Infect Chemother.
2015 Jun;47(2):137-141. 10.3947/ic.2015.47.2.137.
Toxocariasis: A Rare Cause of Multiple Cerebral Infarction
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Daegu Catholic University Medical Center, Daegu, Korea. heeya0035@naver.com
- KMID: 2069002
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2015.47.2.137
Abstract
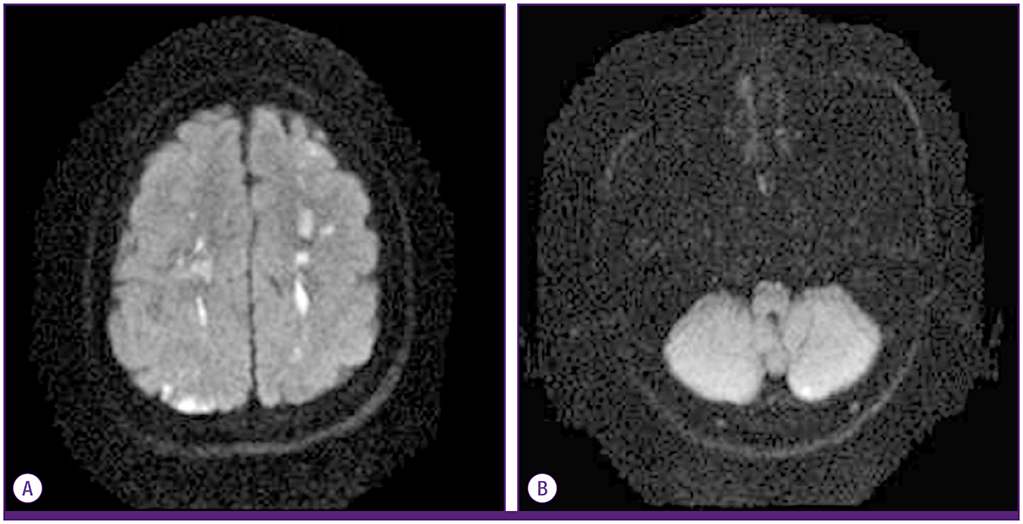
- Toxocariasis is a parasitic infection caused by the roundworms Toxocara canis or Toxocara cati, mostly due to accidental ingestion of embryonated eggs. Clinical manifestations vary and are classified as visceral larva migrans or ocular larva migrans according to the organs affected. Central nervous system involvement is an unusual complication. Here, we report a case of multiple cerebral infarction and concurrent multi-organ involvement due to T. canis infestation of a previous healthy 39-year-old male who was admitted for right leg weakness. After treatment with albendazole, the patient's clinical and laboratory results improved markedly.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Status of common parasitic diseases in Korea in 2019
Sun Huh
J Korean Med Assoc. 2019;62(8):437-456. doi: 10.5124/jkma.2019.62.8.437.
Reference
-
1. Despommier D. Toxocariasis: clinical aspects, epidemiology, medical ecology, and molecular aspects. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2003; 16:265–272.
Article2. Chang S, Lim JH, Choi D, Park CK, Kwon NH, Cho SY, Choi DC. Hepatic visceral larva migrans of Toxocara canis: CT and sonographic findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006; 187:W622–W629.3. Choi D, Lim JH, Choi DC, Lee KS, Paik SW, Kim SH, Choi YH, Huh S. Transmission of Toxocara canis via ingestion of raw cow liver: a cross-sectional study in healthy adults. Korean J Parasitol. 2012; 50:23–27.
Article4. Abdel Razek AA, Watcharakorn A, Castillo M. Parasitic diseases of the central nervous system. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2011; 21:815–841.
Article5. Jacquier P, Gottstein B, Stingelin Y, Eckert J. Immunodiagnosis of toxocarosis in humans: evaluation of a new enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit. J Clin Microbiol. 1991; 29:1831–1835.
Article6. Kwon NH, Oh MJ, Lee SP, Lee BJ, Choi DC. The prevalence and diagnostic value of toxocariasis in unknown eosinophilia. Ann Hematol. 2006; 85:233–238.
Article7. Dauriac-Le Masson V, Chochon F, Demeret S, Pierrot-Deseilligny C. Toxocara canis meningomyelitis. J Neurol. 2005; 252:1267–1268.
Article8. Duprez TP, Bigaignon G, Delgrange E, Desfontaines P, Hermans M, Vervoort T, Sindic CJ, Buysschaert M. MRI of cervical cord lesions and their resolution in Toxocara canis myelopathy. Neuroradiology. 1996; 38:792–795.
Article9. Finsterer J, Auer H. Neurotoxocarosis. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 2007; 49:279–287.
Article10. Liao CW, Cho WL, Kao TC, Su KE, Lin YH, Fan CK. Blood-brain barrier impairment with enhanced SP, NK-1R, GFAP and claudin-5 expressions in experimental cerebral toxocariasis. Parasite Immunol. 2008; 30:525–534.
Article11. Kim YB, Ko YC, Jeon SH, Park HM, Shin WC, Lee YB, Ha KS, Shin DJ, Lim YH, Ryu JS, Chung MS. Toxocariasis: an unusual cause of cerebral infarction. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 2003; 21:651–654.12. Han WH, Kim JE, Do JK, Jung BW, Kwon HH. Cerebral infarctions associated with toxocariasis-induced secondary hypereosinophilia. Korean J Stroke. 2010; 12:109–111.13. Xinou E, Lefkopoulos A, Gelagoti M, Drevelegas A, Diakou A, Milonas I, Dimitriadis AS. CT and MR imaging findings in cerebral toxocaral disease. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003; 24:714–718.14. Torvik A. The pathogenesis of watershed infarcts in the brain. Stroke. 1984; 15:221–223.
Article15. Grigoryan M, Geisler SD, St Louis EK, Baumbach GL, Davis PH. Cerebral arteriolar thromboembolism in idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome. Arch Neurol. 2009; 66:528–531.
Article16. Prick JJ, Gabreëls-Festen AA, Korten JJ, van der Wiel TW. Neurological manifestations of the hypereosinophilic syndrome. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 1988; 90:269–273.17. Vidal JE, Sztajnbok J, Seguro AC. Eosinophilic meningoencephalitis due to Toxocara canis: case report and review of the literature. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2003; 69:341–343.
Article18. Jung H, Hurtado M, Medina MT, Sanchez M, Sotelo J. Dexamethasone increases plasma levels of albendazole. J Neurol. 1990; 237:279–280.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Neurotoxocariasis Case Manifesting Multiple Cerebral Infarction and Eosinophilic Meningoencephalitis
- Cerebral Toxocariasis Presented With Seizure and Memory Disturbance
- Toxocariasis: An Unusual Cause of Cerebral Infarction
- Transient global amnesia associated with toxocariasis and secondary hypereosinophilia
- A Case of Cerebral Infarction Caused by Tumor Emboli from the Site of