J Korean Med Sci.
2014 Sep;29(Suppl 2):S87-S90. 10.3346/jkms.2014.29.S2.S87.
Estimation of Daily Salt Intake through a 24-Hour Urine Collection in Pohang, Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Armed Forces Capital Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Research institute of Salt and Health, Seoul K-clinic, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea. mednep@snubh.org
- 5Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 6Kidney Research Institute, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2069797
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2014.29.S2.S87
Abstract
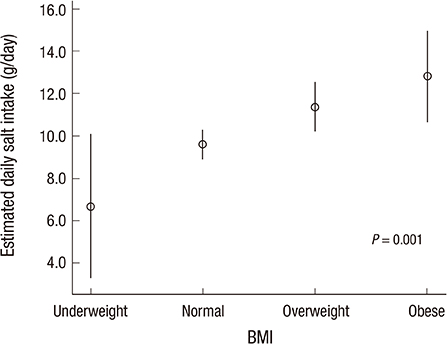
- There is an established relationship between a high salt diet and public health problems, especially hypertension and cardiovascular disease. We estimated daily salt intake in a group of adults and assessed its association with related variables in Pohang, Korea. We conducted a cross-sectional survey in 2013 with 242 adults. Urine was collected for 24 hr to estimate daily salt intake, and questionnaires about salt preference were administered. The mean daily salt intake was 9.9+/-4.6 g. There was no difference in salt intake between high systolic blood pressure (SBP) participants and normal SBP participants (10.5+/-4.7 g/d vs. 9.6+/-4.3 g/d, P=0.339), but high diastolic blood pressure (DBP) participants reported more salt intake than normal DBP participants (10.4+/-4.9 g/d vs. 9.7+/-4.1 g/d, P=0.049). Salt intake and body mass index demonstrated a positive correlation (P=0.001). A preference for Korean soup or stew was associated with high salt intake (P=0.038). Dietary salt intake in Korean adults is still higher than the recommendation from the World Health Organization. More efforts should be made to reduce the salt consumption of Korean adults.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Burdens of Cardiometabolic Diseases Attributable to Dietary and Metabolic Risks in Korean Adults 2012–2013
Yoonsu Cho, Frederick Cudhea, Ju-Hyun Park, Dariush Mozaffarian, Gitanjali Singh, Min-Jeong Shin
Yonsei Med J. 2017;58(3):540-551. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2017.58.3.540.
Reference
-
1. Stamler J. The INTERSALT Study: background, methods, findings, and implications. Am J Clin Nutr. 1997; 65:626s–642s.2. Sacks FM, Svetkey LP, Vollmer WM, Appel LJ, Bray GA, Harsha D, Obarzanek E, Conlin PR, Miller ER 3rd, Simons-Morton DG, et al. DASH-Sodium Collaborative Research Group. Effects on blood pressure of reduced dietary sodium and the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet. N Engl J Med. 2001; 344:3–10.3. He FJ, MacGregor GA. Effect of modest salt reduction on blood pressure: a meta-analysis of randomized trials. Implications for public health. J Hum Hypertens. 2002; 16:761–770.4. Cook NR, Cutler JA, Obarzanek E, Buring JE, Rexrode KM, Kumanyika SK, Appel LJ, Whelton PK. Long term effects of dietary sodium reduction on cardiovascular disease outcomes: observational follow-up of the trials of hypertension prevention (TOHP). BMJ. 2007; 334:885–888.5. He FJ, MacGregor GA. A comprehensive review on salt and health and current experience of worldwide salt reduction programmes. J Hum Hypertens. 2009; 23:363–384.6. Joossens JV, Hill MJ, Elliott P, Stamler R, Lesaffre E, Dyer A, Nichols R, Kesteloot H. European Cancer Prevention (ECP) and the INTERSALT Cooperative Research Group. Dietary salt, nitrate and stomach cancer mortality in 24 countries. Int J Epidemiol. 1996; 25:494–504.7. Brown IJ, Tzoulaki I, Candeias V, Elliott P. Salt intakes around the world: implications for public health. Int J Epidemiol. 2009; 38:791–813.8. Diet, nutrition and the prevention of chronic diseases. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser. 2003; 916:i–viii. 1–149. backcover.9. Bingham SA, Williams R, Cole TJ, Price CP, Cummings JH. Reference values for analytes of 24-h urine collections known to be complete. Ann Clin Biochem. 1988; 25(Pt 6):610–619.10. van Dam RM, Hunter D. Biochemical indicators of dietary intake. In : Willett W, editor. Nutritional epidemiology. New York: Oxford University Press;1998. p. 174–243.11. Rhee MY, Shin SJ, Park SH, Kim SW. Sodium intake of a city population in Korea estimated by 24-h urine collection method. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2013; 67:875–880.12. Son SM, Park YS, Lim HJ, Kim SB, Jeong YS. Sodium Intakes of Korean Adults with 24-hour Urine Analysis and Dish Frequency Questionnaire and Comparison of Sodium Intakes According to the Regional Area and Dish Group. Korean J Community Nutr. 2007; 12:545–558.13. Intersalt Cooperative Research Group. Intersalt: an international study of electrolyte excretion and blood pressure. Results for 24 hour urinary sodium and potassium excretion. BMJ. 1988; 297:319–328.14. Angell SY, Yi S, Eisenhower D, Kerker BD, Curtis CJ, Bartley K, Silver LD, Farley TA. Sodium Intake in a Cross-Sectional, Representative Sample of New York City Adults. Am J Public Health. 2014.15. Sadler K, Nicholson S, Steer T, Gill V, Bates B, Tipping S, Cox L, Lennox A, Prentice A. National diet and nutrition survey: assessment of dietary sodium in adults (aged 19 to 64 yr) in England, 2011. London: Department of Health;2012.16. Murakami K, Sasaki S, Takahashi Y, Uenishi K, Watanabe T, Kohri T, Yamasaki M, Watanabe R, Baba K, Shibata K, et al. Sensitivity and specificity of published strategies using urinary creatinine to identify incomplete 24-h urine collection. Nutrition. 2008; 24:16–22.17. Kim YS, Paik HY. Measurement of Na intake in Korean adult females. Korean J Nutr. 1987; 20:341–349.18. Nam HW, Lee KY. A study on the sodium and potassium intakes and their metabolism of the pregnant women in Korea. Korean J Nutr. 1985; 18:194–200.19. O'Donnell MJ, Yusuf S, Mente A, Gao P, Mann JF, Teo K, McQueen M, Sleight P, Sharma AM, Dans A, et al. Urinary sodium and potassium excretion and risk of cardiovascular events. JAMA. 2011; 306:2229–2238.20. Hoffmann IS, Cubeddu LX. Salt and the metabolic syndrome. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2009; 19:123–128.21. Taylor EN, Curhan GC. Body size and 24-hour urine composition. Am J Kidney Dis. 2006; 48:905–915.22. He FJ, Marrero NM, MacGregor GA. Salt intake is related to soft drink consumption in children and adolescents: a link to obesity? Hypertension. 2008; 51:629–634.23. Xu J, Wang M, Chen Y, Zhen B, Li J, Luan W, Ning F, Liu H, Ma J, Ma G. Estimation of salt intake by 24-hour urinary sodium excretion: a cross-sectional study in Yantai, China. BMC Public Health. 2014; 14:136.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Study on the Validity of Filter Paper Method in Estimation of the Amount of Daily Salt Intake
- Methodological issues in estimating sodium intake in the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Estimation of Microalbuminuria by Urinary Albumin to Creatinine Concentration Ratio
- 24-hour urine sodium excretion among renal donors in India: a cross-sectional study
- Comparison of Salt Taste Threshold and Salt Intake between Hypertensive and Normotensive Group