Y, Zhai W, et al. Anatomical and functional volume concordance between FDG PET, and T2 and diffusion-weighted MRI for cervical cancer: a hybrid PET/MR study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2014; 41:898–905.64. Souvatzoglou M, Eiber M, Takei T, Fürst S, Maurer T, Gaertner F, et al. Comparison of integrated whole-body [11C]choline PET/MR with PET/CT in patients with prostate cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2013; 40:1486–1499.65. Gaertner FC, Beer AJ, Souvatzoglou M, Eiber M, Fürst S, Ziegler SI, et al. Evaluation of feasibility and image quality of 68Ga-DOTATOC positron emission tomography/magnetic resonance in comparison with positron emission tomography/computed tomography in patients with neuroendocrine tumors. Invest Radiol. 2013; 48:263–272.66. Somer EJ, Marsden PK, Benatar NA, Goodey J, O'Doherty MJ, Smith MA. PET-MR image fusion in soft tissue sarcoma: accuracy, reliability and practicality of interactive point-based and automated mutual information techniques. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2003; 30:54–62.67. Park H, Wood D, Hussain H, Meyer CR, Shah RB, Johnson TD, et al. Introducing parametric fusion PET/MRI of primary prostate cancer. J Nucl Med. 2012; 53:546–551.68. Jambor I, Borra R, Kemppainen J, Lepomäki V, Parkkola R, Dean K, et al. Improved detection of localized prostate cancer using co-registered MRI and 11C-acetate PET/CT. Eur J Radiol. 2012; 81:2966–2972.69. Takei T, Souvatzoglou M, Beer AJ, Drzezga A, Ziegler S, Rummeny EJ, et al. A case of multimodality multiparametric 11C-choline PET/MR for biopsy targeting in prior biopsy-negative primary prostate cancer. Clin Nucl Med. 2012; 37:918–919.70. Afshar-Oromieh A, Haberkorn U, Schlemmer HP, Fenchel M, Eder M, Eisenhut M, et al. Comparison of PET/CT and PET/MRI hybrid systems using a 68Ga-labelled PSMA ligand for the diagnosis of recurrent prostate cancer: initial experience. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2014; 41:887–897.71. Schuler MK, Richter S, Beuthien-Baumann B, Platzek I, Kotzerke J, van den Hoff J, et al. PET/MRI Imaging in High-Risk Sarcoma: First Findings and Solving Clinical Problems. Case Rep Oncol Med. 2013; 2013:793927.72. Gaeta CM, Vercher-Conejero JL, Sher AC, Kohan A, Rubbert C, Avril N. Recurrent and metastatic breast cancer PET, PET/CT, PET/MRI: FDG and new biomarkers. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2013; 57:352–366.73. Kubiessa K, Purz S, Gawlitza M, Kühn A, Fuchs J, Steinhoff KG, et al. Initial clinical results of simultaneous 18F-FDG PET/MRI in comparison to 18F-FDG PET/CT in patients with head and neck cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2014; 41:639–648.74. Collins CD. PET/CT in oncology: for which tumours is it the reference standard? Cancer Imaging. 2007; 7(Spec No A):S77–S87.75. Kohan AA, Kolthammer JA, Vercher-Conejero JL, Rubbert C, Partovi S, Jones R, et al. N staging of lung cancer patients with PET/MRI using a three-segment model attenuation correction algorithm: initial experience. Eur Radiol. 2013; 23:3161–3169.76. Thorek DL, Ulmert D, Diop NF, Lupu ME, Doran MG, Huang R, et al. Non-invasive mapping of deep-tissue lymph nodes in live animals using a multimodal PET/MRI nanoparticle. Nat Commun. 2014; 5:3097.77. Antoch G, Vogt FM, Freudenberg LS, Nazaradeh F, Goehde SC, Barkhausen J, et al. Whole-body dual-modality PET/CT and whole-body MRI for tumor staging in oncology. JAMA. 2003; 290:3199–3206.78. Schmidt GP, Schoenberg SO, Schmid R, Stahl R, Tiling R, Becker CR, et al. Screening for bone metastases: whole-body MRI using a 32-channel system versus dual-modality PET-CT. Eur Radiol. 2007; 17:939–949.79. Ohno Y, Koyama H, Onishi Y, Takenaka D, Nogami M, Yoshikawa T, et al. Non-small cell lung cancer: whole-body MR examination for M-stage assessment--utility for whole-body diffusion-weighted imaging compared with integrated FDG PET/CT. Radiology. 2008; 248:643–654.80. Coenegrachts K, De Geeter F, ter Beek L, Walgraeve N, Bipat S, Stoker J, et al. Comparison of MRI (including SS SE-EPI and SPIO-enhanced MRI) and FDG-PET/CT for the detection of colorectal liver metastases. Eur Radiol. 2009; 19:370–379.81. Takenaka D, Ohno Y, Matsumoto K, Aoyama N, Onishi Y, Koyama H, et al. Detection of bone metastases in non-small cell lung cancer patients: comparison of whole-body diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI), whole-body MR imaging without and with DWI, whole-body FDG-PET/CT, and bone scintigraphy. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2009; 30:298–308.82. Niekel MC, Bipat S, Stoker J. Diagnostic imaging of colorectal liver metastases with CT, MR imaging, FDG PET, and/or FDG PET/CT: a meta-analysis of prospective studies including patients who have not previously undergone treatment. Radiology. 2010; 257:674–684.83. Yong TW, Yuan ZZ, Jun Z, Lin Z, He WZ, Juanqi Z. Sensitivity of PET/MR images in liver metastases from colorectal carcinoma. Hell J Nucl Med. 2011; 14:264–268.84. Kwee SA, Ko JP, Jiang CS, Watters MR, Coel MN. Solitary brain lesions enhancing at MR imaging: evaluation with fluorine 18 fluorocholine PET. Radiology. 2007; 244:557–565.85. Yoon SH, Goo JM, Lee SM, Park CM, Seo HJ, Cheon GJ. Positron emission tomography/magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of lung cancer: current status and future prospects. J Thorac Imaging. 2014; 29:4–16.86. Chandarana H, Heacock L, Rakheja R, DeMello LR, Bonavita J, Block TK, et al. Pulmonary nodules in patients with primary malignancy: comparison of hybrid PET/MR and PET/CT imaging. Radiology. 2013; 268:874–881.87. Wahl RL, Jacene H, Kasamon Y, Lodge MA. From RECIST to PERCIST: Evolving Considerations for PET response criteria in solid tumors. J Nucl Med. 2009; 50:Suppl 1. 122S–150S.88. Heijmen L, Verstappen MC, Ter Voert EE, Punt CJ, Oyen WJ, de Geus-Oei LF, et al. Tumour response prediction by diffusion-weighted MR imaging: ready for clinical use? Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2012; 83:194–207.89. Afaq A, Andreou A, Koh DM. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging for tumour response assessment: why, when and how? Cancer Imaging. 2010; 10(Spec no A):S179–S188.90. Platzek I, Beuthien-Baumann B, Langner J, Popp M, Schramm G, Ordemann R, et al. PET/MR for therapy response evaluation in malignant lymphoma: initial experience. MAGMA. 2013; 26:49–55.91. Purz S, Sabri O, Viehweger A, Barthel H, Kluge R, Sorge I, et al. Potential Pediatric Applications of PET/MR. J Nucl Med. 2014; 55:Supplement 2. 32S–39S.92. Hirsch FW, Sattler B, Sorge I, Kurch L, Viehweger A, Ritter L, et al. PET/MR in children. Initial clinical experience in paediatric oncology using an integrated PET/MR scanner. Pediatr Radiol. 2013; 43:860–875.93. Punwani S, Taylor SA, Bainbridge A, Prakash V, Bandula S, De Vita E, et al. Pediatric and adolescent lymphoma: comparison of whole-body STIR half-Fourier RARE MR imaging with an enhanced PET/CT reference for initial staging. Radiology. 2010; 255:182–190.94. Lin C, Luciani A, Itti E, El-Gnaoui T, Vignaud A, Beaussart P, et al. Whole-body diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging with apparent diffusion coefficient mapping for staging patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Eur Radiol. 2010; 20:2027–2038.95. Baur A, Stäbler A, Nagel D, Lamerz R, Bartl R, Hiller E, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging as a supplement for the clinical staging system of Durie and Salmon? Cancer. 2002; 95:1334–1345.96. Ripa RS, Knudsen A, Hag AM, Lebech AM, Loft A, Keller SH, et al. Feasibility of simultaneous PET/MR of the carotid artery: first clinical experience and comparison to PET/CT. Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2013; 3:361–371.97. Nappi C, El Fakhri G. State of the Art in Cardiac Hybrid Technology: PET/MR. Curr Cardiovasc Imaging Rep. 2013; 6:338–345.98. Nensa F, Poeppel TD, Beiderwellen K, Schelhorn J, Mahabadi AA, Erbel R, et al. Hybrid PET/MR imaging of the heart: feasibility and initial results. Radiology. 2013; 268:366–373.99. Rischpler C, Nekolla SG, Dregely I, Schwaiger M. Hybrid PET/MR imaging of the heart: potential, initial experiences, and future prospects. J Nucl Med. 2013; 54:402–415.100. Rischpler C, Nekolla SG, Beer AJ. PET/MR imaging of atherosclerosis: initial experience and outlook. Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2013; 3:393–396.101. Neuner I, Kaffanke JB, Langen KJ, Kops ER, Tellmann L, Stoffels G, et al. Multimodal imaging utilising integrated MR-PET for human brain tumour assessment. Eur Radiol. 2012; 22:2568–2580.102. Heiss WD. The potential of PET/MR for brain imaging. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2009; 36:Suppl 1. S105–S112.103. Leibfarth S, Mönnich D, Welz S, Siegel C, Schwenzer N, Schmidt H, et al. A strategy for multimodal deformable image registration to integrate PET/MR into radiotherapy treatment planning. Acta Oncol. 2013; 52:1353–1359.104. von Schulthess GK. Why buy a PET/MR for high end research? J Magn Reson Imaging. 2014; 40:283–284.105. Boss A, Bisdas S, Kolb A, Hofmann M, Ernemann U, Claussen CD, et al. Hybrid PET/MRI of intracranial masses: initial experiences and comparison to PET/CT. J Nucl Med. 2010; 51:1198–1205.106. Schwenzer NF, Stegger L, Bisdas S, Schraml C, Kolb A, Boss A, et al. Simultaneous PET/MR imaging in a human brain PET/MR system in 50 patients--current state of image quality. Eur J Radiol. 2012; 81:3472–3478.107. Boss A, Kolb A, Hofmann M, Bisdas S, Nägele T, Ernemann U, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging in a human PET/MR hybrid system. Invest Radiol. 2010; 45:270–274.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Potential Clinical Applications of ¹â¸F-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography/Magnetic Resonance Mammography in Breast Cancer
- ¹â¸F-FDG PET/MR Refines Evaluation in Newly Diagnosed Metastatic Urethral Adenocarcinoma
- Use of 18F-FDG PET/CT in Second Primary Cancer
- Clinical Application of Whole-body MRI
- Whole Body Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography