J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2014 Oct;56(4):364-367. 10.3340/jkns.2014.56.4.364.
Endovascular Rescue Method for Undesirably Stretched Coil
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Daegu Catholic University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. fhjhcho@gmail.com
- KMID: 2018092
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2014.56.4.364
Abstract
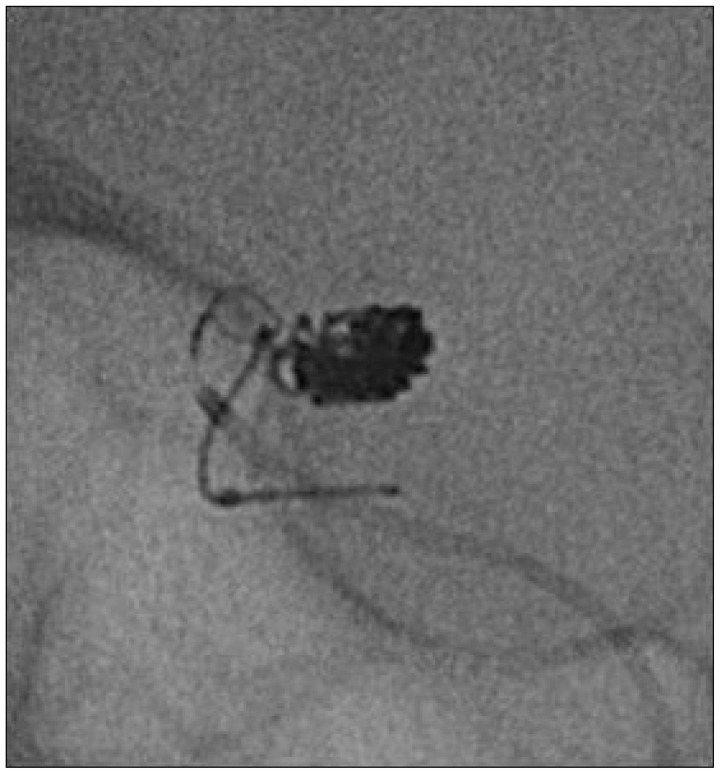
- Undesirable detachment or stretching of coils within the parent artery during aneurysm embolization can be related with thrombus formation, which can be caused occlusion of parent artery or embolic event(s). To escape from this situation, several rescue methods have been reported. A case with undesirably stretched coil in which another rescue method was used, is presented. When the stretched coil is still located in the coil delivery microcatheter, the stretched coil can be removed safely using a snare and a handmade monorail microcatheter. After a snare is lodged in the handmade monorail microcatheter, the snare is introduced over the coil delivery micorcatheter and located in the distal part of the stretched coil. After then, the handmade monorail microcatheter captures the stretched coil and the snare as one unit. This technique using a handmade monorail microcatheter and a snare can be a good rescue modality for the undesirably stretched coil, still remained within the coil delivery microcatheter.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Fiorella D, Albuquerque FC, Deshmukh VR, McDougall CG. Monorail snare technique for the recovery of stretched platinum coils : technical case report. Neurosurgery. 2005; 57(1 Suppl):E210. discussion E210. PMID: 15987594.2. Guglielmi G, Viñuela F, Dion J, Duckwiler G. Electrothrombosis of saccular aneurysms via endovascular approach. Part 2 : Preliminary clinical experience. J Neurosurg. 1991; 75:8–14. PMID: 2045924.3. Guglielmi G, Viñuela F, Sepetka I, Macellari V. Electrothrombosis of saccular aneurysms via endovascular approach. Part 1 : electrochemical basis, technique, and experimental results. J Neurosurg. 1991; 75:1–7. PMID: 2045891.4. Kelly ME, Turner R 4th, Gonugunta V, Rasmussen PA, Woo HH, Fiorella D. Monorail snare technique for the retrieval of an adherent microcatheter from an onyx cast : technical case report. Neurosurgery. 2008; 63(1 Suppl 1):ONSE89. discussion ONSE89. PMID: 18728613.5. Lee CY. Use of wire as a snare for endovascular retrieval of displaced or stretched coils : rescue from a technical complication. Neuroradiology. 2011; 53:31–35. PMID: 20352417.
Article6. Standard SC, Chavis TD, Wakhloo AK, Ahuja A, Guterman LR, Hopkins LN. Retrieval of a Guglielmi detachable coil after unraveling and fracture : case report and experimental results. Neurosurgery. 1994; 35:994–998. discussion 999. PMID: 7838356.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Rescue Therapy of Inadvertent Coil Migration for Endovascular Treatment of Type II Endoleak
- Rescue Balloon Reposition of the Protruding Coil Loops during Endovascular Treatment of An Anterior Communicating Artery Aneurysm: A Case Report
- Migrated coil and damaged stent removal during coil embolization, using an additional, retrievable stent: A case report
- A Complicated Case of Endovascular Stent Assisted Coil Embolization of an Aneurysm
- Recent Trends in the Treatment of Cerebral Aneurysms: Comparison between Endovascular Coil Embolization and Surgical Clipping