J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2012 May;51(5):316-319. 10.3340/jkns.2012.51.5.316.
Cerebral Toxoplasmosis Combined with Disseminated Tuberculosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Dae-Ah Hando General Hospital, Ansan, Korea. ehhwang38@yahoo.co.kr
- 2Department of Anatomy, College of Medicine, Korea University, Brain Korea 21, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2066935
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2012.51.5.316
Abstract
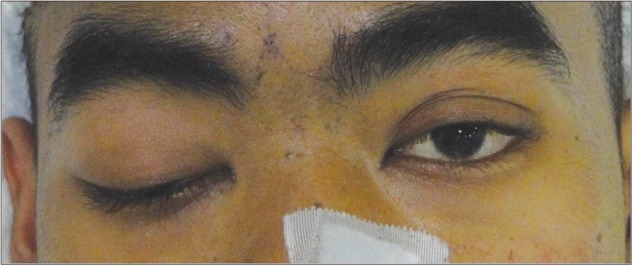
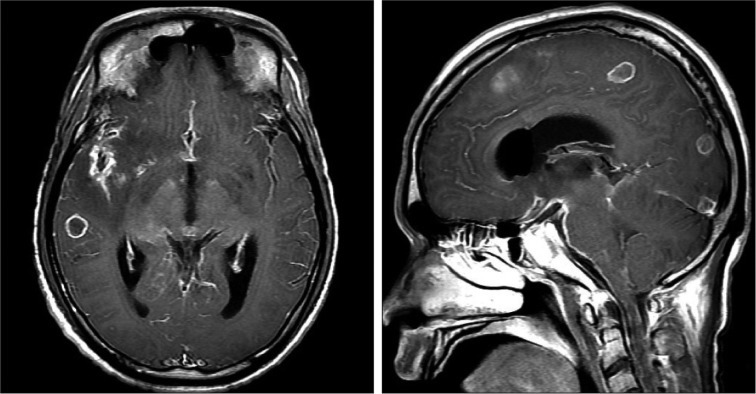
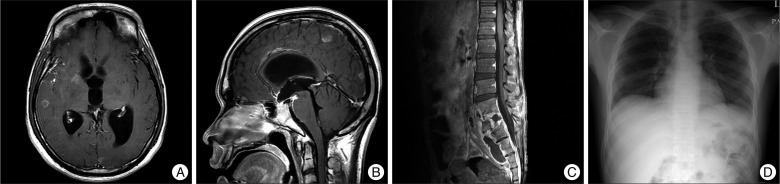
- A 24-year-old man presented with mental change, fever, abdominal pain, tenderness and palpable mass on the lower abdomen. He was a non-Korean engineer and did not accompany a legal guardian, so medical history taking was difficult due to his mental status. Brain magnetic resonance imaging showed multiple rim-enhanced lesions of the brain, and abdominal computed tomography showed huge paraspinal abscess. Chest X-ray and computed tomography showed poorly defined nodular opacities. We initially thought that this patient was infected with toxoplasmosis with typical cerebral image finding and immunoglobulin laboratory finding of cerebrospinal fluid and serum study. The abdominal abscess was confirmed as tuberculosis through the pathologic finding of caseous necrosis. We used anti-tuberculosis medication and anti-toxoplasmosis medication for almost 4 months, and then his clinical state and radiological findings were considerably improved.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
2. Caiaffa WT, Chiari CA, Figueiredo AR, Orefice F, Antunes CM. Toxoplasmosis and mental retardation--report of a case-control study. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 1993; 88:253–261. PMID: 8107587.3. Carruthers VB, Suzuki Y. Effects of Toxoplasma gondii infection on the brain. Schizophr Bull. 2007; 33:745–751. PMID: 17322557.
Article4. Cota GF, Assad EC, Christo PP, Giannetti AV, Santos Filho JA, Xavier MA. Ventriculitis : a rare case of primary cerebral toxoplasmosis in AIDS patient and literature review. Braz J Infect Dis. 2008; 12:101–104. PMID: 18553025.
Article5. Frenkel JK. Pathology and pathogenesis of congenital toxoplasmosis. Bull N Y Acad Med. 1974; 50:182–191. PMID: 4592096.6. Gleason TH, Hamlin WB. Disseminated toxoplasmosis in the compromised host. A report of five cases. Arch Intern Med. 1974; 134:1059–1062. PMID: 4215377.
Article7. Holliman RE. Toxoplasmosis, behaviour and personality. J Infect. 1997; 35:105–110. PMID: 9354342.
Article8. Kumar GG, Mahadevan A, Guruprasad AS, Kovoor JM, Satishchandra P, Nath A, et al. Eccentric target sign in cerebral toxoplasmosis : neuropathological correlate to the imaging feature. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2010; 31:1469–1472. PMID: 20512900.
Article9. Oksenhendler E, Cadranel J, Sarfati C, Katlama C, Datry A, Marche C, et al. Toxoplasma gondii pneumonia in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am J Med. 1990; 88:18N–21N.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Two Cases of Cerebral Toxoplasmosis in AIDS Patients
- Disseminated Bone Tuberculosis
- A Novel Case of Solitary Cerebral Toxoplasmosis Mimicking Glioblastoma as the First Presentation of HIV
- Delayed Cerebral Toxoplasmosis in a Kidney Transplant Patient: a Case Report
- A Case of Congenital Toxoplasmosis in the Neonate