J Korean Diabetes Assoc.
2006 Mar;30(2):112-121. 10.4093/jkda.2006.30.2.112.
The Comparison of Efficacy with alpha-lipoic Acid Treatment Methods in Diabetic Polyneuropathy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Ewha Womans University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Eulji University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2063440
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/jkda.2006.30.2.112
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Diabetic neuropathy represents a major health problem, as it is responsible for substantial morbidity, increased mortality, and impaired quality of life. Antioxidant treatment has been shown to prevent nerve dysfunction, providing a rationale for a potential therapeutic value in diabetic patients. The safety and efficacy of alpha-lipoic acid (ALA) given intravenously were proved in many studies, but the oral treatment remains to be established. Therefore we compare the efficacy and safety of ALA given intravenously followed by oral treatment and given only orally.
METHODS
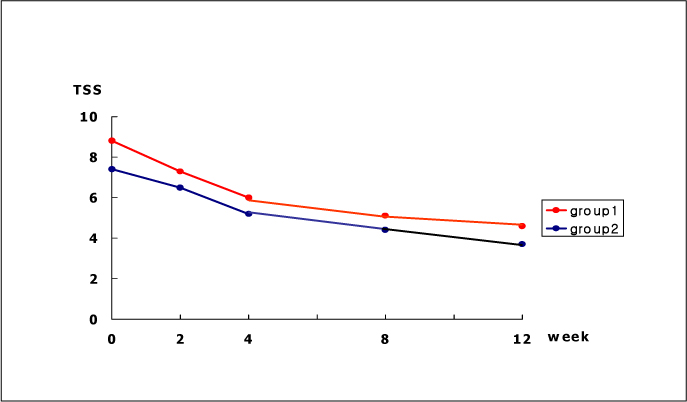
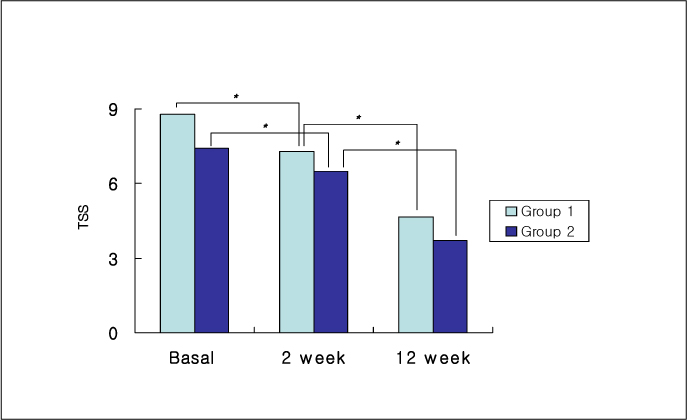
45 outpatients were randomly assigned to sequential treatment with ALA intravenously for 2 weeks, followed by orally for 10 weeks (group 1, n = 21); ALA orally for 12 weeks (group 2, n = 24). The primary end point was change of the sum score of severity and duration of total symptom score (TSS). HbA1c and safety parameters were determined at baseline and after 12 weeks.
RESULTS
The TSS was significantly decreased from baseline to 2 week and 12 week in both groups. But no significant differences between the two groups were noted at 2 week and 12 week. There were no significant changes in HbA1c and safety parameters between baseline and 12 week. The rate of adverse events were 47.6% in group 1 and 12.5% in group 2.
CONCLUSION
We conclude that both methods of ALA treatment are effective to improve the symptoms of diabetic polyneuropathy, and the safety was probably superior in oral treatment method
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ziegler D, Gries FA, Muhlen H, Rathmann W, Spuler M, Lessmann F. The Diacan Multicenter Study Group. Prevalence and clinical correlates of cardiovascular autonomic and peripheral diabetic neuropathy in patients attending diabetes centers. Diabete Metab. 1993. 19:143–151.2. Navarro X, Kennedy WR, Aeppli D, Sutherland DE. Neuropathy and mortality in diabetes: influence of pancreas transplantation. Muscle Nerve. 1996. 19:1009–1016.3. Boyko EJ, Ahroni JH, Smith DG, Davignon D. Increased mortality associated with diabetic foot ulcer. Diabet Med. 1996. 13:967–972.4. UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet. 1998. 352:837–853.5. Henry JA, Alexander CA, Sener EK. Relative mortality from overdose of antidepressants. BMJ. 1995. 310:221–224.6. Faes TJ, Yff GA, DeWeerdt O, Lanting P, Heimans JJ, Bertelsmann FW. Treatment of diabetic autonomic neuropathy with an aldose reductase inhibitor. J Neurol. 1993. 240:156–160.7. Boland OM, Blackwell CC, Clarke BF, Ewing DJ. Effects of ponalrestat, an aldose reductase inhibitor, on neutrophil killing of Escherichia coli and autonomic function in patients with diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1993. 42:336–340.8. Ziegler D, Hanefeld M, Ruhnau KJ, Meissner HP, Lobisch M, Schutte K, Gries FA. Treatment of symptomatic diabetic peripheral neuropathy with the anti-oxidant alpha-lipoic acid. A 3-week multicentre randomized controlled trial (ALADIN Study). Diabetologia. 1995. 38:1425–1433.9. Reljanovic M, Reichel G, Rett K, Lobisch M, Schuette K, Moller W, Tritschler HJ, Mehnert H. Alpha Lipoic Acid in Diabetic Neuropathy. Treatment of diabetic polyneuropathy with the antioxidant thioctic acid (alpha-lipoic acid): a two year multicenter randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial (ALADIN II). Free Radic Res. 1999. 31:171–179.10. Ziegler D, Schatz H, Conrad F, Gries FA, Ulrich H, Reichel G. Effects of treatment with the antioxidant alpha-lipoic acid on cardiac autonomic neuropathy in NIDDM patients. A 4-month randomized controlled multicenter trial (DEKAN Study). Deutsche Kardiale Autonome Neuropathie. Diabetes Care. 1997. 20:369–373.11. Ametov AS, Barinov A, Dyck PJ, Hermann R, Kozlova N, Litchy WJ, Low PA, Nehrdich D, Novosadova M, O'Brien PC, Reljanovic M, Samigullin R, Schuette K, Strokov I, Tritschler HJ, Wessel K, Yakhno N, Ziegler D. SYDNEY Trial Study Group. The sensory symptoms of diabetic polyneuropathy are improved with alpha-lipoic acid: the SYDNEY trial. Diabetes Care. 2003. 26:770–776.12. Judzewitsch RG, Jaspan JB, Polonsky KS, Weinberg CR, Halter JB, Halar E, Pfeifer MA, Vukadinovic C, Bernstein L, Schneider M, Liang KY, Gabbay KH, Rubenstein AH, Porte D Jr. Aldose reductase inhibition improves nerve conduction velocity in diabetic patients. N Engl J Med. 1983. 308:119–125.13. Judzewitsch RG, Jaspan JB, Polonsky KS, Weinberg CR, Halter JB, Halar E, Pfeifer MA, Vukadinovic C, Bernstein L, Schneider M, Liang KY, Gabbay KH, Rubenstein AH, Porte D Jr. Aldose reductase inhibition improves nerve conduction velocity in diabetic patients. N Engl J Med. 1983. 308:119–125.14. Ziegler D, Mayer P, Rathmann W, Gries FA. One-year treatment with the aldose reductase inhibitor, ponalrestat, in diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1991. 14:63–73.15. Ziegler D, Hanefeld M, Ruhnau KJ, Hasche H, Lobisch M, Schutte K, Kerum G, Malessa R. ALADIN III Study Group. Alpha-Lipoic Acid in Diabetic Neuropathy. Treatment of symptomatic diabetic polyneuropathy with the antioxidant alpha-lipoic acid: a 7-month multicenter randomized controlled trial (ALADIN III Study). Diabetes Care. 1999. 22:1296–1301.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of 12-week Oral Treatment with alpha-lipoic acid on the Nerve Conduction in Symptomatic Diabetic Neuropathy
- Efficacy and Safety of α-Lipoic Acid and Low Dose Pregabalin Combination in Painful Diabetic Neuropathy
- Recurrent Insulin Autoimmune Syndrome Caused by alpha-Lipoic Acid in Type 2 Diabetes
- The Effects of Alpha-Lipoic Acid on Epidermal Nerve Preservation in the Diabetic Neuropathy of OLETF Rats
- Comparison of R(+)-α-lipoic acid exposure after R(+)-α-lipoic acid 200 mg and 300 mg and thioctic acid 600 mg in healthy Korean male subjects