Korean J Urol.
2014 Oct;55(10):665-669. 10.4111/kju.2014.55.10.665.
Prophylactic Phenylephrine for Iatrogenic Priapism: A Pilot Study With Peyronie's Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Rutgers-New Jersey Medical School, Newark, NJ, USA. jiangpe@njms.rutgers.edu
- 2Center for Male Reproductive Medicine & Microsurgery, Hackensack University Medical Center, Hackensack, NJ, USA.
- KMID: 2069790
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/kju.2014.55.10.665
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Although penile duplex Doppler ultrasonography (PDDU) is a common and integral procedure in a Peyronie's disease workup, the intracavernosal injection of vasoactive agents can carry a serious risk of priapism. Risk factors include young age, good baseline erectile function, and no coronary artery disease. In addition, patients with Peyronie's disease undergoing PDDU in an outpatient setting are at increased risk given the inability to predict optimal dosing. The present study was conducted to provide support for a standard protocol of early administration of phenylephrine in patients with a sustained erection after diagnostic intracavernosal injection of vasoactive agents to prevent the deleterious effects of iatrogenic priapism.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This was a retrospective review of Peyronie's disease patients who received phenylephrine reversal after intracavernosal alprostadil (prostaglandin E1) administration to look at the priapism rate. Safety was determined on the basis of adverse events reported by subjects and efficacy was determined on the basis of the rate of priapism following intervention.
RESULTS
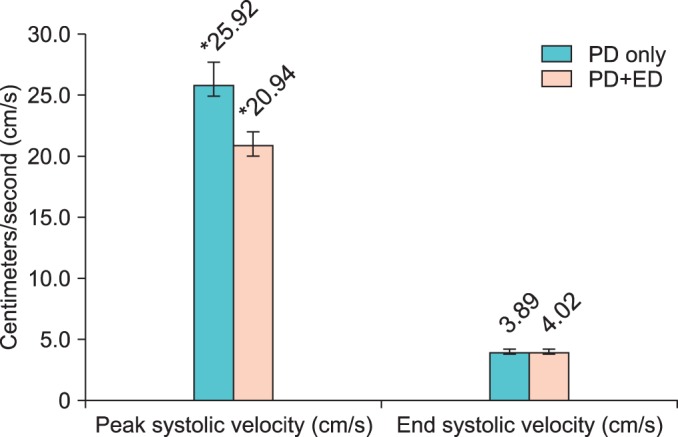
Patients with Peyronie's disease only had better hemodynamic values on PDDU than did patients with Peyronie's disease and erectile dysfunction. All of the patients receiving prophylactic phenylephrine had complete detumescence of erections without adverse events, including no priapism cases.
CONCLUSIONS
The reversal of erections with phenylephrine after intracavernosal injections of alprostadil to prevent iatrogenic priapism can be effective without increased adverse effects.
MeSH Terms
-
Alprostadil/adverse effects/diagnostic use
Drug Evaluation/methods
Humans
Male
Middle Aged
Penile Erection
Penile Induration/*ultrasonography
Phenylephrine/*therapeutic use
Pilot Projects
Priapism/chemically induced/*prevention & control
Retrospective Studies
Ultrasonography, Doppler, Duplex/adverse effects/methods
Vasoconstrictor Agents/*therapeutic use
Vasodilator Agents/adverse effects/diagnostic use
Alprostadil
Phenylephrine
Vasoconstrictor Agents
Vasodilator Agents
Figure
Reference
-
1. Pryor J, Akkus E, Alter G, Jordan G, Lebret T, Levine L, et al. Priapism. J Sex Med. 2004; 1:116–120. PMID: 16422992.
Article2. The European Alprostadil Study Group. The long-term safety of alprostadil (prostaglandin-E1) in patients with erectile dysfunction. Br J Urol. 1998; 82:538–543. PMID: 9806184.3. Coombs PG, Heck M, Guhring P, Narus J, Mulhall JP. A review of outcomes of an intracavernosal injection therapy programme. BJU Int. 2012; 110:1787–1791. PMID: 22564343.
Article4. Domes T, Chung E, DeYoung L, MacLean N, Al-Shaiji T, Brock G. Clinical outcomes of intracavernosal injection in post-prostatectomy patients: a single-center experience. Urology. 2012; 79:150–155. PMID: 22055695.
Article5. Kilic M, Serefoglu EC, Ozdemir AT, Balbay MD. The actual incidence of papaverine-induced priapism in patients with erectile dysfunction following penile colour Doppler ultrasonography. Andrologia. 2010; 42:1–4. PMID: 20078509.
Article6. Linet OI, Ogrinc FG. Efficacy and safety of intracavernosal alprostadil in men with erectile dysfunction. The Alprostadil Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1996; 334:873–877. PMID: 8596569.7. Metawea B, El-Nashar AR, Gad-Allah A, Abdul-Wahab M, Shamloul R. Intracavernous papaverine/phentolamine-induced priapism can be accurately predicted with color Doppler ultrasonography. Urology. 2005; 66:858–860. PMID: 16230153.
Article8. Perimenis P, Athanasopoulos A, Geramoutsos I, Barbalias G. The incidence of pharmacologically induced priapism in the diagnostic and therapeutic management of 685 men with erectile dysfunction. Urol Int. 2001; 66:27–29. PMID: 11150947.
Article9. Porst H. The rationale for prostaglandin E1 in erectile failure: a survey of worldwide experience. J Urol. 1996; 155:802–815. PMID: 8583582.
Article10. Lomas GM, Jarow JP. Risk factors for papaverine-induced priapism. J Urol. 1992; 147:1280–1281. PMID: 1569668.
Article11. Lue TF, Hricak H, Marich KW, Tanagho EA. Vasculogenic impotence evaluated by high-resolution ultrasonography and pulsed Doppler spectrum analysis. Radiology. 1985; 155:777–781. PMID: 3890009.
Article12. LeRoy TJ, Broderick GA. Doppler blood flow analysis of erectile function: who, when, and how. Urol Clin North Am. 2011; 38:147–154. PMID: 21621081.
Article13. Kerfoot WW, Carson CC. Pharmacologically induced erections among geriatric men. J Urol. 1991; 146:1022–1024. PMID: 1895417.
Article14. Deveci S, Palese M, Parker M, Guhring P, Mulhall JP. Erectile function profiles in men with Peyronie's disease. J Urol. 2006; 175:1807–1811. PMID: 16600766.
Article15. Rosen RC, Cappelleri JC, Smith MD, Lipsky J, Pena BM. Development and evaluation of an abridged, 5-item version of the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF-5) as a diagnostic tool for erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res. 1999; 11:319–326. PMID: 10637462.
Article16. Broderick GA, Kadioglu A, Bivalacqua TJ, Ghanem H, Nehra A, Shamloul R. Priapism: pathogenesis, epidemiology, and management. J Sex Med. 2010; 7(1 Pt 2):476–500. PMID: 20092449.
Article17. Juenemann KP, Lue TF, Abozeid M, Hellstrom WJ, Tanagho EA. Blood gas analysis in drug-induced penile erection. Urol Int. 1986; 41:207–211. PMID: 3750584.
Article18. Muneer A, Cellek S, Dogan A, Kell PD, Ralph DJ, Minhas S. Investigation of cavernosal smooth muscle dysfunction in low flow priapism using an in vitro model. Int J Impot Res. 2005; 17:10–18. PMID: 15071490.
Article19. Eland IA, van der Lei J, Stricker BH, Sturkenboom MJ. Incidence of priapism in the general population. Urology. 2001; 57:970–972. PMID: 11337305.
Article20. Dittrich A, Albrecht K, Bar-Moshe O, Vandendris M. Treatment of pharmacological priapism with phenylephrine. J Urol. 1991; 146:323–324. PMID: 1856926.
Article21. Montague DK, Jarow J, Broderick GA, Dmochowski RR, Heaton JP, Lue TF, et al. American Urological Association guideline on the management of priapism. J Urol. 2003; 170(4 Pt 1):1318–1324. PMID: 14501756.
Article22. Munarriz R, Wen CC, McAuley I, Goldstein I, Traish A, Kim N. Management of ischemic priapism with high-dose intracavernosal phenylephrine: from bench to bedside. J Sex Med. 2006; 3:918–922. PMID: 16942536.23. Ralph DJ, Pescatori ES, Brindley GS, Pryor JP. Intracavernosal phenylephrine for recurrent priapism: self-administration by drug delivery implant. J Urol. 2001; 165:1632. PMID: 11342940.
Article24. Sadeghi-Nejad H, Dogra V, Seftel AD, Mohamed MA. Priapism. Radiol Clin North Am. 2004; 42:427–443. PMID: 15136026.
Article25. Staerman F, Nouri M, Coeurdacier P, Cipolla B, Guille F, Lobel B. Treatment of the intraoperative penile erection with intracavernous phenylephrine. J Urol. 1995; 153:1478–1481. PMID: 7714971.
Article26. Azocar Hidalgo G, Van Cauwelaert R, Castillo Cadiz O, Aguirre Aguirre C, Wohler Campos C. Treatment of priapism with phenylephrine. Arch Esp Urol. 1994; 47:785–787. PMID: 7818299.27. Greenfield JM, Levine LA. Peyronie's disease: etiology, epidemiology and medical treatment. Urol Clin North Am. 2005; 32:469–478. PMID: 16291038.
Article28. Gelbard M, Goldstein I, Hellstrom WJ, McMahon CG, Smith T, Tursi J, et al. Clinical efficacy, safety and tolerability of collagenase clostridium histolyticum for the treatment of peyronie disease in 2 large double-blind, randomized, placebo controlled phase 3 studies. J Urol. 2013; 190:199–207. PMID: 23376148.
Article