Electrolyte Blood Press.
2006 Nov;4(2):77-82. 10.5049/EBP.2006.4.2.77.
Pseudohyponatremia:Does It Matter in Current Clinical Practice?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine and Institute of Biomedical Sciences, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kimgh@hanyang.ac.kr
- KMID: 2052275
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5049/EBP.2006.4.2.77
Abstract
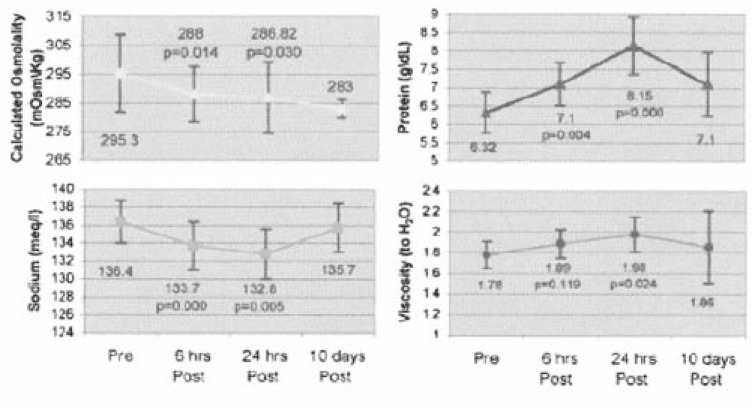
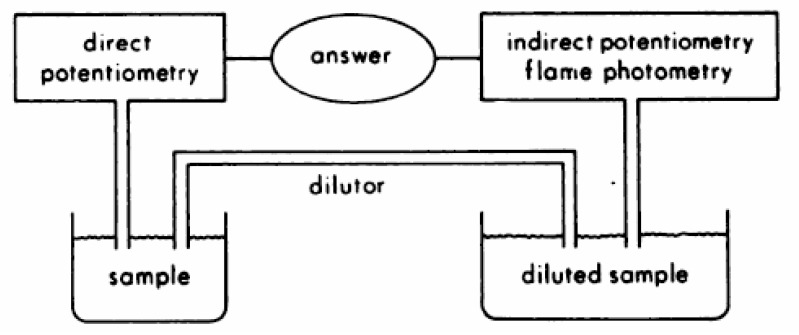
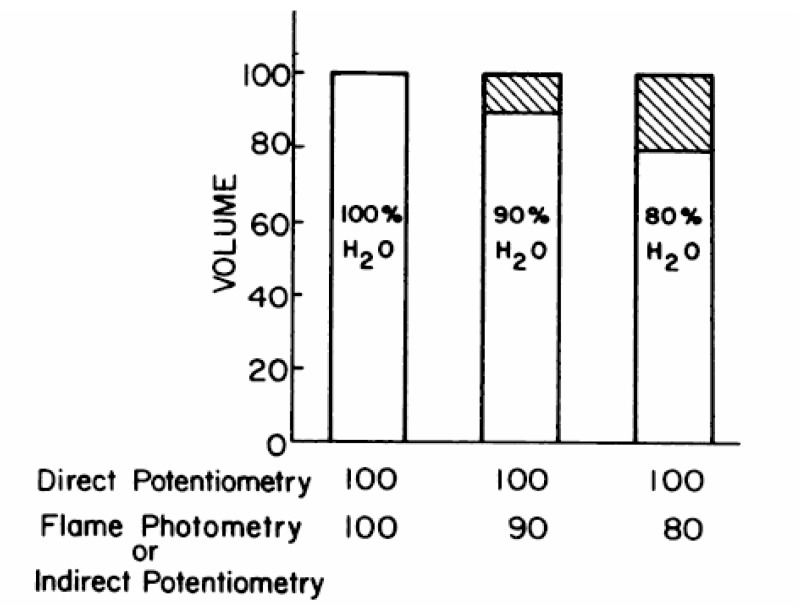
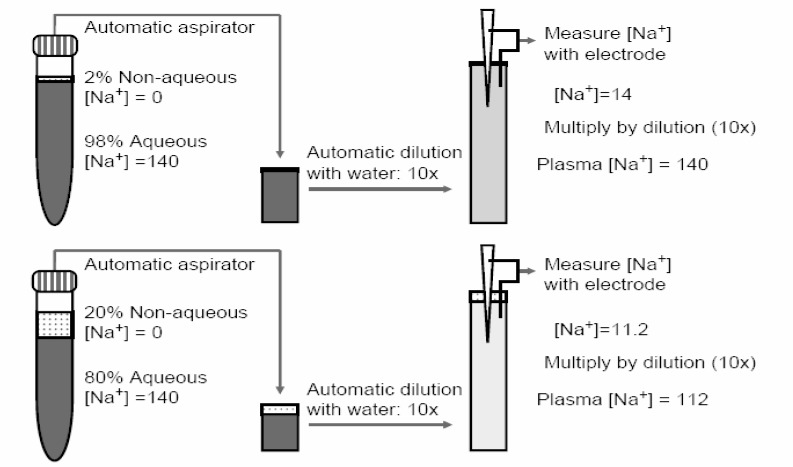
- Serum consists of water (93% of serum volume) and nonaqueous components, mainly lipids and proteins (7% of serum volume). Sodium is restricted to serum water. In states of hyperproteinemia or hyperlipidemia, there is an increased mass of the nonaqueous components of serum and a concomitant decrease in the proportion of serum composed of water. Thus, pseudohyponatremia results because the flame photometry method measures sodium concentration in whole plasma. A sodium-selective electrode gives the true, physiologically pertinent sodium concentration because it measures sodium activity in serum water. Whereas the serum sample is diluted in indirect potentiometry, the sample is not diluted in direct potentiometry. Because only direct reading gives an accurate concentration, we suspect that indirect potentiometry which many hospital laboratories are now using may mislead us to confusion in interpreting the serum sodium data. However, it seems that indirect potentiometry very rarely gives us discernibly low serum sodium levels in cases with hyperproteinemia and hyperlipidemia. As long as small margins of errors are kept in mind of clinicians when serum sodium is measured from the patients with hyperproteinemia or hyperlipidemia, the present methods for measuring sodium concentration in serum by indirect sodium-selective electrode potentiometry could be maintained in the clinical practice.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chonchol M, Berl T. DuBose TD, Hamm LL, editors. Hyponatremia. Acid-base and electrolyte disorders. 2002. Philadelphia: WB Saunders;p. 229–239.2. Sterns RH, Silver SM, Spital A. Seldin DW, Giebisch G, editors. Hyponatremia. The kidney. Physiology & pathophysiology. 2000. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;p. 1217–1238.
Article3. Weisberg LS. Pseudohyponatremia: a reappraisal. Am J Med. 1989; 86:315–318. PMID: 2645773.
Article4. Albrink MJ, Hald PM, Man EB, Peters JP. The displacement of serum water by the lipids of hyperlipemic serum; a new method for the rapid determination of serum water. J Clin Invest. 1955; 34:1483–1488. PMID: 13263427.6. Ladenson JH, Apple FS, Koch DD. Misleading hyponatremia due to hyperlipemia: a method-dependent error. Ann Intern Med. 1981; 95:707–708. PMID: 7305152.
Article7. Koffman BM, Dalakas MC. Effect of high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin on serum chemistry, hematology, and lymphocyte subpopulations: assessments based on controlled treatment trials in patients with neurological diseases. Muscle Nerve. 1997; 20:1102–1107. PMID: 9270664.
Article8. Lawn N, Wijdicks EFM, Burritt MF. Intravenous immune globulin and pseudohyponatremia. N Engl J Med. 1998; 339:632. PMID: 9722438.
Article9. Ng SK. Intravenous immunoglobulin causing pseudohyponatremia. Lupus. 1999; 8:488–490. PMID: 10483022.10. Steinberger BA, Ford SM, Coleman TA. Intravenous immunoglobulin therapy results in post-infusional hyperproteinemia, increased serum viscosity, and pseudohyponatremia. Am J Hematol. 2003; 73:97–100. PMID: 12749010.
Article11. Colls BM. Guillain-Barre syndrome and hyponatremia. Intern Med J. 2003; 33:5–9. PMID: 12534871.12. Nguyen MK, Rastogi A, Kurtz I. True hyponatremia secondary to intravenous immunoglobulin. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2006; 10:124–126. PMID: 16791398.
Article13. Davies AG. Inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone in Guillain-Barre syndrome. Postgrad Med J. 1971; 47:651–653. PMID: 5158839.
Article14. Penney MD, Murphy D, Walters G. Resetting of osmoreceptor response as cause of hyponatraemia in acute idiopathic polyneuritis. Br Med J. 1979; ii:1474–1476. PMID: 526815.
Article15. Hochman MS, Kobetz SA, Handwerker JV. Inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone associated with Guillain-Barre syndrome. Ann Neurol. 1982; 11:322–323. PMID: 7092187.16. Kaneko K, Shioya T, Yabuta K. Inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone and transient hypertension associated with Guillain-Barre syndrome. Pediatr Neurosci. 1989; 15:257–259. PMID: 2488953.17. Hoffmann O, Reuter U, Schielke E, Weber JR. SIADH as the first symptom of Guillain-Barré syndrome. Neurology. 1999; 53:1365. PMID: 10522906.18. Eisenman G, Rudin DO, Casby JU. Glass electrode for measuring sodium ion. Science. 1957; 126:831–834. PMID: 13467284.
Article19. Apple FS, Koch DD, Graves S, Ladenson JH. Relationship between direct-potentiometric and flame-photometric measurement of sodium in blood. Clin Chem. 1982; 28:1931–1935. PMID: 7127808.
Article20. Friedman SM, Wong SL, Walton JH. Glass electrode measurements of blood sodium and potassium in man. J Appl Physiol. 1963; 18:950–954. PMID: 14063266.
Article21. Moe OW, Fuster D. Clinical acid-base pathophysiology: disorders of plasma anion gap. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003; 17:559–574. PMID: 14687589.
Article22. Albrink MJ, Hald PM, Man EB, Peters JP. Displacement of serum water by the lipids of serum. J Clin Invest. 1955; 34:1483–1488. PMID: 13263427.23. Ladenson JH, Apple FS, Aguanno JJ, Koch DD. Sodium measurements in multiple myeloma: two techniques compared. Clin Chem. 1982; 28:2383–2386. PMID: 6814789.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pseudohyponatremia After Intravenous Immunoglobulin Therapy in a Patient With Guillain-Barre Syndrome
- Association of Particulate Matter With ENT Diseases
- White Matter Injury of Prematurity: Its Mechanisms and Clinical Features
- Current Status of Clinical Practice Education in Maternity Nursing in Korea: four-year course nursing schools centered
- Fine Particulate Matter and Urology: Emphasis on the Lower Urinary Tract