J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2003 Jun;10(2):97-103. 10.4184/jkss.2003.10.2.97.
Changes of ESR, CSR and CRP after Posterior Decompression and Posterolateral Fusion of the Lumbar Stenosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Paik Hospital, Inje University, Pusan, Korea.
- KMID: 2003206
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2003.10.2.97
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To help in the early diagnosis of postoperative infections in lumbar stenosis, attempts were made to evaluate a large number of patients having levels of ESR, CSR and CRP at fixed intervals, following an uncomplicated instrumented posterolateral fusion with wide decompression.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
101 lumbar stenosis patients were included in this study. The levels of ESR, CSR and CRP were checked on the 2nd, 3rd, 4th, 7th, 10th and 14th postoperative days. These data were plotted in relation to time in order to follow their changes. The relationships between these and the perioperative factors (operation time, fusion levels, estimated bleeding amount and transfusion amount) were evaluated statistically.
RESULTS
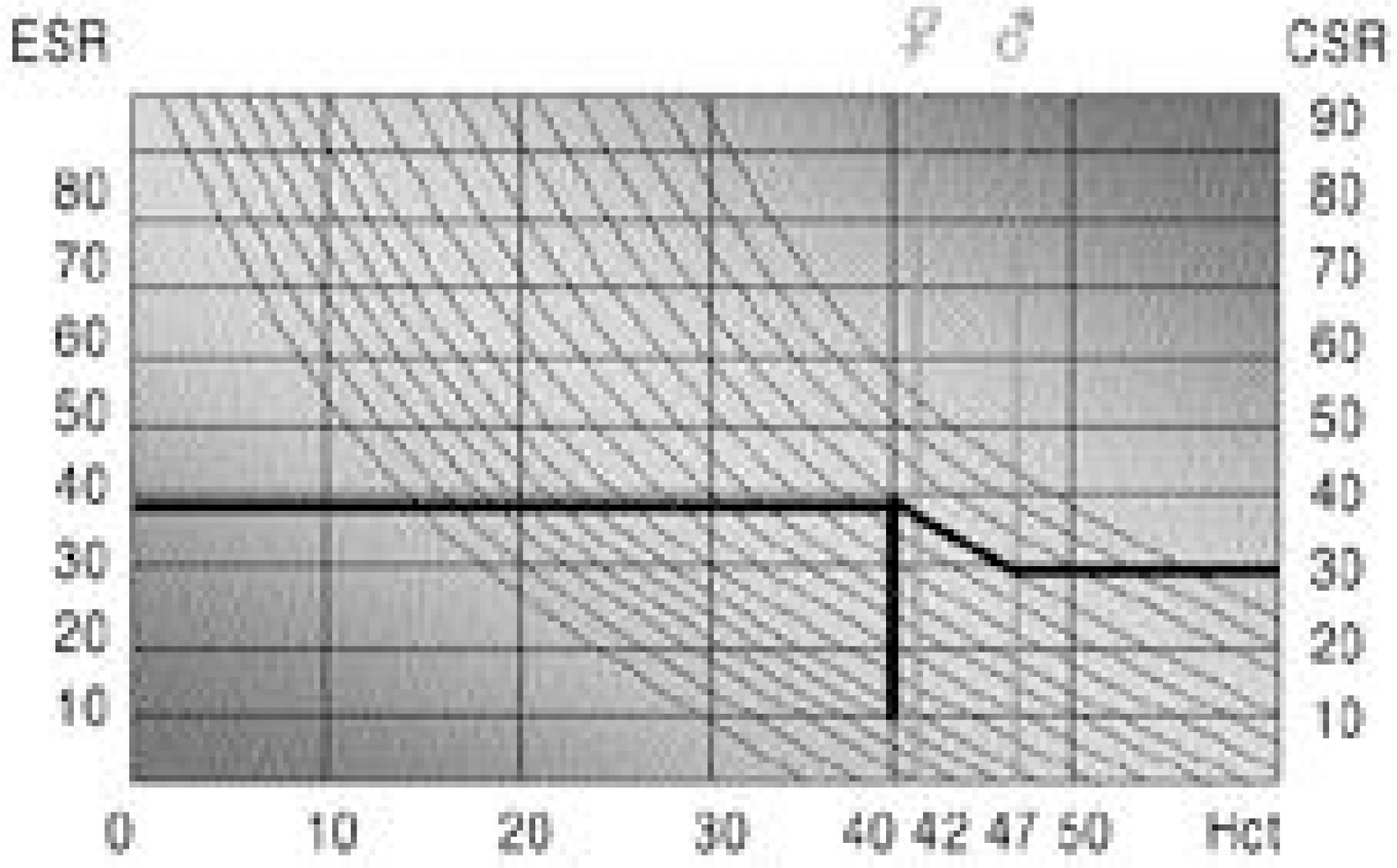
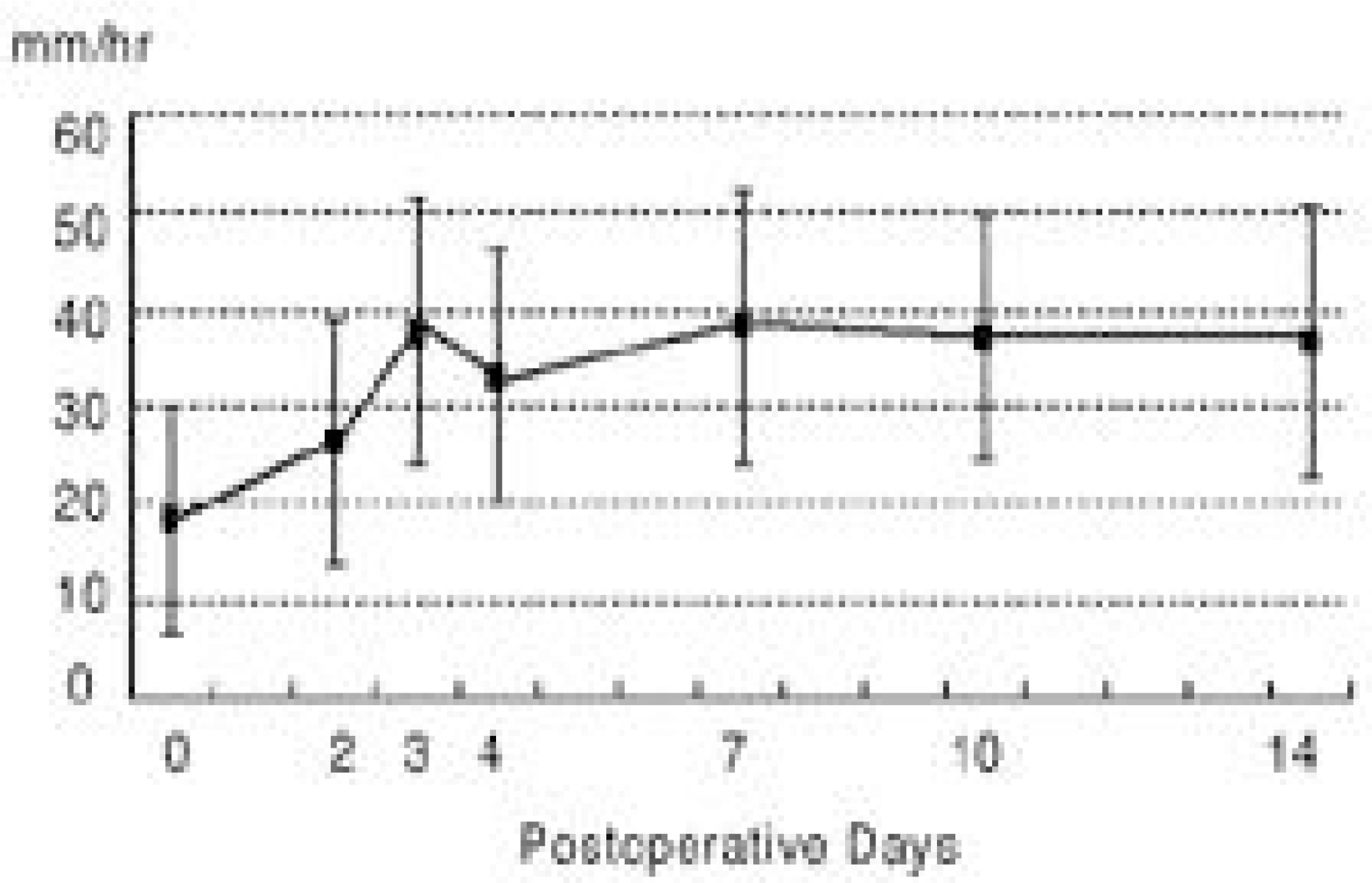
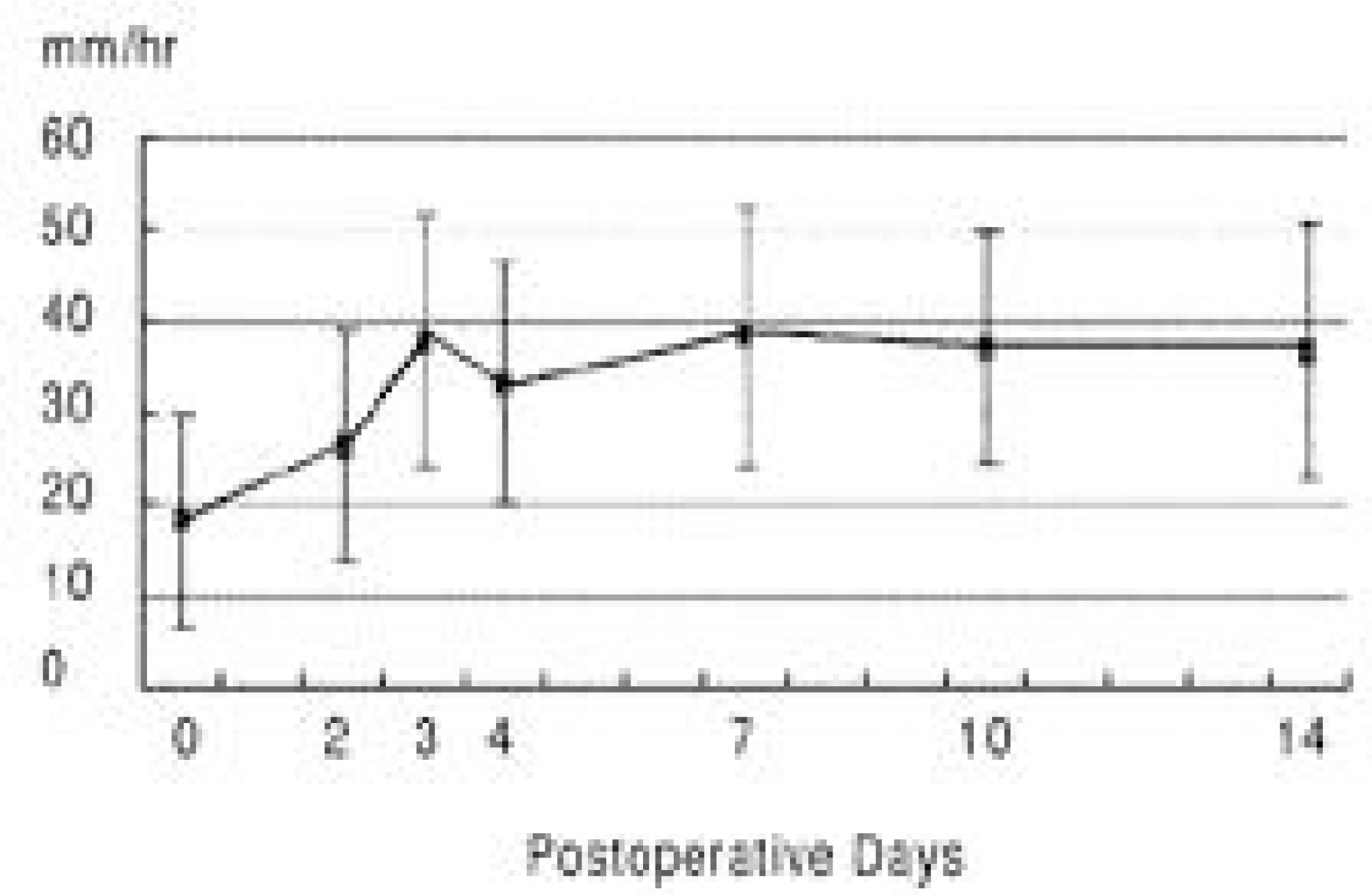
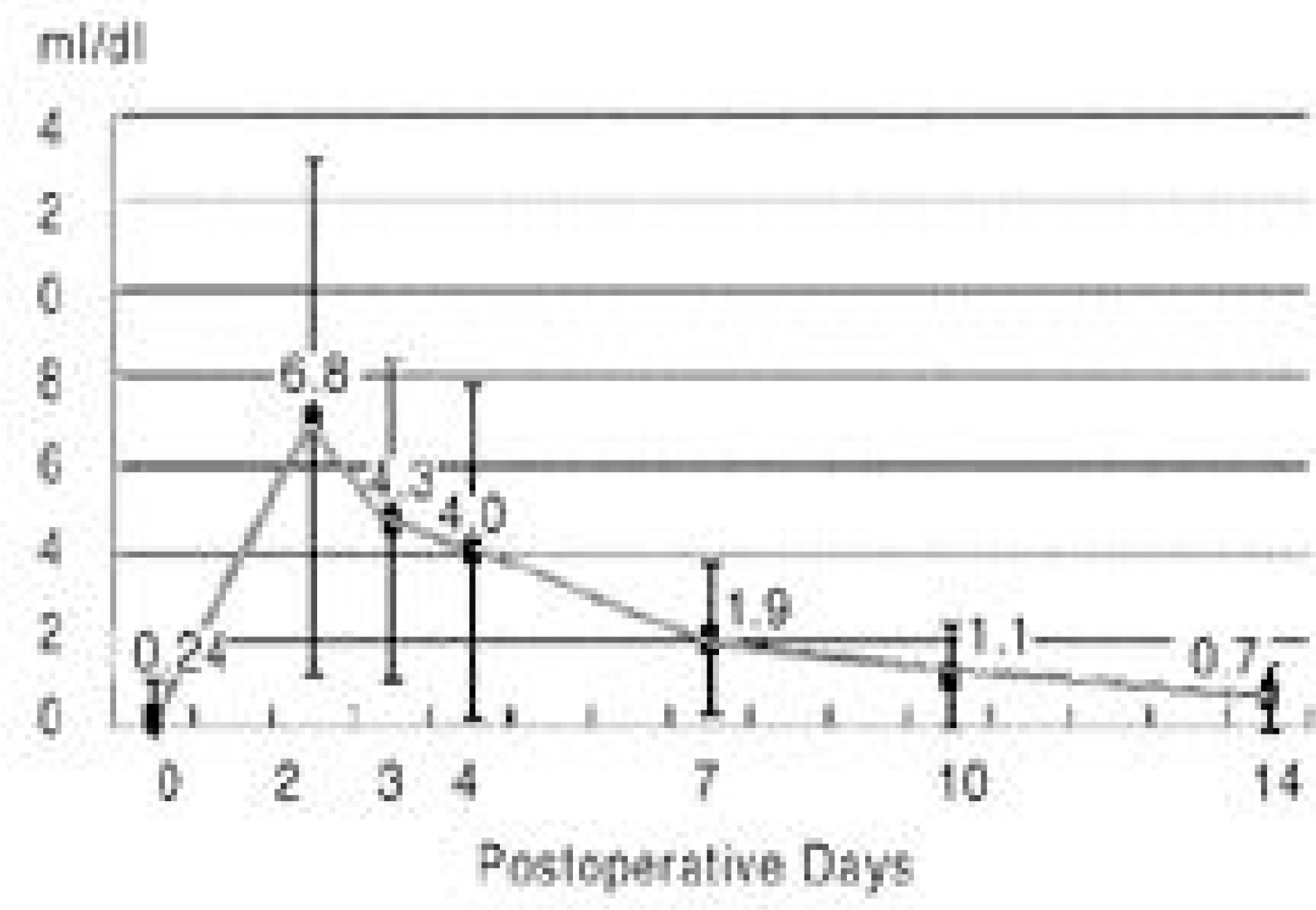
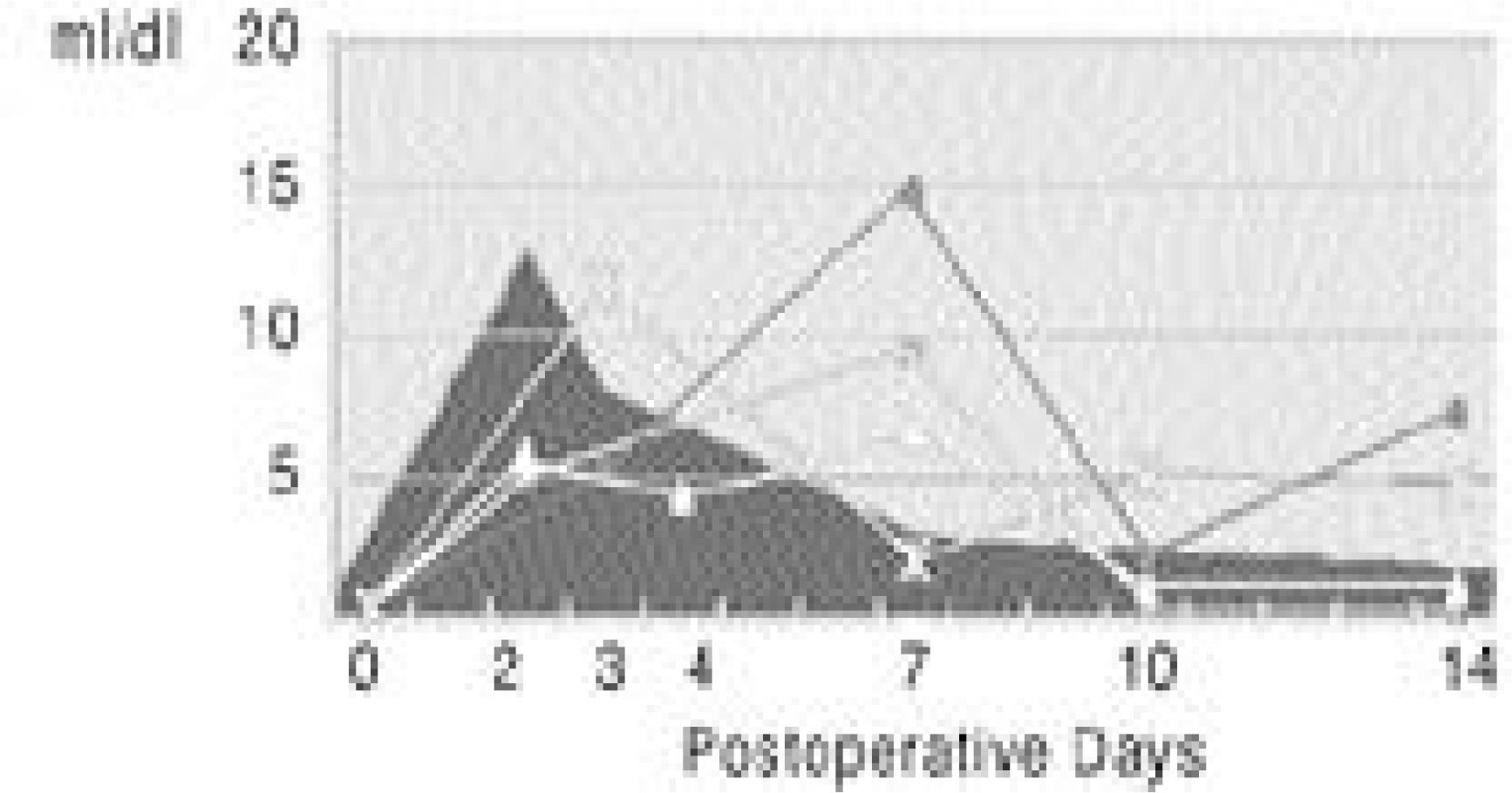
The ESR and CSR had peak levels by the 3rd postoperative day, which then became highly variable until 14 days. The CRP level was highest on the 2nd postoperative day, which decreased rapidly, was and reached nearly normalized levels by 14th day. The ESR and CSR values on the 7th postoperative day showed a tendency to correlate with the perioperative factors, but the CRP value showed no significant correlations.
CONCLUSIONS
Our study revealed the effectiveness of CRP, and ineffectiveness of ESR and CSR, in the early detection of deep infections following surgery for wide lumbar stenosis.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1). Aalto K., Osterman K., Peltola H., Rasanen J. Change in erythrocyte sedimenation rate and C-reactive protein after total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop,. 184:118–120. 1984.2). Bottiger LE., Svedberg CA. Normal erythrocyte sedi -mentation rate and age. Br Med J,. 2:85–89. 1967.3). Brown CA., Eismont FJ. Complication in spinal fusion. Orthop. clin. of north america,. 29(4):679–699. Oct. 1998.4). Colley CM., Fleck A., Coode AW., Muller BR., Myers M A. Early time course of the acute phase protein response in man. J Clin Pathol,. 36:203–207. 1983.
Article5). Curtiss PH. Bone and joint infection in childhood. Instructional Course Lectures. The American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons,. 26:14–19. 1977.6). Deyo RA., Cherkin DC., Loeser JD., Bigos SJ., Ciol MA. Morbidity and mortality in association with operations on the lumbar spine. J Bone Joint Surg,. 74-A(4):536–543. 1992.
Article7). Fisher CL., Gill C., Forrester MG., Nakamura R. Quantitation on acute phase proteins posoperatively. Value in detection and monitoring of complications. Am J Clin Pathol,. 66:840–846. 1976.8). Gewurz H. Biology of C-Reactive Protein and the Acute Phase Response. Hospital Practice,. June:67–81. 1982.
Article9). Harris NH. Some problems in the diagnosis and treat -ment of acute osteomyelitis. J Bone Joint surg,. 42-B:535–541. 1960.10). Jonsson B and Bjorn stromqvist. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate after lumbar spine surgery. Spine,. 16(9):1049–1050. 1991.11). Jung SH., Shim BS. C-reactive protein and acute response. Medical Postgraduates,. 6(18):261–266.12). Kushner I., Gewurz H. C-reactive protein and the acute phase response. J Lab Clin Med,. 97:739–749. 1981.13). Larsson S., Thelander U., Friberg S. C-reactive pro -tein(CRP) levels after elective orthopedic surgery. Clin Orthop,. 275:237–242. 1992.14). Lee HK., Ahn BW., Song HS. Clinical observations on acute pyogenic osteomyelitis and arthritis in infancy. J of Korean Orthop Surgery,. 12:735–745. 1980.
Article15). Mcdonnell MF., Glassman SD., Dimar JR., Puno RM., Johnson JR. Perioperative complication of anterior procedures on the spine. J Bone Joint Surg. 78-A(6):839–847.16). Mustard RA Jr., Bohnen JMA., Haseeb S., Kasina R. C-reactive protein levels predict postoperatice septic com -plications. Arch Surg,. 122:69–73. 1987.17). Park BM., Choi YK. A clinical study of septic arthri -tis in children. J of Korean Orthop Surgery,. 12:746–753. 1980.18). Peltola H., Vahvanen V., Aalto K. Fever, C-Reactive protein, and Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate in Monitoring Recovery from Septic Arthritis: A Preliminary Study. Journal of Pediatric Orthopedics,. 4:170–174. 1984.19). Peltola HO. C-reactive protein for Rapid Monitoring of Infection of the Central Nerve System. The Lancet. May 1, 1982.20). Pepys MB. Acute Phase Response and C-Reactive pro -tein. Oxford Textbook of Medicine. second Ed.p. 157–164. Oxford University Press;Vol. 1-Sectionas 9. 1987.21). Pepys MB. C-reactive protein fifty years on. Lancet,. 1:653–657. 1981.
Article22). Thelander U., Larsson S. Quantitation of c-reactive protein levels and erythrocyte sedimentation rate after spinal surgery. Spine,. 17(4):400–404. 1992.
Article23). Verkkala K., Valtonen V., Jarvinen A., Tolppanen E-M. Fever, leucocytosis and C-reactive protein after open-heart surgery and their value in the diagnosis of postoperative infections. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg,. 35:78. 1987.
Article24). Wintrobe MM., Landsberg JW. A standardized technique for the blood sedimentation test. J Lab and Clin Med,. 19(777):102–115. 1934.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical study on the posterior decompression and posterolateral fusion with instrumentation in lumbar spinal stenosis
- Clinical Comparison between Decompression and Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion in Chronic Lower Back Pain Involving Degenerative Disc Disease and Spinal Stenosis
- Intertransverse Fusion in Spondylolisthesis: Report of a Case
- Result of Pedicle Screw Fixation in Lumbar Stenosis with: A Comparison of Degenerative Type Lumbar Stenosis with Spondylolisthetic type Lumbar Stenosis
- Surgical Outcome of Degenerative Lumbar Spinal Stenosis in Patients over 70 years old: A Comparative Analysis according to Surgical Method