Korean J Obstet Gynecol.
2011 Feb;54(2):107-110. 10.5468/KJOG.2011.54.2.107.
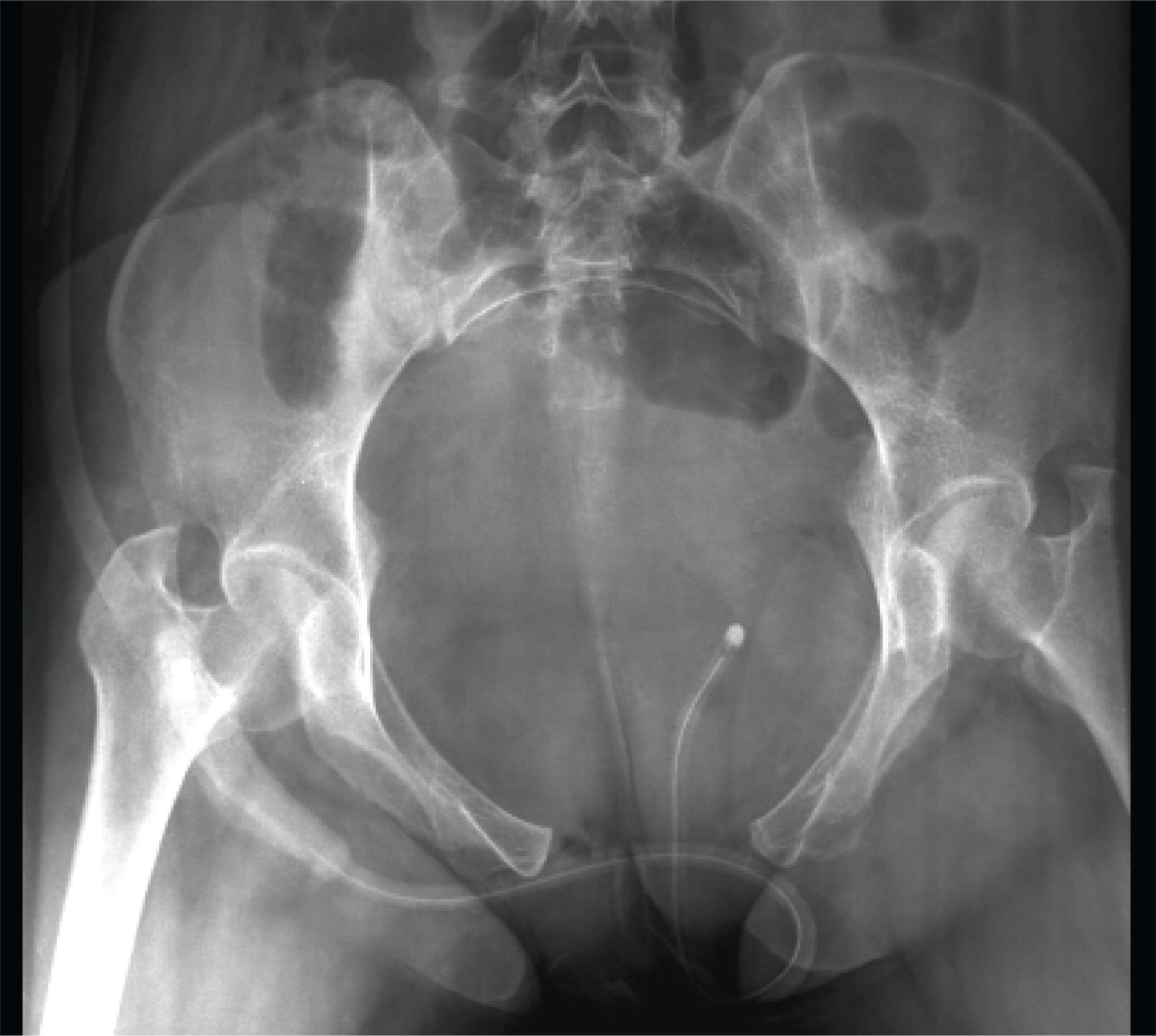
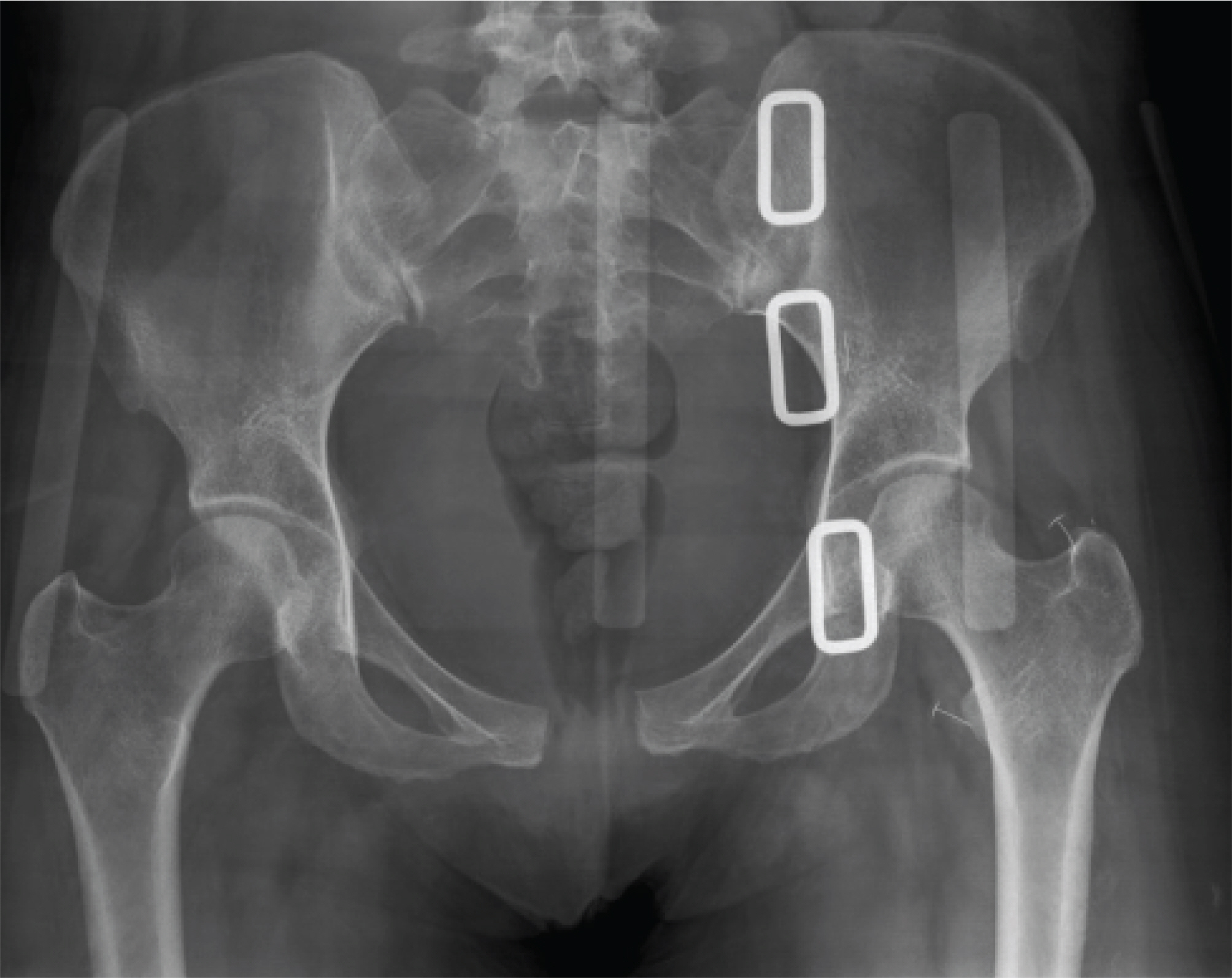
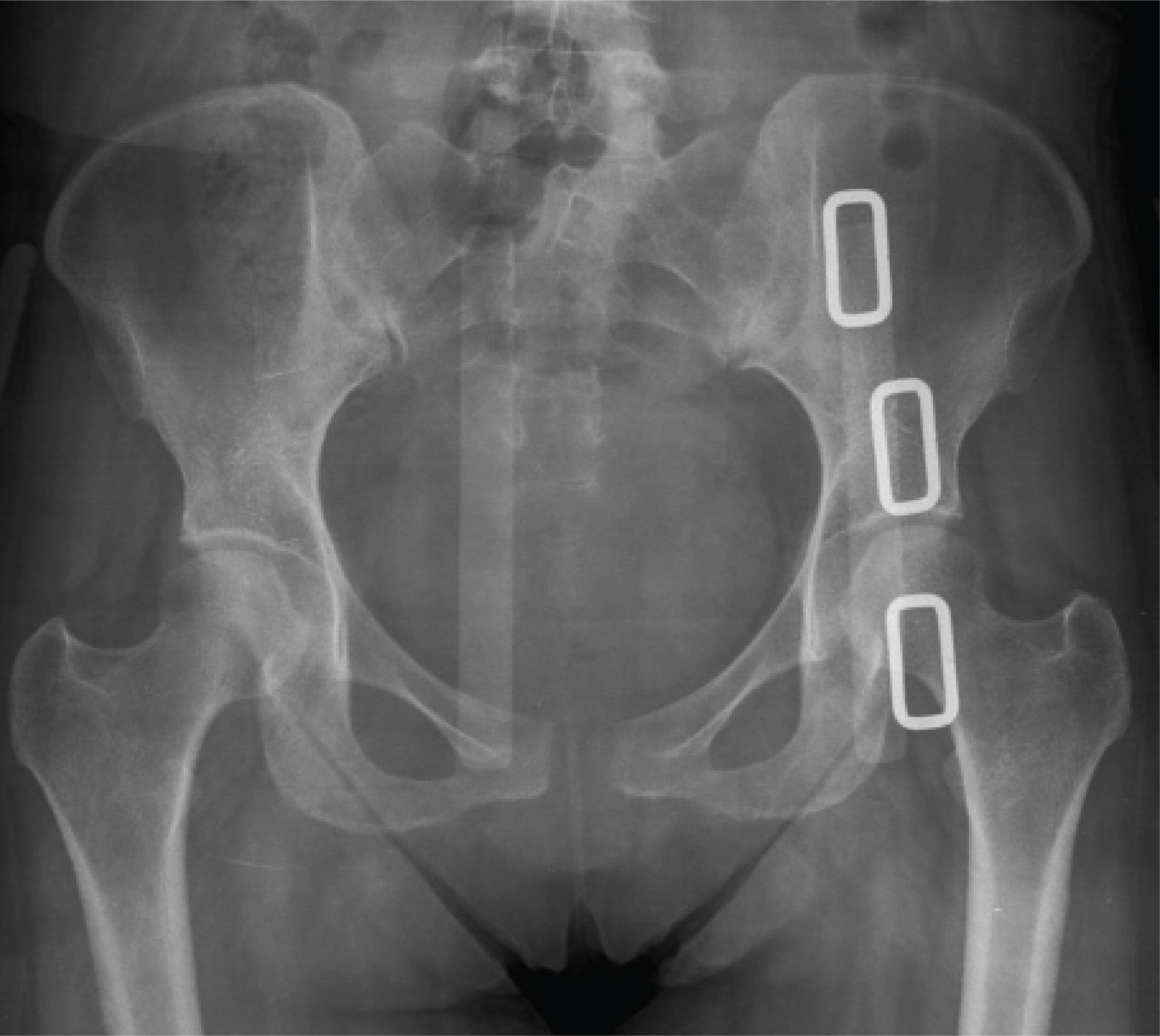
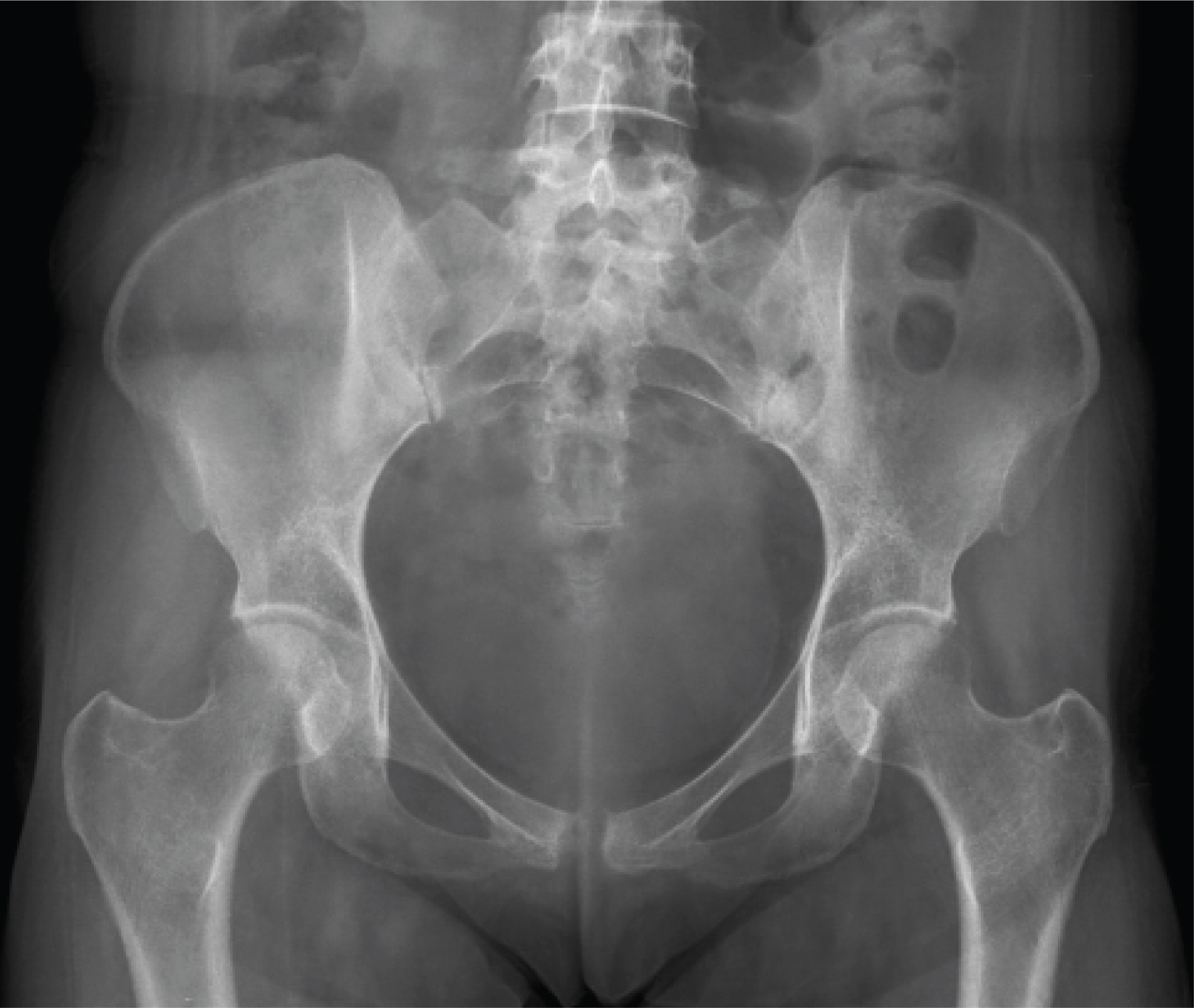
A 80 mm separation of the symphsis pubis during vaginal delivery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, National Health Insurance Corporation Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea. raksumi10@gmail.com
- 2Department of Orthopedics, National Health Insurance Corporation Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- KMID: 2037500
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5468/KJOG.2011.54.2.107
Abstract
- Separation of the symphysis pubis during the vaginal delivery is rare, but a serious complication. Treatment is generally conservative with rest and appropriately fi tted pelvic binder. But surgery may be necessary when symphyseal separation is more than 40 mm. A case of 80 mm separation of symphysis pubis developed after vaginal delivery is presented with review of the literature.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Wurdinger S, Humbsch K, Reichenbach JR, Peiker G, Seewald HJ, Kaiser WA. MRI of the pelvic ring joints postpartum: normal and pathological findings. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2002; 15:324–9.
Article2. Snow RE, Neubert AG. Peripartum pubic symphysis separation: a case series and review of the literature. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 1997; 52:438–43.3. Brehm W, Weirauk HV. Separation of the symphysis pubis during labor. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1928; 15:187–91.
Article4. Taylor RN, Sonson RD. Separation of the pubic symphysis. An underrecognized peripartum complication. J Reprod Med. 1986; 31:203–6.5. Reis RA, Baer JL, Arens RA, Stewart E. Traumatic separation of the symphysis pubis during spontaneous labor. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1932; 55:336–54.6. Cunningham FG, Leveno KJ, Bloom SL, Hauth JC, Rouse DJ, Spong CY. Williams obstetrics. 23rd ed.New York: McGraw-Hill Medical;2010.7. Bahlmann F, Merz E, Macchiella D, Weber G. Ultrasound imaging of the symphysis fissure for evaluating damage to the symphysis in pregnancy and postpartum. Z Geburtshilfe Perinatol. 1993; 197:27–30.8. Heyman J, Lundqvist A. The symphysis pubis in pregnancy and parturition. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 1932; 12:191–226.9. Dhar S, Anderton JM. Rupture of the symphysis pubis during labor. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992; 283:252–7.
Article10. Kharrazi FD, Rodgers WB, Kennedy JG, Lhowe DW. Parturition-induced pelvic dislocation: a report of four cases. J Orthop Trauma. 1997; 11:277–81.
Article11. Cappiello GA, Oliver BC. Rupture of symphysis pubis caused by forceful and excessive abduction of the thighs with labor epidural anesthesia. J Fla Med Assoc. 1995; 82:261–3.12. Heath T, Gherman RB. Symphyseal separation, sacroiliac joint dislocation and transient lateral femoral cutaneous neuropathy associated with McRoberts’ maneuver: a case report. J Reprod Med. 1999; 44:902–4.13. Musumeci R, Villa E. Symphysis pubis separation during vaginal delivery with epidural anesthesia: case report. Reg Anesth. 1994; 19:289–91.14. Hagen R. Pelvic girdle relaxation from an orthopaedic point of view. Acta Orthop Scand. 1974; 45:550–63.
Article15. Culligan P, Hill S, Heit M. Rupture of the symphysis pubis during vaginal delivery followed by two subsequent uneventful pregnancies. Obstet Gynecol. 2002; 100:1114–7.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Three Cases of Separation of Symphysis Pubis during Vaginal Delivery
- Three Cases of Separation of Symphysis Pubis During Vaginal Delivery
- A Case of Separation of the Symphysis Pubis in Association with Delivery
- Diastasis of the Symphysis Pubis During Vaginal Delivery
- Radiographic Appearance of the Symphysis Pubis: Criteria of Diastasis of Symphysis Pubis after Normal Delivery