Clin Orthop Surg.
2015 Mar;7(1):8-14. 10.4055/cios.2015.7.1.8.
External Fixation Using Femoral Less Invasive Stabilization System Plate in Tibial Proximal Metaphyseal Fracture
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Ningbo Sixth Hospital, Ningbo, China. awei3@sohu.com
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of Toledo, Toledo, OH, USA.
- KMID: 2069869
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2015.7.1.8
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
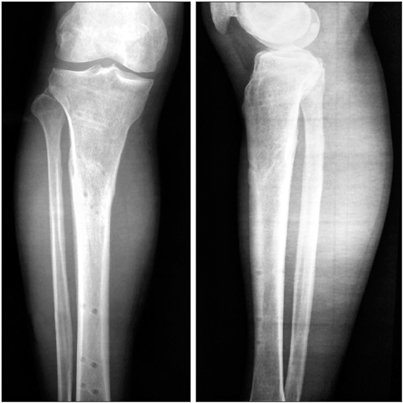
The locking plates are often used for internal fixation of closed tibial fractures. The use of a locking plate as an external fixator is still controversial, particularly for closed fractures. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the results of external fixation using the femoral less invasive stabilization system (LISS) plate in proximal metaphyseal fractures of the tibia.
METHODS
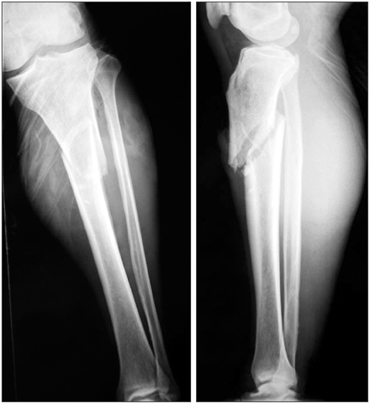
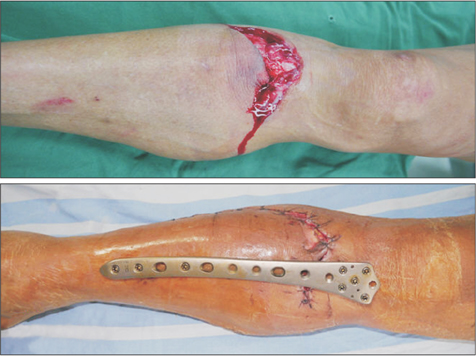
We prospectively evaluated 35 patients (26 males and 9 females) with a mean age of 42 years (range, 21 to 62 years) who presented with fresh tibial proximal metaphyseal fractures. According to the AO Foundation and Orthopaedic Trauma Association (AO/OTA) classification, the fractures were identified as type 41-A2 in 18 cases and type 41-A3 in 17 cases, including 25 closed fractures and 10 open fractures. The femoral LISS plate was used to fix these fractures, which was placed on the anteromedial aspect of the tibia as an external fixator. The mean follow-up period was 18 months (range, 13 to 22 months).
RESULTS
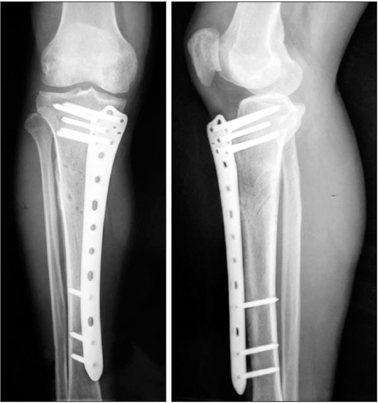
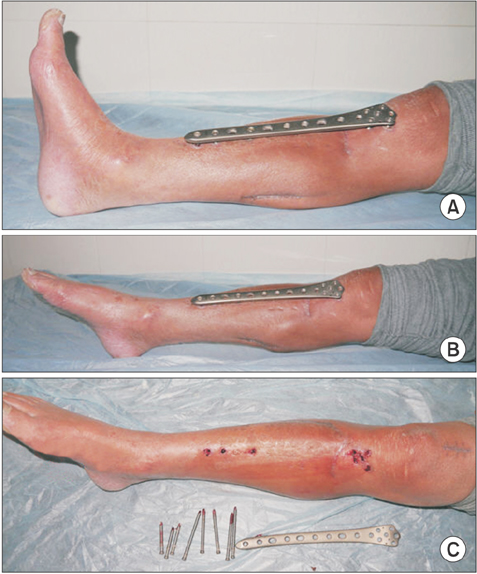
All fractures healed in a mean time of 14 weeks (range, 10 to 20 weeks). There was no case of nonunion, deep infection, and loosening of screws and plates. One month after the appearance of cortical bridging on biplanar radiographs, the locking plate was removed within 3 minutes in the clinic without any difficulty. According to the Hospital for Special Surgery (HSS) knee scoring system and American Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Society (AOFAS) ankle scoring system, the mean HSS score was 91 (range, 85 to 100) and 98 (range, 93 to 100), and the mean AOFAS score was 94 (range, 90 to 100) and 98 (range, 95 to 100) at 4 weeks postoperatively and final follow-up, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
For proximal metaphyseal fracture of the tibia, external fixation using the femoral LISS plate is a safe and reliable technique with minimal complications and excellent outcomes. Its advantages include ease of performing the surgery, use of a less invasive technique, and convenience of plate removal after fracture healing.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Dillin L, Slabaugh P. Delayed wound healing, infection, and nonunion following open reduction and internal fixation of tibial plafond fractures. J Trauma. 1986; 26(12):1116–1119.
Article2. Perren SM. Evolution of the internal fixation of long bone fractures. The scientific basis of biological internal fixation: choosing a new balance between stability and biology. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002; 84(8):1093–1110.3. Lau TW, Leung F, Chan CF, Chow SP. Wound complication of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in distal tibia fractures. Int Orthop. 2008; 32(5):697–703.
Article4. McFerran MA, Smith SW, Boulas HJ, Schwartz HS. Complications encountered in the treatment of pilon fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 1992; 6(2):195–200.
Article5. Pai V, Coulter G, Pai V. Minimally invasive plate fixation of the tibia. Int Orthop. 2007; 31(4):491–496.
Article6. Wagner M. General principles for the clinical use of the LCP. Injury. 2003; 34:Suppl 2. B31–B42.
Article7. Katsoulis E, Court-Brown C, Giannoudis PV. Incidence and aetiology of anterior knee pain after intramedullary nailing of the femur and tibia. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006; 88(5):576–580.
Article8. Keating JF, Orfaly R, O'Brien PJ. Knee pain after tibial nailing. J Orthop Trauma. 1997; 11(1):10–13.
Article9. Lefaivre KA, Guy P, Chan H, Blachut PA. Long-term follow-up of tibial shaft fractures treated with intramedullary nail ing. J Orthop Trauma. 2008; 22(8):525–529.
Article10. Gustilo RB, Anderson JT. Prevention of infection in the treatment of one thousand and twenty-five open fractures of long bones: retrospective and prospective analyses. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1976; 58(4):453–458.
Article11. Fracture and dislocation compendium. Orthopaedic Trauma Association Committee for Coding and Classification. J Orthop Trauma. 1996; 10:Suppl 1. v–ix. 1–154.12. Ibrahim T, Beiri A, Azzabi M, Best AJ, Taylor GJ, Menon DK. Reliability and validity of the subjective component of the American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society clinical rating scales. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2007; 46(2):65–74.
Article13. Ramotowski W, Granowski R. Zespol: an original method of stable osteosynthesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991; (272):67–75.14. Woon CY, Wong MK, Howe TS. LCP external fixation--external application of an internal fixator: two cases and a review of the literature. J Orthop Surg Res. 2010; 5(1):19.15. Kerkhoffs GM, Kuipers MM, Marti RK, Van der Werken C. External fixation with standard AO-plates: technique, indications, and results in 31 cases. J Orthop Trauma. 2003; 17(1):61–64.
Article16. Kloen P. Supercutaneous plating: use of a locking compression plate as an external fixator. J Orthop Trauma. 2009; 23(1):72–75.
Article17. Marti RK, van der Werken C. The AO-plate for external fixation in 12 cases. Acta Orthop Scand. 1991; 62(1):60–62.
Article18. Stoffel K, Dieter U, Stachowiak G, Gachter A, Kuster MS. Biomechanical testing of the LCP: how can stability in locked internal fixators be controlled? Injury. 2003; 34:Suppl 2. B11–B19.19. Dougherty PJ, Kim DG, Meisterling S, Wybo C, Yeni Y. Biomechanical comparison of bicortical versus unicortical screw placement of proximal tibia locking plates: a cadaveric model. J Orthop Trauma. 2008; 22(6):399–403.
Article20. Tulner SA, Strackee SD, Kloen P. Metaphyseal locking compression plate as an external fixator for the distal tibia. Int Orthop. 2012; 36(9):1923–1927.
Article21. Ma CH, Tu YK, Yeh JH, Yang SC, Wu CH. Using external and internal locking plates in a two-stage protocol for treatment of segmental tibial fractures. J Trauma. 2011; 71(3):614–619.
Article22. Buehler KC, Green J, Woll TS, Duwelius PJ. A technique for intramedullary nailing of proximal third tibia fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 1997; 11(3):218–223.
Article23. Ricci WM, OBoyle M, Borrelli J, Bellabarba C, Sanders R. Fractures of the proximal third of the tibial shaft treated with intramedullary nails and blocking screws. J Orthop Trauma. 2001; 15(4):264–270.
Article24. Toivanen JA, Vaisto O, Kannus P, Latvala K, Honkonen SE, Jarvinen MJ. Anterior knee pain after intramedullary nailing of fractures of the tibial shaft: a prospective, randomized study comparing two different nail-insertion techniques. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002; 84(4):580–585.
Article25. Vaisto O, Toivanen J, Kannus P, Jarvinen M. Anterior knee pain and thigh muscle strength after intramedullary nailing of tibial shaft fractures: a report of 40 consecutive cases. J Orthop Trauma. 2004; 18(1):18–23.26. Gautier E, Sommer C. Guidelines for the clinical application of the LCP. Injury. 2003; 34:Suppl 2. B63–B76.
Article27. Namazi H, Mozaffarian K. Awful considerations with LCP instrumentation: a new pitfall. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2007; 127(7):573–575.
Article28. Phisitkul P, McKinley TO, Nepola JV, Marsh JL. Complications of locking plate fixation in complex proximal tibia injuries. J Orthop Trauma. 2007; 21(2):83–91.
Article29. Raja S, Imbuldeniya AM, Garg S, Groom G. Difficulties encountered removing locked plates. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2012; 94(7):502–505.
Article30. Shuler FD, Obremskey WT. Tibial shaft fractures. In : Stannard JP, Schmidt AH, Kregor PJ, editors. Surgical treatment of orthopaedic trauma. New York: Thieme;2007. p. 742–766.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Stabilization Using a Medial Locking Plate for Proximal Tibial Fractures: Technical Note
- Lateral Plate Fixation of Distal Tibial Metaphyseal Fracture Using Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis Technique
- Dual Plate Fixation Compared with Hybrid External Fixator Application for Complex Tibial Plateau Fractures
- Treatment of the Distal Metaphyseal Fractures of Tibia - Comparison between Internal Fixation with a Plate and screws and External Fixation with Ilizarov Device
- Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis for Distal Tibial Metaphyseal Fracture