Clin Orthop Surg.
2015 Mar;7(1):135-139. 10.4055/cios.2015.7.1.135.
Lessons Learnt from an Atypical Mycobacterium Infection Post-Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Changi General Hospital, Singapore. stacy.ng@mohh.com.sg
- KMID: 2069886
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2015.7.1.135
Abstract
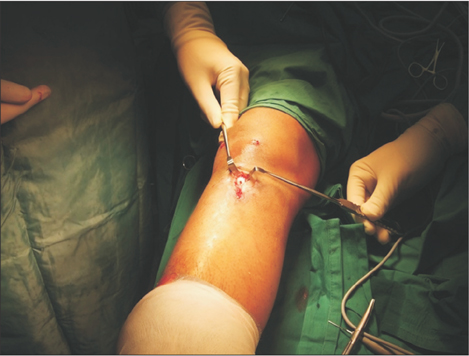
- Infections following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction are rare, with no previous reports citing Mycobacterium abscessus as the culprit pathogen. A 22-year-old man presented twice over three years with a painful discharging sinus over his right tibia tunnel site necessitating repeated arthroscopy and washout, months of antibiotic therapy, and ultimately culminating in the removal of the implants. In both instances, M. abscessus was present in the wound cultures, along with a coinfection of Staphyloccocus aureus during the second presentation. Though rare, M. abscessus is an important pathogen to consider in postoperative wounds presenting with chronic discharging sinuses, even in healthy non-immunocompromised patients. This case illustrates how the organism can cause an indolent infection, and how the removal of implants can be necessary to prevent the persistence of infection. Coinfection with a second organism is not uncommon and necessitates a timely change in treatment regime as well.
MeSH Terms
-
Anterior Cruciate Ligament/injuries/surgery
Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction/*adverse effects
Anti-Bacterial Agents/administration & dosage
Arthritis, Infectious/etiology/*microbiology
Arthroscopy
Coinfection
Device Removal
Humans
Male
Mycobacterium Infections, Nontuberculous/*microbiology
Recurrence
Reoperation
Staphylococcal Infections/*microbiology
*Staphylococcus aureus
Therapeutic Irrigation
Young Adult
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sajovic M, Nic Ar GL, Dernovs Ek MZ. Septic arthritis of the knee following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Orthop Rev (Pavia). 2009; 1(1):e3.2. Nag HL, Neogi DS, Nataraj AR, Kumar VA, Yadav CS, Singh U. Tubercular infection after arthroscopic anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Arthroscopy. 2009; 25(2):131–136.3. Oh HL, Chen DB, Seeto BG, Macdessi SJ. Mycobacterium fortuitum infection after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction using a polylactic acid bioabsorbable screw: case report. Knee. 2010; 17(2):176–178.4. Nessar R, Cambau E, Reyrat JM, Murray A, Gicquel B. Mycobacterium abscessus: a new antibiotic nightmare. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2012; 67(4):810–818.5. Chang CY, Tsay RW, Lin LC, Liu CE. Venous catheter-associated bacteremia caused by rapidly growing mycobacteria at a medical center in central Taiwan. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2009; 42(4):343–350.6. McAllister DR, Parker RD, Cooper AE, Recht MP, Abate J. Outcomes of postoperative septic arthritis after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Am J Sports Med. 1999; 27(5):562–570.7. Lee YS, Nam SW, Park YS, Lee BK. Mycobacterium wolinskyi infection after total knee arthroplasty in a healthy woman. J Orthop Sci. 2015; 20(1):229–231.8. Berbari EF, Marculescu C, Sia I, et al. Culture-negative prosthetic joint infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2007; 45(9):1113–1119.9. Bal AM, Ashcroft G, Gould I, Laing R. Listeria monocytogenes and Staphylococcus aureus coinfection of a prosthetic joint. Joint Bone Spine. 2008; 75(5):619–620.10. Badrul B, Ruslan G. Candida albicans infection of a prosthetic knee replacement: a case report. Med J Malaysia. 2000; 55:Suppl C. 93–96.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ligament Reconstruction in Congenital Absence of the Anterior Cruciate Ligament: A Case Report
- Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction with Achilles Tendon Allograft
- The Effect of Cyclic Tensile Load on Various Tibial Fixation Techniques in Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction
- Open anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction using inside-out femoral drilling
- Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: The Long Road from Science to Clinical Relevance