International Live Endoscopic Multichannel Demonstration Using Superfast Broadband Internet Connections
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Hanyang University Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. hamjs@hanyang.ac.kr
- 2Department of Computer Sciences and Engineering, Hanyang University College of Engineering, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Endoscopic Diagnostics and Therapeutics, Kyushu University Faculty of Medicine, Fukuoka, Japan.
- KMID: 2048835
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2012.45.1.73
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/AIMS
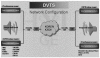
Telemedicine is a convenient and efficient tool for remote education in various fields. The telemedicine system can also be used to educate doctors and medical students. The aim of our study was to establish the effectiveness of the telemedical system for use in a live endoscopic multichannel demonstration conference and to test the effectiveness and usefulness of a multicenter-based live endoscopic demonstration through live, interactive, high resolution video transmission using advanced networks and the digital video transport system (DVTS).
METHODS
This study is a prospective multicenter pilot study. A live demonstration of an endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) and an endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) using advanced network technology was performed.
RESULTS
The DVTS successfully transmitted uncompressed, high-resolution, digital lectures with endoscopy video during a multichannel endoscopic live demonstration of ESD and ERCP over multiple advanced networks. The overall satisfaction rating when the endoscopic lecture demonstration was performed by combining DVTS was generally good.
CONCLUSIONS
We believe that a multicenter-based live endoscopic demonstration is a very effective conferencing method when using advanced networks and DVTS.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Live Endoscopy Demonstration Using Superfast Broadband Internet Connections: The Future of Medical Education and Conferences
Jimin Han
Clin Endosc. 2012;45(1):1-1. doi: 10.5946/ce.2012.45.1.1.Sketch of International Digestive Endoscopy Network 2012 Meeting: Overview
Ho Gak Kim
Clin Endosc. 2012;45(3):211-213. doi: 10.5946/ce.2012.45.3.211.International Digestive Endoscopy Network 2012: A Patchwork of Networks for the Future
Kwang An Kwon, Il Ju Choi, Eun Young Kim, Seok Ho Dong, Ki Baik Hahm
Clin Endosc. 2012;45(3):209-210. doi: 10.5946/ce.2012.45.3.209.Highlights of the 48th Seminar of Korean Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy
Kwang An Kwon, Il Ju Choi, Eun Young Kim, Seok Ho Dong, Ki Baik Hahm
Clin Endosc. 2013;46(3):203-211. doi: 10.5946/ce.2013.46.3.203.
Reference
-
1. Harris BA Jr. Telemedicine: a glance into the future. Mayo Clin Proc. 1994; 69:1212–1214. PMID: 7967785.
Article2. Broderick TJ, Harnett BM, Doarn CR, Rodas EB, Merrell RC. Real-time Internet connections: implications for surgical decision making in laparoscopy. Ann Surg. 2001; 234:165–171. PMID: 11505061.
Article3. Hahm JS, Lee HL, Choi HS, Shimizu S. Telemedicine system using a high-speed network: past, present, and future. Gut Liver. 2009; 3:247–251. PMID: 20431756.
Article4. Hahm JS, Lee HL, Kim SI, et al. A remote educational system in medicine using digital video. Hepatogastroenterology. 2007; 54:373–376. PMID: 17523277.5. Hahm JS, Shimizu S, Nakashima N, et al. Telemedicine with digital video transport system. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2004; 43:370–375. PMID: 15220555.6. Heatley DJ, Bell GD. Telemedicine in gastrointestinal endoscopy. Endoscopy. 2003; 35:624–626. PMID: 12822103.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Live Endoscopy Demonstration Using Superfast Broadband Internet Connections: The Future of Medical Education and Conferences
- Ethics of Live Surgery Demonstration or Broadcast: Is It Beneficial to the Patients?
- The Effects of Hearing Aid Digital Noise Reduction and Directionality on Acceptable Noise Level
- Succesful Treatment of Pruritus in Pregnancy with Broadband UVB Phototherapy
- Biological Model and Pharmacotherapy in Internet Addiction