J Korean Surg Soc.
2009 Sep;77(3):153-160. 10.4174/jkss.2009.77.3.153.
Surgical Treatment for Idiopathic Granulomatous Mastitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Bucheon, Korea. cwlim@schbc.ac.kr
- KMID: 2004213
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2009.77.3.153
Abstract
- PURPOSE
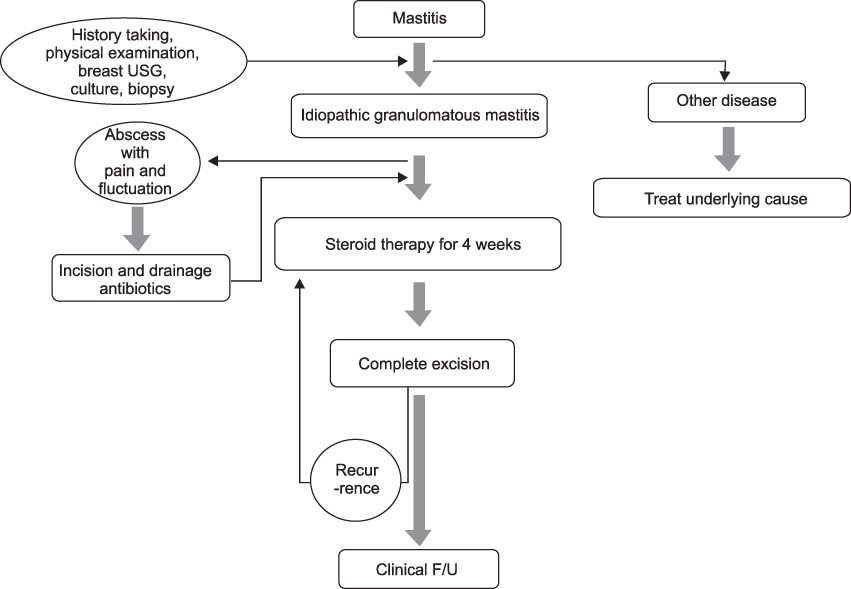
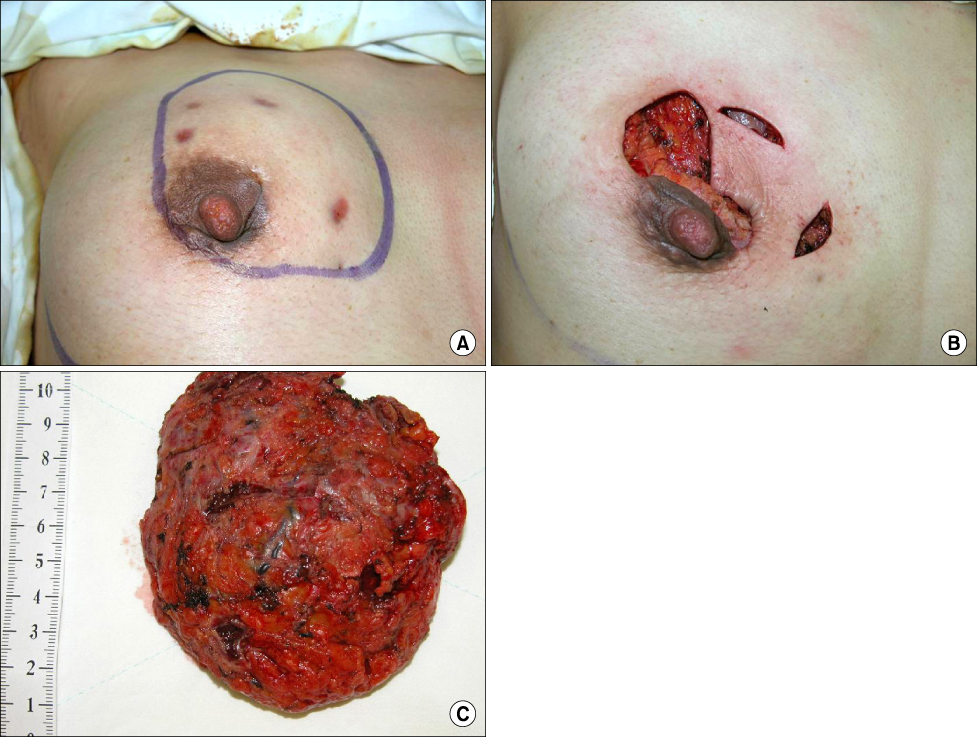
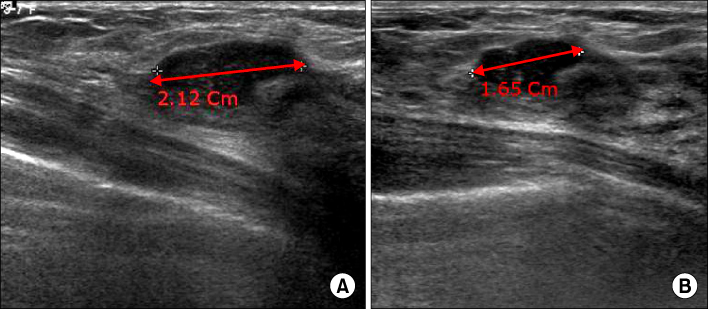
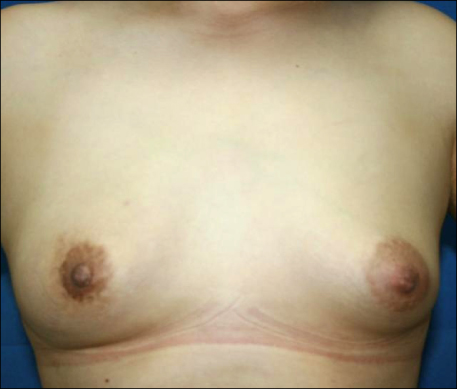
Idiopathic granulomatous mastitis is a rare benign inflammatory breast disease of an unknown etiology and the optimal treatment remains controversial. The aim of this study is to evaluate the efficacy of surgically complete excision in patients with idiopathic granulomatous mastitis. METHODS: Between March 2005 and November 2008, we treated 14 cases that were diagnosed with idiopathic granulomatous mastitis. Prospectively, we treated the cases with complete surgical excision with or without steroid therapy in all patients. RESULTS: The mean age of the patients was 36 years (range 30 to 53 years). All cases performed were complete excision with or without steroid therapy. The median follow up period was 26 months (range 5 to 50 months) and all cases had no recurrence. 13 patients out of the 14 were satisfied with the cosmesis of the treated breast. CONCLUSION: We conclude that the treatment of choice for idiopathic granulomatous mastitis is surgically complete excision.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Plastic and reconstructive breast surgery techniques in the surgical treatment of idiopathic granulomatous mastitis: a single-center experience
Şeref Dokcu, Salim İlksen Başçeken
Ann Surg Treat Res. 2022;103(5):253-263. doi: 10.4174/astr.2022.103.5.253.
Reference
-
1. Bani-Hani KE, Yaghan RJ, Matalka II, Shatnawi NJ. Idiopathic granulomatous mastitis: time to avoid unnecessary mastectomies. Breast J. 2004. 10:318–322.2. Fletcher A, Magrath IM, Riddell RH, Talbot IC. Granulomatous mastitis: a report of seven cases. J Clin Pathol. 1982. 35:941–945.3. Diesing D, Axt-Fliedner R, Hornung D, Weiss JM, Diedrich K, Friedrich M. Granulomatous mastitis. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2004. 269:233–236.4. Lee JH, Kim HA, Moon BI, Lee RA, Sung SH. Granulomatous mastitis. J Korean Surg Soc. 2007. 72:94–100.5. Kim YJ, Choi YJ, Kim JY, Kim HJ, Park YS, Hong SW, et al. Clinicopathologic features of granulomatous mastitis. Korean J Pathol. 2005. 39:181–186.6. Wilson JP, Massoll N, Marshall J, Foss RM, Copeland EM, Grobmyer SR. Idiopathic granulomatous mastitis: in search of a therapeutic paradigm. Am Surg. 2007. 73:798–802.7. Ayeva-Derman M, Perrotin F, Lefrancq T, Roy F, Lansac J, Body G. Idiopathic granulomatous mastitis. Review of the literature illustrated by 4 cases. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris). 1999. 28:800–807.8. Newnham MS, Shirley SE, McDonald AH. Granulomatous lobular mastitis. A case report and review of the literature. West Indian Med J. 2001. 50:236–238.9. Kessler E, Wolloch Y. Granulomatous mastitis: a lesion clinically simulating carcinoma. Am J Clin Pathol. 1972. 58:642–646.10. Erhan Y, Veral A, Kara E, Ozdemir N, Kapkac M, Ozdedeli E, et al. A clinicopthologic study of a rare clinical entity mimicking breast carcinoma: idiopathic granulomatous mastitis. Breast. 2000. 9:52–56.11. Lee SD, Park HL, Nam SJ, Ko YH, Ree HJ, Han BK, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of granulomatous mastitis: a study of 12 cases. J Korean Surg Soc. 2000. 58:487–493.12. Memis A, Bilgen I, Ustun EE, Ozdemir N, Erhan Y, Kapkac M. Granulomatous mastitis: imaging findings with histopathologic correlation. Clin Radiol. 2002. 57:1001–1006.13. Asoglu O, Ozmen V, Karanlik H, Tunaci M, Cabioglu N, Igci A, et al. Feasibility of surgical management in patients with granulomatous mastitis. Breast J. 2005. 11:108–114.14. Tse GM, Poon CS, Ramachandram K, Ma TK, Pang LM, Law BK, et al. Granulomatous mastitis: a clinicopathological review of 26 cases. Pathology. 2004. 36:254–257.15. DeHertogh DA, Rossof AH, Harris AA, Economou SG. Prednisone management of granulomatous mastitis. N Engl J Med. 1980. 303:799–800.16. Katz U, Molad Y, Ablin J, Ben-David D, Paran D, Gutman M, et al. Chronic idiopathic granulomatous mastitis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007. 1108:603–608.17. Al-Khaffaf B, Knox F, Bundred NJ. Idiopathic granulomatous mastitis: a 25-year experience. J Am Coll Surg. 2008. 206:269–273.18. Lai EC, Chan WC, Ma TK, Tang AP, Poon CS, Leong HT. The role of conservative treatment in idiopathic granulomatous mastitis. Breast J. 2005. 11:454–456.19. Azlina AF, Ariza Z, Arni T, Hisham AN. Chronic granulomatous mastitis: diagnostic and therapeutic considerations. World J Surg. 2003. 27:515–518.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Topical Steroids to Treat Granulomatous Mastitis: A Case Report
- Erythema Nodosum Associated with Idiopathic Granulomatous Mastitis in Young Pregnant Woman
- Granulomatous Mastitis during Chronic Antidepressant Therapy: Is It Possible a Conservative Therapeutic Approach?
- Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Bilateral Granulomatous Mastitis: A Cese Report
- Granulomatous mastitis