J Periodontal Implant Sci.
2014 Oct;44(5):216-221. 10.5051/jpis.2014.44.5.216.
Comparison of autogenous tooth bone graft and synthetic bone graft materials used for bone resorption around implants after crestal approach sinus lifting: a retrospective study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery, Section of Dentistry, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 2Department of Periodontology, Seoul National University School of Dentistry, Seoul, Korea. junholeedds@gmail.com
- 3Department of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery, Seoul National University School of Dentistry, Seoul, Korea.
- 4R&D Institute, Korea Tooth Bank, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2027818
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2014.44.5.216
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This retrospective study compares the amount of bone resorption around implants between an autogenous tooth bone graft (AutoBT) and a synthetic bone graft after a bone-added crestally approached sinus lift with simultaneous implant placements.
METHODS
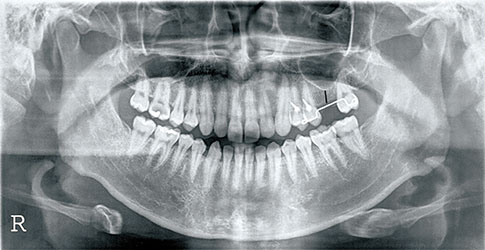
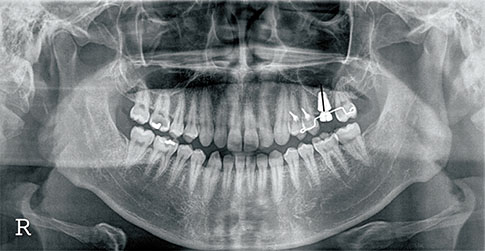
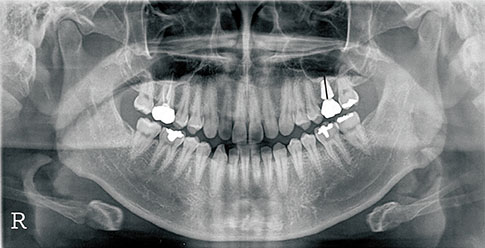
In all, 37 patients participated in this study. Seventeen patients were grouped as group I and underwent an AutoBT-added sinus lift using the crestal approach. The remaining 20 patients were grouped as group II and underwent synthetic bone grafting. Both groups received the implant placements simultaneously. Of the 37 participating patients, only 22 patients were included in the final results: Eleven patients of group I and 11 patients of group II. Before the surgery, the distance from the alveolar crest to the sinus floor was measured using panoramic radiography. After the surgery, the distance was measured again from the neck of the implant thread to the most superior border of the added graft materials. Then, the amount of sinus lift was calculated by comparing the two panoramic radiographs. After a year, a panoramic radiograph was taken to calculate the resorption of the bone graft material from the radiograph that was taken after the surgery. The significance of the resorption amount between the two types of graft materials was statistically analyzed.
RESULTS
The bone height was increased to an average of 4.89 mm in group I and 6.22 mm in group II. The analysis of panoramic radiographs 1 year after the surgery showed an average bone resorption of 0.76 mm and 0.53 mm, respectively. However, the degree of lifting (P=0.460) and the amount of bone-grafted material resorption (P=0.570) showed no statistically significant difference.
CONCLUSIONS
Based on this limited study, AutoBT can be considered a good alternative bone graft to a synthetic bone graft in a bone-added sinus lift, when extraction is necessary prior to the surgery.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Comparison of immunohistochemical analysis on sinus augmentation using demineralized tooth graft and bovine bone
Dong-Seok Sohn, Ji-Rak Kim, Hyung-Gyun Kim, Hyun-Suk Choi, Yong-Suk Moon
J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2021;47(4):269-278. doi: 10.5125/jkaoms.2021.47.4.269.Autogenous tooth bone graft block for sinus augmentation with simultaneous implant installation: a technical note
Kwang-Ho Lee, Young-Kyun Kim, Woo-Jin Cho, In-Woong Um, Masaru Murata, Masaharu Mitsugi
J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2015;41(5):284-289. doi: 10.5125/jkaoms.2015.41.5.284.
Reference
-
1. Jaffin RA, Berman CL. The excessive loss of Branemark fixtures in type IV bone: a 5-year analysis. J Periodontol. 1991; 62:2–4.
Article2. Buchmann R, Khoury F, Faust C, Lange DE. Peri-implant conditions in periodontally compromised patients following maxillary sinus augmentation: a long-term post-therapy trial. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1999; 10:103–110.
Article3. Raghoebar GM, Timmenga NM, Reintsema H, Stegenga B, Vissink A. Maxillary bone grafting for insertion of endosseous implants: results after 12-124 months. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2001; 12:279–286.
Article4. Kim SM, Park JW, Suh JY, Sohn DS, Lee JM. Bone-added osteotome technique versus lateral approach for sinus floor elevation: a comparative radiographic study. Implant Dent. 2011; 20:465–470.
Article5. Summers RB. A new concept in maxillary implant surgery: the osteotome technique. Compendium. 1994; 15:152154–156. 158 passim.6. Zitzmann NU, Scharer P. Sinus elevation procedures in the resorbed posterior maxilla. Comparison of the crestal and lateral approaches. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1998; 85:8–17.7. Kim YK, Kim SG, Byeon JH, Lee HJ, Um IU, Lim SC, et al. Development of a novel bone grafting material using autogenous teeth. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2010; 109:496–503.
Article8. Block MS, Kent JN. Sinus augmentation for dental implants: the use of autogenous bone. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1997; 55:1281–1286.
Article9. Kim YK, Kim SG, Yun PY, Yeo IS, Jin SC, Oh JS, et al. Autogenous teeth used for bone grafting: a comparison with traditional grafting materials. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2014; 117:e39–e45.
Article10. Bessho K, Tagawa T, Murata M. Purification of rabbit bone morphogenetic protein derived from bone, dentin, and wound tissue after tooth extraction. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1990; 48:162–169.
Article11. Urist MR, Nakata N, Felser JM, Nogami H, Hanamura H, Miki T, et al. An osteosarcoma cell and matrix retained morphogen for normal bone formation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1977; (124):251–266.
Article12. Urist MR, Mikulski A, Boyd SD. A chemosterilized antigen-extracted autodigested alloimplant for bone banks. Arch Surg. 1975; 110:416–428.
Article13. Yeomans JD, Urist MR. Bone induction by decalcified dentine implanted into oral, osseous and muscle tissues. Arch Oral Biol. 1967; 12:999–1008.
Article14. Ritchie HH, Ritchie DG, Wang LH. Six decades of dentinogenesis research. Historical and prospective views on phosphophoryn and dentin sialoprotein. Eur J Oral Sci. 1998; 106:Suppl 1. 211–220.15. Kim YK, Kim SG, Oh JS, Jin SC, Son JS, Kim SY, et al. Analysis of the inorganic component of autogenous tooth bone graft material. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2011; 11:7442–7445.
Article16. Kim YK, Yun PY, Lim SC, Kim SG, Lee HJ, Ong JL. Clinical evaluations of OSTEON as a new alloplastic material in sinus bone grafting and its effect on bone healing. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2008; 86:270–277.
Article17. Bae JH, Kim YK, Kim SG, Yun PY, Kim JS. Sinus bone graft using new alloplastic bone graft material (Osteon)-II: clinical evaluation. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2010; 109:e14–e20.
Article18. Kim YK. Development of autogenous teeth bone graft material and clinical evaluation. J Korean Dent Assoc. 2011; 49:159–169.19. Kim GW, Yeo IS, Kim SG, Um IW, Kim YK. Analysis of crystalline structure of autogenous tooth bone graft material: X-Ray diffraction analysis. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011; 37:225–228.
Article20. Kim YK, Lee HJ, Kim KW, Kim SG, Um IW. Guide bone regeneration using autogenous teeth: case reports. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011; 37:142–147.
Article21. Zins JE, Whitaker LA. Membranous versus endochondral bone: implications for craniofacial reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1983; 72:778–785.22. Lee JY, Kim YK, Bae JH, Kim SG. Clinical study of sinus membrane elevation using minimally invasive crestal approach. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Implantol. 2008; 12:4–16.23. Kim YK, Yun PY, Kim SG, Kim BS, Ong JL. Evaluation of sinus bone resorption and marginal bone loss after sinus bone grafting and implant placement. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2009; 107:e21–e28.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Study on the Efficacy of the Autogenous Tooth Bone Graft Material (AutoBT)
- Maxillary Sinus Augmentation Using Autogenous Teeth: Preliminary Report
- Familial tooth bone graft for ridge and sinus augmentation: a report of two cases
- Ridge Augmentation Using Block Type of Autogenous Tooth Bone Graft Material in Severe Alveolar Bone Resorption of Single Tooth: Case Report
- Resorption of bone graft after maxillary sinus grafting and simultaneous implant placement