Lab Med Online.
2015 Oct;5(4):169-175. 10.3343/lmo.2015.5.4.169.
Perspectives on Next-Generation Newborn Screening
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Health Sciences and Technology, Samsung Advanced Institute for Health Sciences and Technology, Sungkyunkwan University, Seoul, Korea. kimjw@skku.edu
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine and Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2046378
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/lmo.2015.5.4.169
Abstract
- Newborn screening (NBS) has been effective for detecting asymptomatic newborns with inherited metabolic diseases and has facilitated early clinical intervention, which has resulted in significant decreases in the rates of morbidity and mortality caused by these diseases. The outcome of the NBS program heavily depends on technological advances. Since Dr. Robert Guthrie developed a bacterial inhibition assay to screen for metabolic diseases in the early 1960s, use of the NBS program has spread to many countries. Tandem mass spectrometry (TMS) was a second major technological breakthrough that has allowed screening to be extended to disorders of fatty acid and organic acid metabolism as well as to those of amino acid metabolism, and recently screening has also been expanded to include lysosomal storage diseases. TMS can detect multiple analytes rapidly and simultaneously and is currently applied to nearly 80% of the newborn population in Korea. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) technology could be another major breakthrough to improve the current NBS program. To integrate NGS into the NBS program, various considerations about its analytical validity, clinical validity, clinical utility, and ethical, legal, and social implications should be addressed on the basis of population screening. Here, the authors review population screening criteria, the current status of NBS, and recent advances in NGS. In addition, we discuss the practical and ethical issues, opportunities, and challenges regarding the implementation of NGS in NBS.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
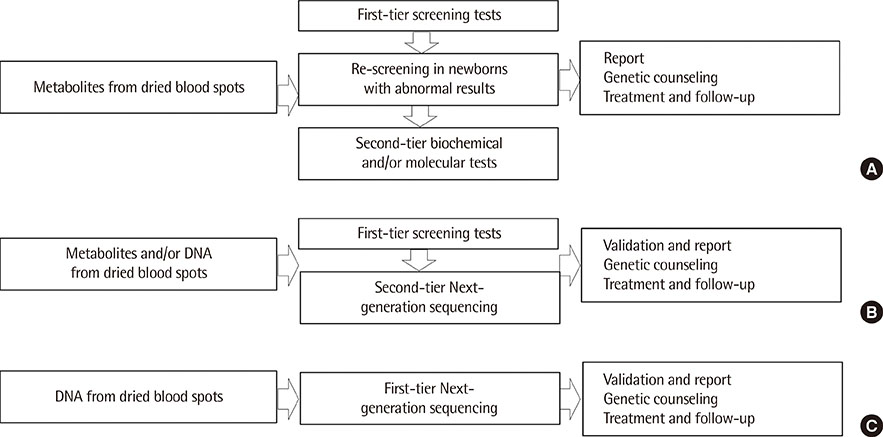
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A New Integrated Newborn Screening Workflow Can Provide a Shortcut to Differential Diagnosis and Confirmation of Inherited Metabolic Diseases
Jung Min Ko, Kyung Sun Park, Yeeok Kang, Seong-Hyeuk Nam, Yoonjung Kim, Inho Park, Hyun Wook Chae, Soon Min Lee, Kyung-A Lee, Jong-Won Kim
Yonsei Med J. 2018;59(5):652-661. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2018.59.5.652.
Reference
-
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Ten great public health achievements--United States, 2001-2010. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2011; 60:619–623.2. Guthrie R, Susi A. A simple phenylalanine method for detecting phenylketonuria in large populations of newborn infants. Pediatrics. 1963; 32:338–343.
Article3. Millington DS, Kodo N, Norwood DL, Roe CR. Tandem mass spectrometry: a new method for acylcarnitine profiling with potential for neonatal screening for inborn errors of metabolism. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1990; 13:321–324.
Article4. Lee DH. Neonatal screening for inborn errors of metabolism. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1987; 30:9–16.5. Lee DH. Neonatal screening test. J Korean Med Assoc. 1994; 37:1464–1480.6. Han YJ, Lee DH, Kim ES. Plans to improve the mass screening tests on inborn errors of metabolism in Korea. Seoul: Korean Public Health and Society Research Center in Department of Ministry of Health and Welfare in Korea;2000. p. 51–68.7. Lee DH, Choi TY, Jun BY, Kang JK, editors. The analysis of the current status and improvement of neonatal screening test for prevention of mental retardation. 2004. p. 1–167.8. Choi TY, editor. Analysis of blood sample records for neonatal screening test and external quality assessment for inborn errors of metabolism in Korea. Ministry of Health & Welfare, Planned Population Federation of Korea;2005.9. Yoon HR, Lee KR, Kang S, Lee DH, Yoo HW, Min WK, et al. Screening of newborns and high-risk group of children for inborn metabolic disorders using tandem mass spectrometry in South Korea: a three-year report. Clin Chim Acta. 2005; 354:167–180.
Article10. Pampols T. Inherited metabolic rare disease. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010; 686:397–431.
Article11. National Institutes of Health. NIH program explores the use of genomic sequencing in newborn healthcare. Updated on Sep 2013. http://www.nih.gov/news/health/sep2013/nhgri-04.htm.12. Wilson JM, Jungner YG. Principles and practice of mass screening for disease. Bol Oficina Sanit Panam. 1968; 65:281–393.13. Bredenoord AL, de Vries MC, van Delden JJ. Next-generation sequencing: does the next generation still have a right to an open future? Nat Rev Genet. 2013; 14:306.
Article14. Schulze A, Mayatepek E, Hoffmann GF. Evaluation of 6-year application of the enzymatic colorimetric phenylalanine assay in the setting of neonatal screening for phenylketonuria. Clin Chim Acta. 2002; 317:27–37.
Article15. Schulze A, Lindner M, Kohlmüller D, Olgemöller K, Mayatepek E, Hoffmann GF. Expanded newborn screening for inborn errors of metabolism by electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry: results, outcome, and implications. Pediatrics. 2003; 111:1399–1406.
Article16. Wilcken B, Wiley V, Hammond J, Carpenter K. Screening newborns for inborn errors of metabolism by tandem mass spectrometry. N Engl J Med. 2003; 348:2304–2312.
Article17. Mak CM, Lee HC, Chan AY, Lam CW. Inborn errors of metabolism and expanded newborn screening: review and update. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2013; 50:142–162.
Article18. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. FDA News Release: FDA allows marketing of four "next generation" gene sequencing devices. Updated on Nov 2013. http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm375742.htm.19. FDAnews Device Daily Bulletin. Thermo Fisher lists its ion PGM DX System as class II clinical medical device. http://www.fdanews.com/articles/167266-thermo-fisher-lists-its-ion-pgm-dx-system-as-class-ii-clinical-medical-device.20. Almond B. Genetic profiling of newborns: ethical and social issues. Nat Rev Genet. 2006; 7:67–71.
Article21. . Profiling the Newborn: a Prospective Gene Technology. UK: Human Genetic Commission;2005.22. Dehm SM. Test-firing ammunition for spliceosome inhibition in cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2013; 19:6064–6066.
Article23. van El CG, Cornel MC, Borry P, Hastings RJ, Fellmann F, Hodgson SV, et al. Whole-genome sequencing in health care: recommendations of the European Society of Human Genetics. Eur J Hum Genet. 2013; 21:580–584.24. Goldenberg AJ, Dodson DS, Davis MM, Tarini BA. Parents' interest in whole-genome sequencing of newborns. Genet Med. 2014; 16:78–84.
Article25. Bhattacharjee A, Sokolsky T, Wyman SK, Reese MG, Puffenberger E, Strauss K, et al. Development of DNA confirmatory and high-risk diagnostic testing for newborns using targeted next-generation DNA sequencing. Genet Med. 2015; 17:337–347.
Article26. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. ACCE model process for evaluating genetic tests. Updated on Jan 2010. http://www.cdc.gov/genomics/gtesting/ACCE/.27. Hollegaard MV, Grauholm J, Nielsen R, Grove J, Mandrup S, Hougaard DM. Archived neonatal dried blood spot samples can be used for accurate whole genome and exome-targeted next-generation sequencing. Mol Genet Metab. 2013; 110:65–72.
Article28. Holtzman NA. ACMG recommendations on incidental findings are flawed scientifically and ethically. Genet Med. 2013; 15:750–751.
Article29. ACMG Board of Directors. ACMG policy statement: updated recommendations regarding analysis and reporting of secondary findings in clinical genome-scale sequencing. Genet Med. 2015; 17:68–69.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Newborn Hearing Loss and Newborn Hearing Screening
- Short Term Follow-Up Result of Unilateral Hearing Loss Referred Patient by Newborn Hearing Screening
- Implementation of a Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing Panel for Constitutional Newborn Screening in High-Risk Neonates
- The prevalence of pediatric endocrine and metabolic diseases in Korea
- Current Status of and Perspectives on Cervical Cancer Screening in Korea