Yonsei Med J.
2014 May;55(3):773-778. 10.3349/ymj.2014.55.3.773.
The Prevalence of Idiopathic Scoliosis in Eleven Year-Old Korean Adolescents: A 3 Year Epidemiological Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Medical College of Hallym University, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Spine and Scoliosis Service, Hospital for Special Surgery, New York, NY, USA.
- 4Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, Medical College of Hallym University, Anyang, Korea. amhangpark@gmail.com
- KMID: 2068690
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2014.55.3.773
Abstract
- PURPOSE
School screening allows for early detection and early treatment of scoliosis, with the purpose of reducing the number of patients requiring surgical treatment. Children between 10 and 14 years old are considered as good candidates for school screening tests of scoliosis. The purpose of the present study was to assess the epidemiological findings of idiopathic scoliosis in 11-year-old Korean adolescents.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
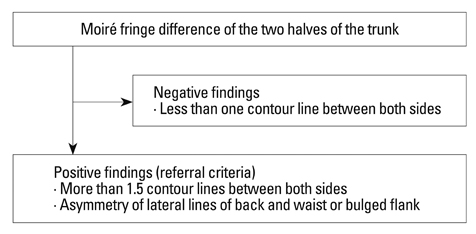
A total of 37856 11-year-old adolescents were screened for scoliosis. There were 17110 girls and 20746 boys. Adolescents who were abnormal by Moire topography were subsequently assessed by standardized clinical and radiological examinations. A scoliotic curve was defined as 10degrees or more.
RESULTS
The prevalence of scoliosis was 0.19% and most of the curves were small (10degrees to 19degrees). The ratio of boys to girls was 1:5.5 overall. Sixty adolescents (84.5%) exhibited single curvature. Thoracolumbar curves were the most common type of curve identified, followed by thoracic and lumbar curves.
CONCLUSION
The prevalence of idiopathic scoliosis among 11-year-old Korean adolescents was 0.19%.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Weinstein SL. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: prevalence and natural history. Instr Course Lect. 1989; 38:115–128.2. Landman Z, Oswald T, Sanders J, Diab M. Spinal Deformity Study Group. Prevalence and predictors of pain in surgical treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011; 36:825–829.
Article3. Smorgick Y, Mirovsky Y, Baker KC, Gelfer Y, Avisar E, Anekstein Y. Predictors of back pain in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis surgical candidates. J Pediatr Orthop. 2013; 33:289–292.
Article4. Renshaw TS. Screening school children for scoliosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988; 26–33.
Article5. Lonstein JE. Screening for spinal deformities in Minnesota schools. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1977; 33–42.
Article6. Lonstein JE, Bjorklund S, Wanninger MH, Nelson RP. Voluntary school screening for scoliosis in Minnesota. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1982; 64:481–488.
Article7. Rogala EJ, Drummond DS, Gurr J. Scoliosis: incidence and natural history. A prospective epidemiological study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1978; 60:173–176.8. Scoliosis Research Society (U.S.). Scoliosis: a handbook for patients. IL, USA: The Society;1986.9. Soucacos PN, Zacharis K, Soultanis K, Gelalis J, Xenakis T, Beris AE. Risk factors for idiopathic scoliosis: review of a 6-year prospective study. Orthopedics. 2000; 23:833–838.
Article10. Stirling AJ, Howel D, Millner PA, Sadiq S, Sharples D, Dickson RA. Late-onset idiopathic scoliosis in children six to fourteen years old. A cross-sectional prevalence study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1996; 78:1330–1336.
Article11. Wong HK, Hui JH, Rajan U, Chia HP. Idiopathic scoliosis in Singapore schoolchildren: a prevalence study 15 years into the screening program. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005; 30:1188–1196.12. Suh SW, Modi HN, Yang JH, Hong JY. Idiopathic scoliosis in Korean schoolchildren: a prospective screening study of over 1 million children. Eur Spine J. 2011; 20:1087–1094.
Article13. Sahlstrand T. The clinical value of Moiré topography in the management of scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1986; 11:409–417.
Article14. Adobor RD, Rimeslatten S, Steen H, Brox JI. School screening and point prevalence of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis in 4000 Norwegian children aged 12 years. Scoliosis. 2011; 6:23.
Article15. Dickson RA, Stamper P, Sharp AM, Harker P. School screening for scoliosis: cohort study of clinical course. Br Med J. 1980; 281:265–267.
Article16. Grivas TB, Koukos K, Koukou UI, Maziotou C, Polyzois BD. The incidence of idiopathic scoliosis in Greece--analyais of domestic school screening programs. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2002; 91:71–75.17. Karachalios T, Sofianos J, Roidis N, Sapkas G, Korres D, Nikolopoulos K. Ten-year follow-up evaluation of a school screening program for scoliosis. Is the forward-bending test an accurate diagnostic criterion for the screening of scoliosis? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1999; 24:2318–2324.
Article18. Morais T, Bernier M, Turcotte F. Age- and sex-specific prevalence of scoliosis and the value of school screening programs. Am J Public Health. 1985; 75:1377–1380.
Article19. Soucacos PN, Soucacos PK, Zacharis KC, Beris AE, Xenakis TA. School-screening for scoliosis. A prospective epidemiological study in northwestern and central Greece. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1997; 79:1498–1503.
Article20. Willner S, Udén A. A prospective prevalence study of scoliosis in Southern Sweden. Acta Orthop Scand. 1982; 53:233–237.
Article21. Smyrnis PN, Valavanis J, Alexopoulos A, Siderakis G, Giannestras NJ. School screening for scoliosis in Athens. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1979; 61-B:215–217.
Article22. Ueno M, Takaso M, Nakazawa T, Imura T, Saito W, Shintani R, et al. A 5-year epidemiological study on the prevalence rate of idiopathic scoliosis in Tokyo: school screening of more than 250,000 children. J Orthop Sci. 2011; 16:1–6.
Article23. Grivas TB, Vasiliadis E, Savvidou OD, Triantafyllopoulos G. What a school screening program could contribute in clinical research of idiopathic scoliosis aetiology. Disabil Rehabil. 2008; 30:752–762.
Article24. Laulund T, Søjbjerg JO, Hørlyck E. Moiré topography in school screening for structural scoliosis. Acta Orthop Scand. 1982; 53:765–768.
Article25. Daruwalla JS, Balasubramaniam P. Moiré topography in scoliosis. Its accuracy in detecting the site and size of the curve. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1985; 67:211–213.26. Adair IV, Van Wijk MC, Armstrong GW. Moiré topography in scoliosis screening. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1977; 165–171.
Article27. Willner S. Moiré topography for the diagnosis and documentation of scoliosis. Acta Orthop Scand. 1979; 50:295–302.
Article28. Lee CF, Fong DY, Cheung KM, Cheng JC, Ng BK, Lam TP, et al. Costs of school scoliosis screening: a large, population-based study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010; 35:2266–2272.29. Sanders JO, Newton PO, Browne RH, Herring AJ. Bracing in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis, surrogate outcomes, and the number needed to treat. J Pediatr Orthop. 2012; 32:Suppl 2. S153–S157.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Idiopathic Scoliosis in the Eleven Years Old: Prevalence Study
- Comparisons of Postural Habits, Body Image, and Peer Attachment for Adolescents with Idiopathic Scoliosis and Healthy Adolescents
- The Classification of Idiopathic Scoliosis
- Low Body Mass Index for Early Screening of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Comparison Based on Standardized Body Mass Index Classifications
- Is There a Role for Conservative Treatment for Large Curvatures in Patients With Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis?: Commentary on “The Effect of Brace Treatment on Large Curves of 40° to 55° in Adolescents With Idiopathic Scoliosis Who Have Avoided Surgery: A Retrospective Cohort Study”