J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2014 Oct;40(5):246-249. 10.5125/jkaoms.2014.40.5.246.
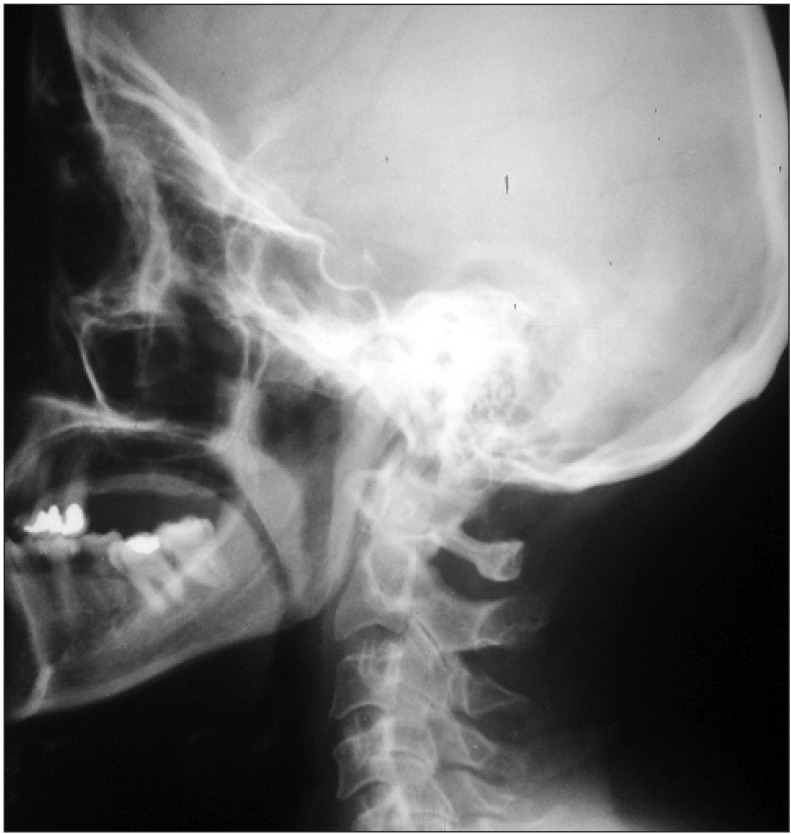
Nonsurgical treatment of stylohyoid (Eagle) syndrome: a case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Management, Amir Alam Hospital, Tehran University of Medical Science, Tehran, Iran. taheria@sina.tums.ac.ir
- KMID: 2005455
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2014.40.5.246
Abstract
- Eagle syndrome is a rare condition caused by elongation of the styloid process or calcification of the stylohyoid ligament. Patients with Eagle syndrome typically present with dysphagia, dysphonia, cough, voice changes, otalgia, sore throat, facial pain, foreign body sensation, headache, vertigo, and neck pain. Here we report a case in which the patient initially presented with sore throat, left-sided facial pain, and cough. This case report provides a brief review of the diagnosis and nonsurgical management of this rare syndrome.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Balbuena L Jr, Hayes D, Ramirez SG, Johnson R. Eagle's syndrome (elongated styloid process). South Med J. 1997; 90:331–334. PMID: 9076308.
Article2. Eagle WW. Elongated styloid processes: report of two cases. Arch Otolaryngol. 1937; 25:584–587.
Article3. Murtagh RD, Caracciolo JT, Fernandez G. CT findings associated with Eagle syndrome. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001; 22:1401–1402. PMID: 11498437.4. Soldati AB, Miguelote C, Quero C, Pereira R, Santos R, Soares C. Eagle's syndrome. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2013; 71:265–266. PMID: 23588292.
Article5. More CB, Asrani MK. Evaluation of the styloid process on digital panoramic radiographs. Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2010; 20:261–265. PMID: 21423900.
Article6. Phulambrikar T, Rajeshwari A, Rao BB, Warhekar A, Reddy P. Incidence of elongated styloid process: a radiographic study. J Indian Acad Oral Med Radiol. 2011; 23:S344–S346.
Article7. Bagga MB, Kumar CA, Yeluri G. Clinicoradiologic evaluation of styloid process calcification. Imaging Sci Dent. 2012; 42:155–161. PMID: 23071965.
Article8. de Andrade KM, Rodrigues CA, Watanabe PC, Mazzetto MO. Styloid process elongation and calcification in subjects with tmd: clinical and radiographic aspects. Braz Dent J. 2012; 23:443–450. PMID: 23207864.9. Ilgüy M, Ilgüy D, Güler N, Bayirli G. Incidence of the type and calcification patterns in patients with elongated styloid process. J Int Med Res. 2005; 33:96–102. PMID: 15651721.
Article10. Moon CS, Lee BS, Kwon YD, Choi BJ, Lee JW, Lee HW, et al. Eagle's syndrome: a case report. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014; 40:43–47. PMID: 24627843.
Article11. Gorlin RJ, Cohen MM, Levin LS. Syndromes of the head and neck. New York: Oxford University Press;1990.12. Goaz PW, White SC. Oral radiology: principles and interpretation. St. Louis, Missouri: Mosby;1994.13. Casale M, Rinaldi V, Quattrocchi C, Bressi F, Vincenzi B, Santini D, et al. Atypical chronic head and neck pain: don't forget Eagle's syndrome. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2008; 12:131–133. PMID: 18575165.14. Gelabert-González M, García-Allut A. Eagle syndrome. An unusual cause of neck pain. Neurocirugia(Astur). 2008; 19:254–256. PMID: 18654725.15. Chi J, Harkness M. Elongated stylohyoid process: a report of three cases. N Z Dent J. 1999; 95:11–13. PMID: 10208079.16. Nishihara K, Hanakita J, Kinuta Y, Kondo A, Yamamoto Y, Kishimoto S. Three cases of Eagle's syndrome. No Shinkei Geka. 1986; 14(3 Suppl):441–445. PMID: 3703148.17. Eversole LR. Clinical outline of oral pathology: diagnosis and treatment. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Lea and Febiger;1978.18. Prasad KC, Kamath MP, Reddy KJ, Raju K, Agarwal S. Elongated styloid process (Eagle's syndrome): a clinical study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2002; 60:171–175. PMID: 11815916.
Article19. Mortellaro C, Biancucci P, Picciolo G, Vercellino V. Eagle's syndrome: importance of a corrected diagnosis and adequate surgical treatment. J Craniofac Surg. 2002; 13:755–758. PMID: 12457088.
Article20. Han MK, Kim DW, Yang JY. Non surgical treatment of Eagle's syndrome: a case report. Korean J Pain. 2013; 26:169–172. PMID: 23614080.