J Korean Med Sci.
2014 Nov;29(11):1501-1506. 10.3346/jkms.2014.29.11.1501.
Long-Term Outcomes of Complete Versus Incomplete Revascularization for Patients with Multivessel Coronary Artery Disease and Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction in Drug-Eluting Stent Era
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine, Gangneung Asan Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Gangneung, Korea.
- 2Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine, Cardiac and Vascular Center, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. sh1214.choi@samsung.com
- 3Department of Critical Care Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Emergency Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2069931
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2014.29.11.1501
Abstract
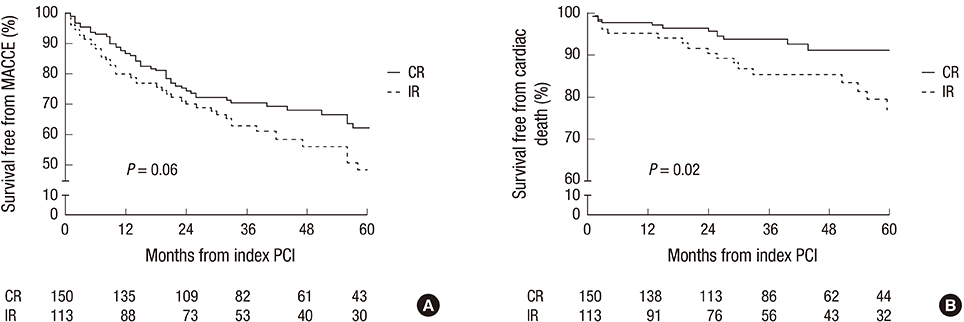
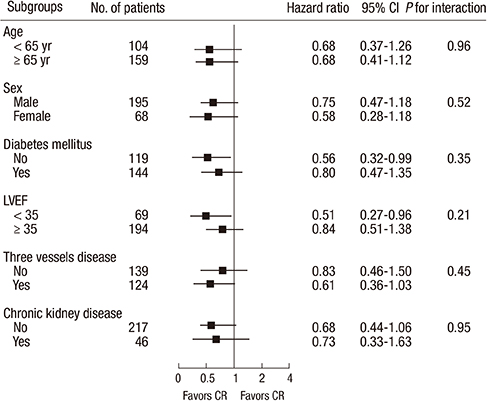
- We aimed to investigate that complete revascularization (CR) would be associated with a decreased mortality in patients with multivessel disease (MVD) and reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF). We enrolled a total of 263 patients with MVD and LVEF <50% who had undergone percutaneous coronary intervention with drug-eluting stent between March 2003 and December 2010. We compared major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular accident (MACCE) including all-cause death, myocardial infarction, any revascularization, and cerebrovascular accident between CR and incomplete revascularization (IR). CR was achieved in 150 patients. During median follow-up of 40 months, MACCE occurred in 52 (34.7%) patients in the CR group versus 51 (45.1%) patients in the IR group (P=0.06). After a Cox regression model with inverse-probability-of-treatment-weighting using propensity score, the incidence of MACCE of the CR group were lower than those of the IR group (34.7% vs. 45.1%; adjusted hazard ratio [HR], 0.65; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.44-0.95, P=0.03). The rate of all-cause death was significantly lower in patients with CR than in those with IR (adjusted HR, 0.48; 95% CI, 0.29-0.80, P<0.01). In conclusion, the achievement of CR with drug-eluting stent reduces long-term MACCE in patients with MVD and reduced LVEF.
MeSH Terms
-
Age Factors
Aged
Coronary Artery Disease/*drug therapy/mortality/physiopathology
Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2/complications
*Drug-Eluting Stents
Female
Follow-Up Studies
Humans
Kaplan-Meier Estimate
Male
Middle Aged
Myocardial Infarction/etiology
Myocardial Revascularization
Percutaneous Coronary Intervention/adverse effects
Proportional Hazards Models
Renal Insufficiency, Chronic/complications
Retrospective Studies
Sex Factors
Treatment Outcome
Ventricular Dysfunction, Left/physiopathology
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bell MR, Gersh BJ, Schaff HV, Holmes DR Jr, Fisher LD, Alderman EL, Myers WO, Parsons LS, Reeder GS. Effect of completeness of revascularization on long-term outcome of patients with three-vessel disease undergoing coronary artery bypass surgery. A report from the Coronary Artery Surgery Study (CASS) Registry. Circulation. 1992; 86:446–457.2. Scott R, Blackstone EH, McCarthy PM, Lytle BW, Loop FD, White JA, Cosgrove DM. Isolated bypass grafting of the left internal thoracic artery to the left anterior descending coronary artery: late consequences of incomplete revascularization. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2000; 120:173–184.3. Bangalore S. Complete revascularization in contemporary practice. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2013; 6:5–7.4. van den Brand MJ, Rensing BJ, Morel MA, Foley DP, de Valk V, Breeman A, Suryapranata H, Haalebos MM, Wijns W, Wellens F, et al. The effect of completeness of revascularization on event-free survival at one year in the ARTS trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002; 39:559–564.5. Ijsselmuiden AJ, Ezechiels J, Westendorp IC, Tijssen JG, Kiemeneij F, Slagboom T, van der Wieken R, Tangelder G, Serruys PW, Laarman G. Complete versus culprit vessel percutaneous coronary intervention in multivessel disease: a randomized comparison. Am Heart J. 2004; 148:467–474.6. McLellan CS, Ghali WA, Labinaz M, Davis RB, Galbraith PD, Southern DA, Shrive FM, Knudtson ML. Association between completeness of percutaneous coronary revascularization and postprocedure outcomes. Am Heart J. 2005; 150:800–806.7. Hannan EL, Racz M, Holmes DR, King SB 3rd, Walford G, Ambrose JA, Sharma S, Katz S, Clark LT, Jones RH. Impact of completeness of percutaneous coronary intervention revascularization on long-term outcomes in the stent era. Circulation. 2006; 113:2406–2412.8. Wu C, Dyer AM, King SB 3rd, Walford G, Holmes DR Jr, Stamato NJ, Venditti FJ, Sharma SK, Fergus I, Jacobs AK, et al. Impact of incomplete revascularization on long-term mortality after coronary stenting. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2011; 4:413–421.9. Lehmann R, Fichtlscherer S, Schächinger V, Held L, Hobler C, Baier G, Zeiher AM, Spyridopoulos I. Complete revascularization in patients undergoing multivessel PCI is an independent predictor of improved long-term survival. J Interv Cardiol. 2010; 23:256–263.10. Kim YH, Park DW, Lee JY, Kim WJ, Yun SC, Ahn JM, Song HG, Oh JH, Park JS, Kang SJ, et al. Impact of angiographic complete revascularization after drug-eluting stent implantation or coronary artery bypass graft surgery for multivessel coronary artery disease. Circulation. 2011; 123:2373–2381.11. Head SJ, Mack MJ, Holmes DR Jr, Mohr FW, Morice MC, Serruys PW, Kappetein AP. Incidence, predictors and outcomes of incomplete revascularization after percutaneous coronary intervention and coronary artery bypass grafting: a subgroup analysis of 3-year SYNTAX data. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2012; 41:535–541.12. Song YB, Lee SY, Hahn JY, Choi SH, Choi JH, Lee SH, Hong KP, Park JE, Gwon HC. Complete versus incomplete revascularization for treatment of multivessel coronary artery disease in the drug-eluting stent era. Heart Vessels. 2012; 27:433–442.13. Serruys PW, Morice MC, Kappetein AP, Colombo A, Holmes DR, Mack MJ, Ståhle E, Feldman TE, van den Brand M, Bass EJ, et al. Percutaneous coronary intervention versus coronary-artery bypass grafting for severe coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med. 2009; 360:961–972.14. Hannan EL, Wu C, Walford G, Holmes DR, Jones RH, Sharma S, King SB 3rd. Incomplete revascularization in the era of drug-eluting stents: impact on adverse outcomes. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2009; 2:17–25.15. Robins JM, Hernán MA, Brumback B. Marginal structural models and causal inference in epidemiology. Epidemiology. 2000; 11:550–560.16. Heinze G, Jüni P. An overview of the objectives of and the approaches to propensity score analyses. Eur Heart J. 2011; 32:1704–1708.17. Wu C, Dyer AM, Walford G, Holmes DR Jr, King SB 3rd, Stamato NJ, Sharma S, Jacobs AK, Venditti FJ, Hannan EL. Incomplete revascularization is associated with greater risk of long-term mortality after stenting in the era of first generation drug-eluting stents. Am J Cardiol. 2013; 112:775–781.18. Kirschbaum SW, Springeling T, Boersma E, Moelker A, van der Giessen WJ, Serruys PW, de Feyter PJ, van Geuns RJ. Complete percutaneous revascularization for multivessel disease in patients with impaired left ventricular function: pre- and post-procedural evaluation by cardiac magnetic resonance imaging. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2010; 3:392–400.19. Reffelmann T, Könemann S, Kloner RA. Promise of blood- and bone marrow-derived stem cell transplantation for functional cardiac repair: putting it in perspective with existing therapy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009; 53:305–308.20. Latib A, Colombo A, Castriota F, Micari A, Cremonesi A, De Felice F, Marchese A, Tespili M, Presbitero P, Sgueglia GA, et al. A randomized multicenter study comparing a paclitaxel drug-eluting balloon with a paclitaxel-eluting stent in small coronary vessels: the BELLO (Balloon Elution and Late Loss Optimization) study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012; 60:2473–2480.21. Valenti R, Migliorini A, Signorini U, Vergara R, Parodi G, Carrabba N, Cerisano G, Antoniucci D. Impact of complete revascularization with percutaneous coronary intervention on survival in patients with at least one chronic total occlusion. Eur Heart J. 2008; 29:2336–2342.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Drug-Eluting Stent: Present and Future
- Past, Present, and Future of Left Main Coronary Artery PCI
- Diffuse Long Coronary Artery Disease is Still an Obstacle for Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in the Second-Generation Drug-Eluting Stent Era?
- Revascularization for Left Main and Multivessel Coronary Artery Disease: Current Status and Future Prospects after the EXCEL and NOBLE Trials
- Complete Versus Culprit-Only Revascularization for ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction and Multivessel Disease in the 2(nd) Generation Drug-Eluting Stent Era: Data from the INTERSTELLAR Registry