J Korean Fract Soc.
2008 Jul;21(3):200-206. 10.12671/jkfs.2008.21.3.200.
The Treatment of IM Nailing of Femoral Shaft Fracture: Piriformis Fossa versus Trochanteric Entry Portal
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Yeungnam University Medical Center, Daegu, Korea. ossoj@med.yu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2015442
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2008.21.3.200
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: To compare the results of IM nailing of femur shaft fractures using trochanteric and piriformis fossa entry portal.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
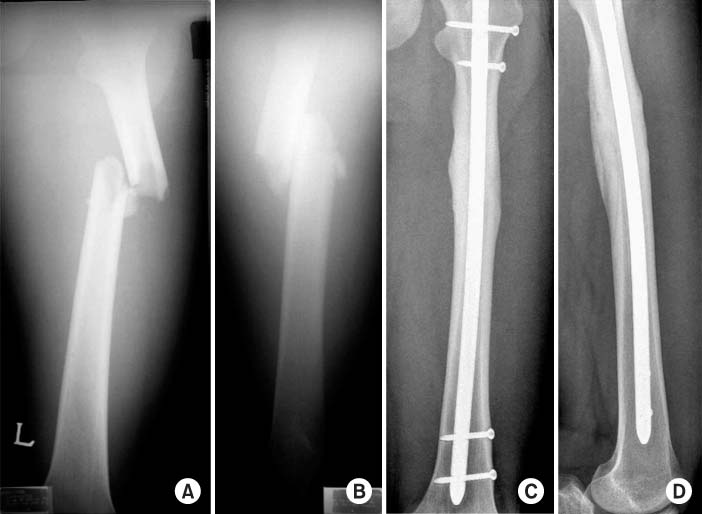
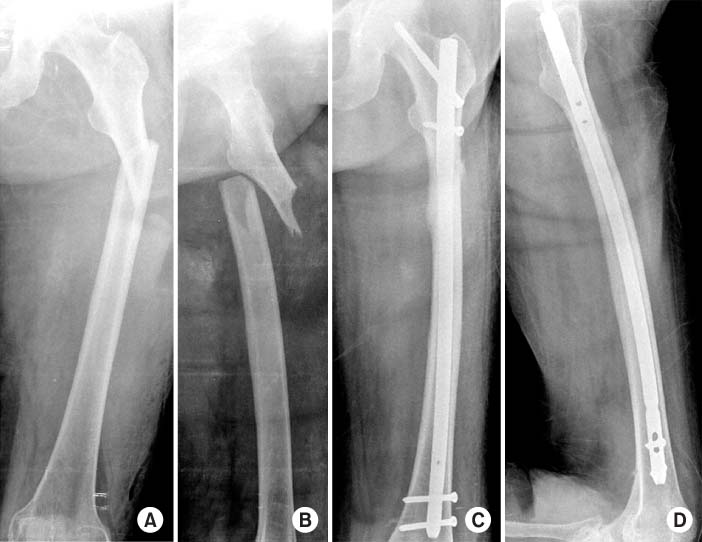
37 patients were treated with IM nail using Trochanteric (Trochanter group: TG, n=17) and piriformis fossa entry portal (piriformis group: PG, n=20) and were followed from February 2004 to 2007. The outcomes were assessed based on the clinical and radiographic findings.
RESULTS
The functional result, ROM and union time were similar in both groups. The alignment was similar in both groups but PG showed variable alignment in proximal 1/3. Incision was larger in PG (PG=8.7 cm, TG=5.8 cm, p<0.05) and there was a difference between overweight and normal weight group. Operative time was 95 minutes in PG, 87 minutes in TG (p>0.05), there was statistically significant difference in overweight groups (PG=125 minutes, TG=90 minutes, p<0.05). Blood loss was 313 cc in PG, 268 cc in TG and less in TG in overweight patients (p<0.05). There was 5.7degrees of varus angulation in PG, 2 nonunion cases in both groups.
CONCLUSION
The femoral nail specially designed for trochanteric insertion resulted in high union rates, low complication rates similar to conventional nail and the trochanteric nail can be the alternative choice especially in proximal femur fracture and overweight patients.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bick EM. The intramedullary nailing of fractures by G. Küntscher. Translation of article in Archiv für Klinische Chirurgie, 200: 443, 1940. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1968; 60:5–12.2. Böhler L. Medullary nailing of Küntscher. 1st English ed. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins Co;1948.3. Browner B, Wiss DA. The Grosse-Kempf locking nail for the femur. In : Browner B, Edwards C, editors. The science and practice of intramedullary nailing. 1st ed. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger;1987. p. 150–159.4. Gausepohl T, Pennig D, Koebke J, Harnoss S. Antegrade femoral nailing: an anatomical determination of the correct entry point. Injury. 2002; 33:701–705.
Article5. Harper MC, Carson WL. Curvature of the femur and the proximal entry point for an intramedullary rod. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1987; 220:155–161.
Article6. Johnson EE. Letters to the editor. J Orthop Trauma. 2001; 15:533–534.
Article7. Johnson KD, Tencer AF, Sherman MC. Biomechanical factors affecting fracture stability and femoral bursting in closed intramedullary nailing of femoral shaft fractures, with illustrative case presentations. J Orthop Trauma. 1987; 1:1–11.
Article8. Kempf I, Grosse A, Beck G. Closed locked intramedullary nailing. Its application to comminuted fractures of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1985; 67:709–720.
Article9. Kim SD, Sohn OJ, Kwack BH. The comparison of LC-DCP versus LCP fixation in the plate augmentation for the nonunion of femur shaft fractures after intramedullary nail fixation. J Korean Fract Soc. 2008; 21:117–123.
Article10. Klemm K, Schellmann WD. Dynamic and static locking of the intramedullary nail. Monatsschr Unfallheilkd Versicher Versorg Verkehrsmed. 1972; 75:568–575.11. Küntscher G. Die makknaelunguon knochen brchen. Langenbecks Archive Klin Chir. 1940; 200:443–455.12. Küntscher G. Herman H. Rinne . Practice of intramedullary nailing. 1st ed. Springfield: Charles C Thomas;1967. With a foreword by Hugh Smith.13. McKee MD, Waddell JP. Intramedullary nailing of femoral fractures in morbidly obese patients. J Trauma. 1994; 36:208–210.
Article14. Moein CM, Verhofstad MH, Bleys RL, van der Werken C. Soft tissue injury related to choice of entry point in antegrade femoral nailing: piriform fossa or greater trochanter tip. Injury. 2005; 36:1337–1342.
Article15. Oh CW, Oh JK, Min WK, et al. Comparison of operative methods between retrograde and antegrade nailing for ipsilateral femoral shaft and neck fracture. J Korean Fract Soc. 2007; 20:135–140.
Article16. Ostrum RF. A greater trochanteric insertion site for femoral intramedullary nailing in lipomatous patients. Orthopedics. 1996; 19:337–340.
Article17. Ostrum RF, Marcantonio A, Marburger R. A critical analysis of the eccentric starting point for trochanteric intramedullary femoral nailing. J Orthop Trauma. 2005; 19:681–686.
Article18. Ricci WM, Devinney S, Haidukewych G, Herscovici D, Sanders R. Trochanteric nail insertion for the treatment of femoral shaft fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2005; 19:511–517.
Article19. Ricci WM, Schwappach J, Tucker M, et al. Trochanteric versus piriformis entry portal for the treatment of femoral shaft fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2006; 20:663–667.
Article20. Robinson CM, Houshian S, Khan LA. Trochanteric-entry long cephalomedullary nailing of subtrochanteric fractures caused by low-energy trauma. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005; 87:2217–2226.
Article21. Starr AJ, Hay MT, Reinert CM, Borer DS, Christensen KC. Cephalomedullary nails in the treatment of high-energy proximal femur fractures in young patients: a prospective, randomized comparison of trochanteric versus piriformis fossa entry portal. J Orthop Trauma. 2006; 20:240–246.
Article22. Tucker MC, Schwappach JR, Leighton RK, Coupe K, Ricci WM. Results of femoral intramedullary nailing in patients who are obese versus who are not obese: a prospective multicenter comparison study. J Orthop Trauma. 2007; 21:523–529.23. Veith RG, Hansen STJ, Winquist RA. Closed Kuntscher nailing of femoral fractures. In : Browner B, Edwards C, editors. The science and practive of intramedullary nailing. 2nd ed. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins;1996. p. 141–160.24. Winquist RA, Hansen ST Jr, Clawson DK. Closed intramedullary nailing of femoral fractures. A report of five hundred and twenty cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1984; 66:529–539.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Results of Intramedullary Nailing of Femoral Shaft Fracture: Trochanteric Entry Portal (Sirus Nail) versus Piriformis Entry Portal (M/DN Nail)
- Comparison of Greater Trochanter Versus Piriformis Entry Nail for Treatment of Femur Shaft Fracture
- Percutaneous Interlocking Intramedullary Nailing of Femoral Shaft Fracture with Retrograde Guide Wire Insertion Technique
- Subtrochanteric Femoral Fracture during Trochanteric Nailing for the Treatment of Femoral Shaft Fracture
- Interlocking Intramedullary Nailing Versus conventional Kuntscher Intramedullary Nailing for Fracture of the Femoral Shaft