J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2003 Jun;10(2):202-207. 10.4184/jkss.2003.10.2.202.
SMA Syndrome after Corrective Surgery of Thoracic Kyphoscoliosis: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. choonki@plaza.snu.ac.kr
- 2Asan Medical Center, Ulsan University, College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2003219
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2003.10.2.202
Abstract
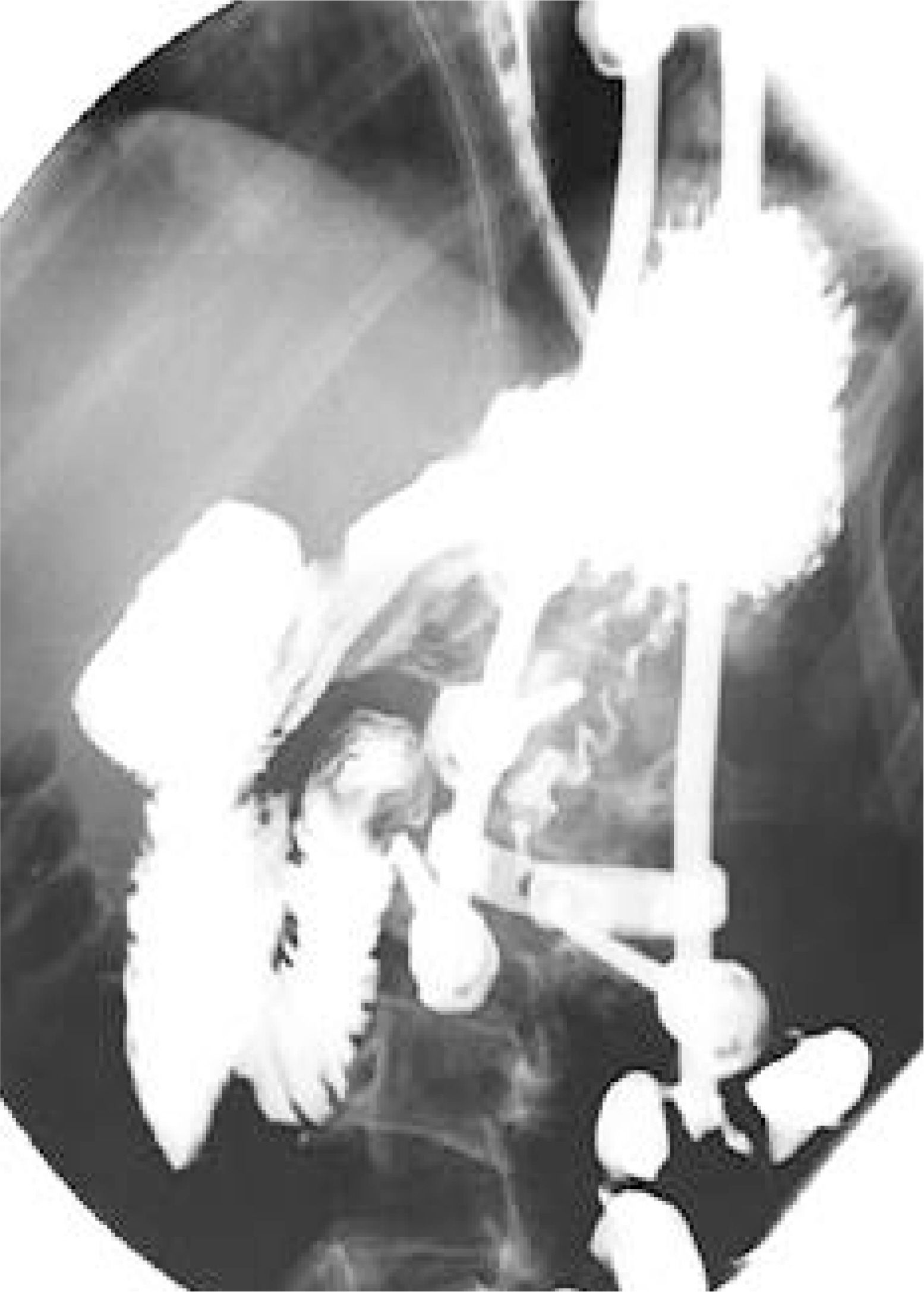
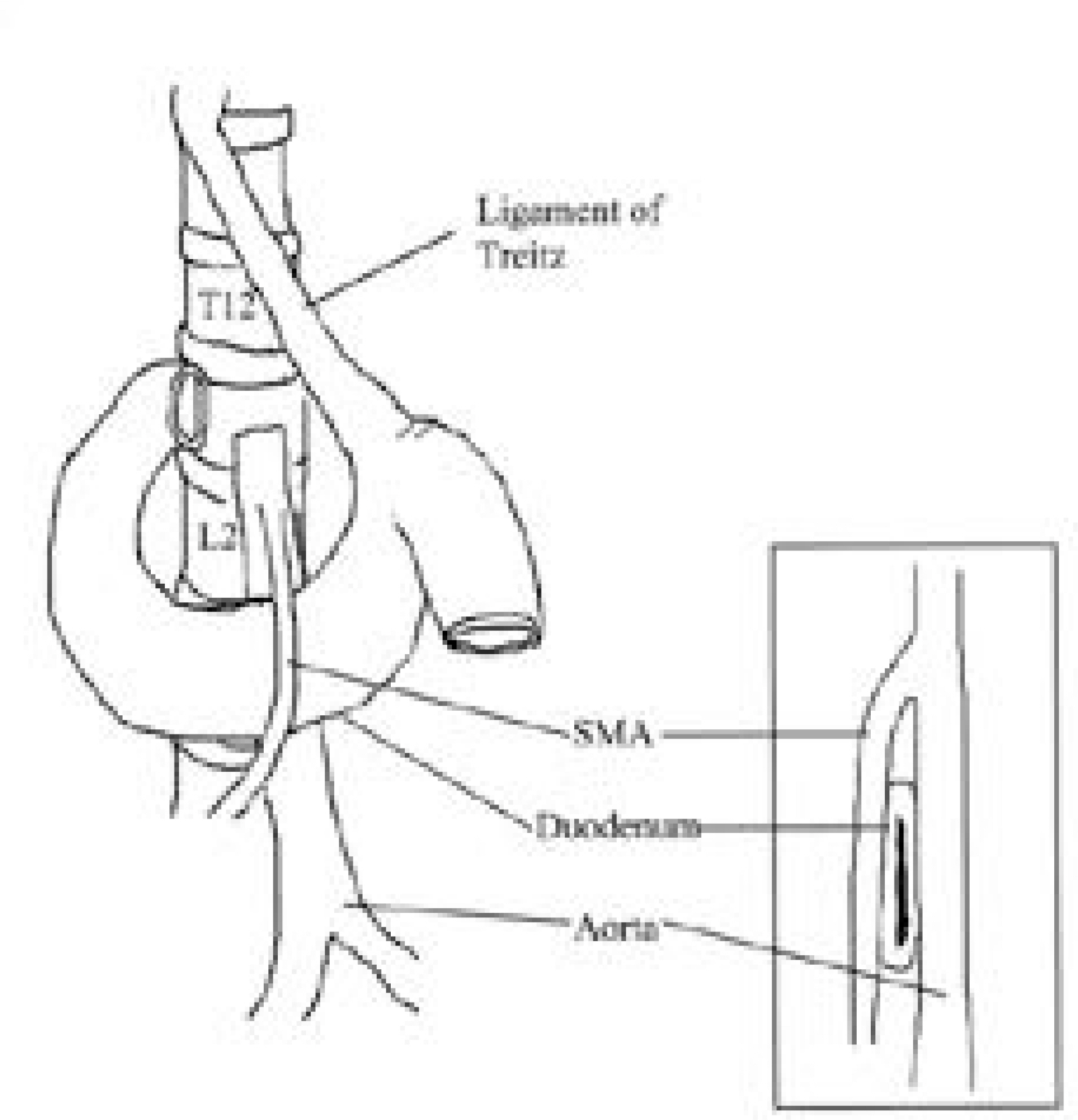
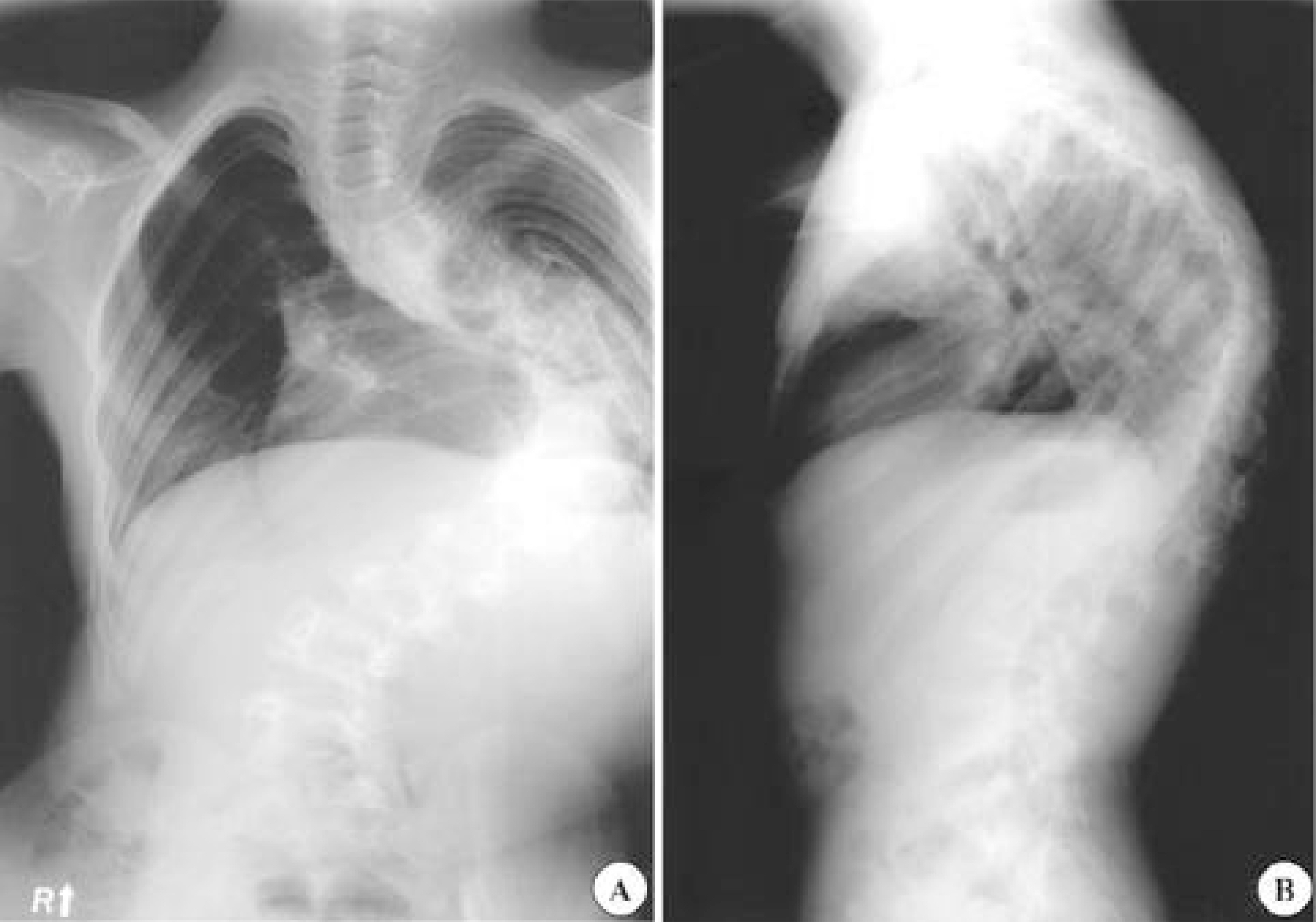
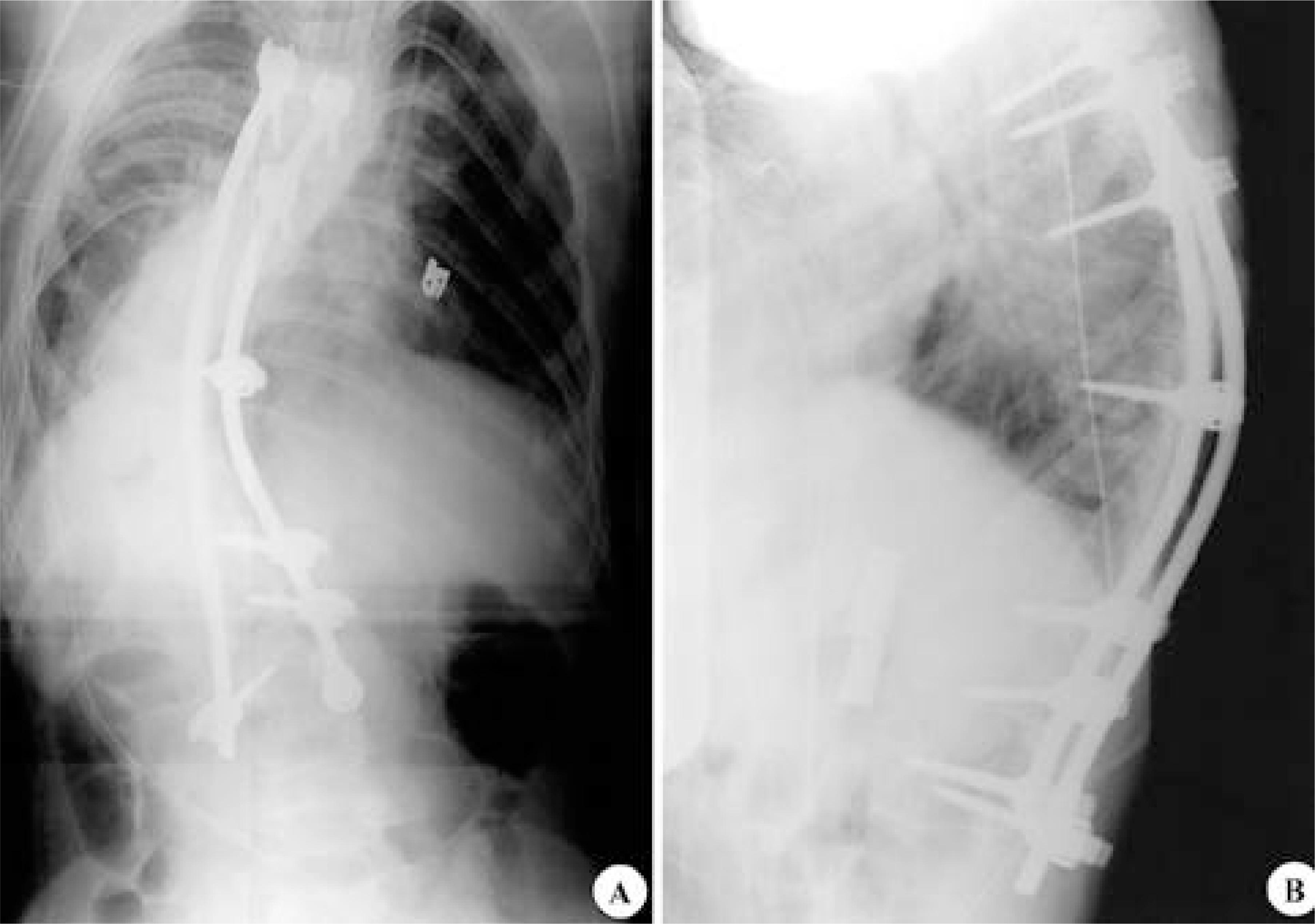
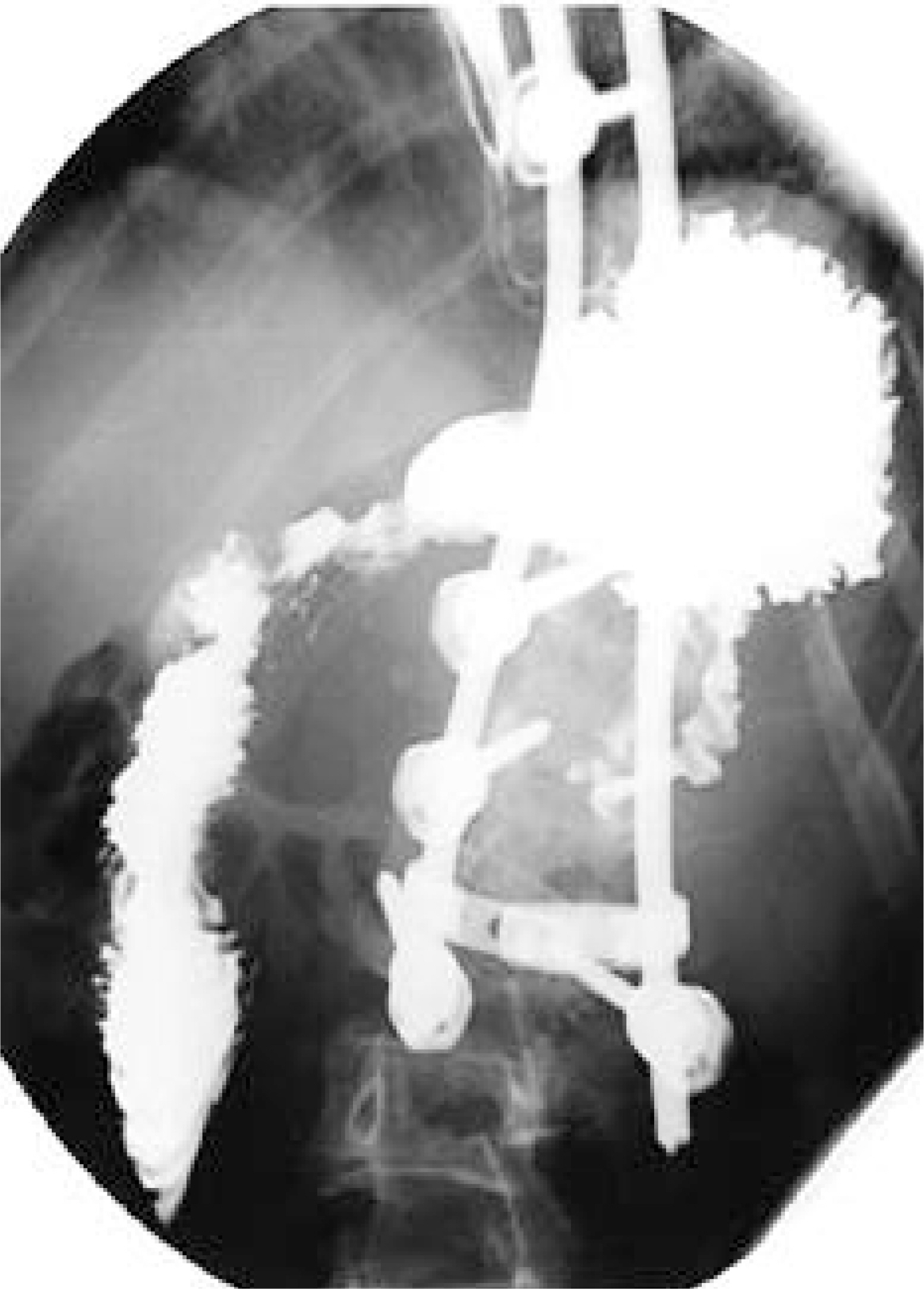
- Superior mesenteric artery (SMA) syndrome is a rare condition that results from an extrinsic compression of the third portion of the duodenum, between the SMA and the aorta. The symptoms for the condition consist of abdominal pain and recurrent vomiting, caused by ileus, and can be followed by an electrolyte imbalance and nutrient deficiency. SMA syndrome can follow surgical correction of a spinal deformity, as the aorta migrates forward as the degree of the lumbar lordosis increases, and the retroperitoneal fat tissue decreases, during perioperative abstinence. Any symptoms suggestive of SMA syndrome, after correction of a spinal deformity, should be investigated, as SMA syndrome carries a prolonged hospital stay, with the potential for mortality. An 11 year 10 month old boy, who underwent correction for thoracic kyphoscoliosis, developed postoperative abdominal distension, pain and bilious vomiting. An upper gastrointestinal contrast study revealed SMA syndrome, which required a laparotomy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Ahmed AR., Taylor I. Superior mesenteric artery syndrome. Postgrad Med J,. 73:776–778. 1997.
Article2). Bunch W., Delaney J. Scoliosis and acute vascular compression of the duodenum. Surgery,. 67:901–906. 1985.3). Crowther MA., Webb PJ., Eyre-Brook IA. Superior mesenteric artery syndrome following surgery for scolio -sis. Spine,. 27:528–533. 2002.4). Dorph MH. The cast syndrome. N Eng J Med,. 243:440–442. 1950.
Article5). Evarts CM., Winter RB., Hall JE. Vascular compression of the duodenum associated with the treatment of sco -liosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am,. 53:431–444. 1971.6). Fromm S., Cash J. Superior mesenteric artery syndrome: an approach to diagnosis and management of upper gastrointestinal obstruction of unclear etiology. S D J Med,. 43:5–10. 1990.7). Hutchinson DT., Bassett GS. Superior mesenteric artery syndrome in pediatric orthopedic patients. Clin Orthop,. 250:250–257. 1990.
Article8). Jones PA., Wastell C. Superior mesenteric artery syndrome. Postgrad Med J,. 59:376–379. 1983.
Article9). Kellogg EL., Kellogg WA. Chronic duodenal obstruction with duodenojejunostomy as a method of treatment: Report of forty-one operations. Ann Surg,. 73:578–608. 1921.10). Kennedy RH., Cooper MJ. An unusually severe case of the cast syndrome. Postgrad Med J,. 59:539–540. 1983.
Article11). Munns SW., Morrissy RT., Golladay ES., McKenzie CN. Hyperalim-entation for superior mesenteric artery (cast) syndrome follwing correction of spinal deformity. J Bone Joint Surg (Am),. 66:1175–1177. 1984.12). Shah MA., Moreland MS. Superior mesenteric artery syndrome in scoliosis surgery: weight percentile for height as an indicator of risk. Am Acad Pediatr,. 98:567–568. 1996.
Article13). Shapiro G., Green DW., Fatica NS., Boachie-Adjei O. Medical complications in scoliosis surgery. Curr Opin Pediatr,. 13:36–41. 2001.
Article14). Strong E. Mechanics of arteriomesenteric duodenal obstruction and direct surgical attack upon etiology. Ann Surg,. 148:725–730. 1958.
Article15). Transfeldt EE. Moe's textbook of scoliosis and other spinal deformites. Lonstein JE, Bradford DS, Winter RB, editors. Complications of treatment. 3rd ed.Philadel -phia, W.B. Saunders, 451-482;1995.16). Vitale MG., Higgs GB., Liebling MS., Roth N., Roye DP Jr. Superior Mesenteric artery syndrome after seg -mental instrumentation: a biomechanical analysis. Am J Orthop,. 28:461–467. 1999.17). Wilkie DPD. Chronic duodenal ileus. Br J Surg,. 9:204–214. 1921.
Article18). Zein NN., Perrault J., and Camilleri M. Recurrent vomiting following Harrington rod instrumentation of the spine. J Pedriatr Gastroenterol Nutrition,. 22:318–320. 1996.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Surgical Therapy of Airway Compression with Severe Kyphoscoliosis
- Nutcracker Syndrome combined with Superior Mesenteric Artery Syndrome in a Pediatric Patient: A Case Report
- Superior Mesenteric Artery Syndrome Diagnosed with Linear Endoscopic Ultrasound (with Video) in a Patient with Normal Body Mass Index
- Surgical Treatment of Thoracic Menigocele Associated with Neurofibromatosis and Kyphoscoliosis
- Anesthesia for elective bilateral sagittal slip osteotomy of the mandible and genioplasty in a young man with Klippel-Feil syndrome, Sprengel deformity, and mandibular prognathism