Infect Chemother.
2012 Aug;44(4):303-306. 10.3947/ic.2012.44.4.303.
A Case of Septic Arthritis of the Knee Joint due to Group D Non-typhoidal Salmonella
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Cheongju St. Mary's Hospital, Cheongju, Korea. evergreenlee@nate.com
- KMID: 2045551
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2012.44.4.303
Abstract
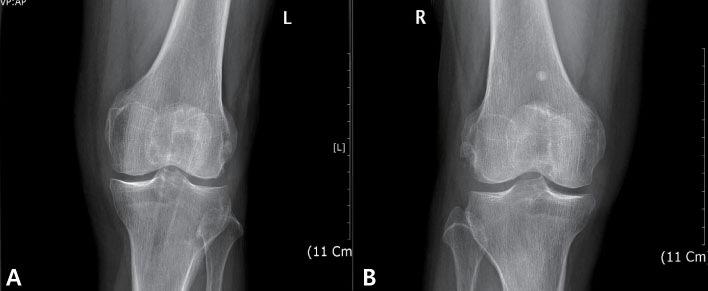
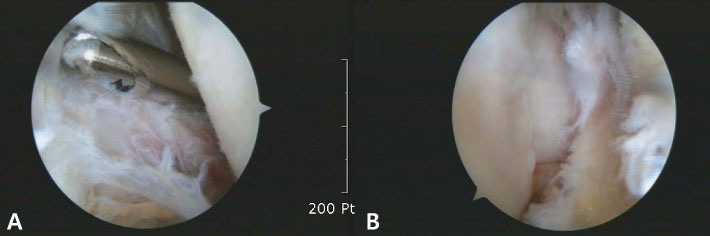
- Osteoarticular infections due to non-typhoidal Salmonella are rare, occurring with an incidence rate of 0.1-0.2%. An immunocompromised state and the existence of sickle cell anemia are known risk factors for development of septic arthritis due to Salmonella. In this report, we describe a patient with septic arthritis of the left knee caused by non-typhoidal Salmonella . An 82-year-old woman visited the emergency room presenting with left knee pain, fever and dyspnea. The patient had osteoarthritis and was treated with oral analgesics, but not with an intra-articular injection. Upon assessment of the patient's joint fluid and blood culture results, non-typhoidal Salmonella (Salmonella group D) was detected. Arthroscopy-guided irrigation and debridement, and administration of oral antibiotics (fluoroquinolone) over six weeks were required in order to achieve a full recovery from the infection.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Cervical Lymphadenitis Caused by Group D Non-typhoidal Salmonella Associated with Concomitant Lymphoma
Seungjin Lim, Sun Young Cho, Jungok Kim, Doo Ryeon Chung, Kyong Ran Peck, Jae-Hoon Song, Kyung Sun Park, Nam Yong Lee, Seok Jin Kim, Cheol-In Kang
Infect Chemother. 2013;45(2):234-238. doi: 10.3947/ic.2013.45.2.234.
Reference
-
1. Cohen JI, Bartlett JA, Corey GR. Extra-intestinal manifestations of salmonella infections. Medicine (Baltimore). 1987. 66:349–388.
Article2. Pegues DA, Miller SL. Mandell GL, Bennett JE, Dolin R, editors. Salmonella species, including Salmonella typhi. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 2009. 7th ed. Philadelphia: Churchill Livingstone;2887–2904.3. Kim KH, Lee HS, Lee HC, Koh KS, Kim HJ, Chun RW, Chung MH, Nho JW, Koh YP, Song CM, Chung YG. A case of pyogenic arthritis of hip joint caused by salmonella typhi. Korean J Med. 1997. 53:Suppl 3. S797–S800.4. Kim KY, Suh HJ. A case of arthritis of knee joint caused by salmonella typhi. Korean J Infect Dis. 1991. 23:45–49.5. Ko KS, Suh HJ. A case of arthritis of hip joint caused by salmonella typhi. Korean J Infect Dis. 1992. 24:71–75.6. Cho YJ, Yoo MC, Kim KI, Chun YS, Soh JH. Septic Arthritis of Hip Joint Caused by Salmonellosis. Kyung Hee Univ Med J. 1998. 14:365–370.7. Cho YJ, Suh CH, Kim JS, Lee DH, Song J, Lee WK, Park YB, Lee CH, Lee JS, Lee SK. A case of septic arthritis caused by salmonella group D in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 1999. 6:69–74.8. Fernández Guerrero ML, Ramos JM, Núñez A, Núñez A, de Górgolas M. Focal infections due to non-typhi Salmonella in patients with AIDS: report of 10 cases and review. Clin Infect Dis. 1997. 25:690–697.
Article9. Hernigou P, Daltro G, Flouzat-Lachaniette CH, Roussignol X, Poignard A. Septic arthritis in adults with sickle cell disease often is associated with osteomyelitis or osteonecrosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010. 468:1676–1681.
Article10. Muñoz-Mahamud E, Casanova L, Font L, Fernández-Valencia JA, Bori G. Septic arthritis of the hip caused by nontyphi Salmonella after urinary tract infection. Am J Emerg Med. 2009. 27:373.e5–373.e8.
Article11. Govender S, Chotai PR. Salmonella osteitis and septic arthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1990. 72:504–506.
Article12. Chang SP, Lee SH, Kim KY, Suh HJ. Changing patterns of salmonella infection & changes in antimicrobial resistance of salmonella strains isolated in 1987-1995. Korean J Med. 1998. 54:7–16.13. Ha BH, Kim YO, Min JK, Choi JY, Lee SK, Yoon SA, Bahk WJ, Lee HK, Chun KA. Salmonella osteomyelitis with osteonecrosis in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. Korean J Med. 2000. 58:112–116.14. Hwang BY, Kim YH, Rho YH, Lee YH, Ji JD, Song GG. A case of thyroid abscess caused by salmonella group D in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 2003. 10:442–445.15. Yoon HK, Cho DY, Han SH, Kim JH, Kim JR. Salmonella pyomyositis in a multiple myeloma patient: a case report. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2006. 41:156–159.
Article16. Kim JM, Park YH, Kim D, Park MJ, Ahn HJ, Ryoo BY, Yang SH. Salmonella vertebral osteomyelitis with sepsis in healthy adult. Korean J Med. 2005. 69:Suppl 3. S1003–S1008.17. Kim YS, Yang JW, Park SY, Song SH, Yu JM, Choi SO, Han BG. A case of rhabdomyolysis and acute renal failure associated with salmonella enteritidis. Korean J Nephrol. 2010. 29:509–512.18. Cho CS, Kim CS, Lee JC. Splenic abscess caused by salmonella group B. J Korean Surg Soc. 1994. 46:904–907.19. Chae SY, Liu SY, Kim KY, Lim BU, Hur BW, Kim HK, Kim HJ. A case of ruptured infected aneurysm of abdominal aorta caused by septic salmonellosis. Korean J Med. 2003. 65:Suppl 3. S747–S751.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Septic Arthritis Caused by Salmonella Group D in a Patient with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- A case of arthritis of Knee joint caused by salmonella typhi
- A Case of Septic Knee Arthritis Caused by Salmonella Enteritidis
- Septic Knee Arthritis Caused by Group B Salmonella Species in a Patient with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- Outbreak of Non-typhoidal Salmonellosis in Neonates