J Korean Soc Radiol.
2011 Dec;65(6):569-572. 10.3348/jksr.2011.65.6.569.
Self-Expandable Stenting over a Stent Graft for the Exclusion of a Carotid Stump: Troubleshooting for Device Incompatibility
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Catholic University of Daegu School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. youthmdkhk@cu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Neurology, Catholic University of Daegu School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiology, Keimyung University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2002923
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2011.65.6.569
Abstract
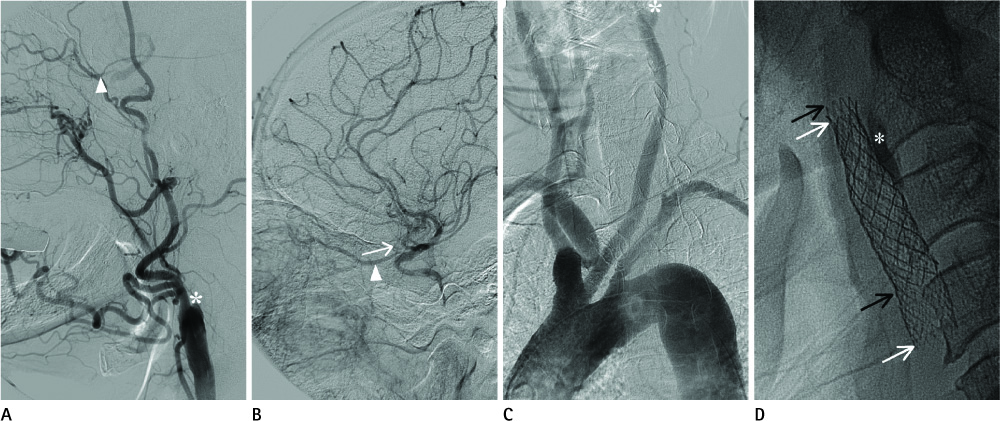
- Carotid stump, the blind remnant of an occluded internal carotid artery, can be a potential source of microemboli, and warrants its exclusion from the vascular lumen to prevent the recurrence of a microembolism. In a 69-year-old male with a symptomatic carotid stump and acute angle between left common carotid artery and aortic arch, a 7-Fr. shuttle sheath was scarcely placed into the left carotid artery but the 7-mm-diameter stent-graft-loading balloon could not be inserted into the 7-Fr. shuttle sheath. With the mounting a stent graft over a 5-mm balloon, the balloon-expandable stent graft was unfolded. The self-expandable stent was placed over the stent graft, and an 8-mm balloon was subsequently expanded. Self-expanding stenting can be useful for troubleshooting in a case of device incompatibility coming from the different calibers of the external and common carotid arteries for the successful exclusion of a symptomatic carotid stump.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Barnett HJ, Peerless SJ, Kaufmann JC. "Stump" on internal carotid artery--a source for further cerebral embolic ischemia. Stroke. 1978; 9:448–456.2. Kumar SM, Wang JC, Barry MC, Farrell L, Kelly CJ, Fitzgerald PH, et al. Carotid stump syndrome: outcome from surgical management. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2001; 21:214–219.3. Naylor AR, Bell PR, Bolia A. Endovascular treatment of carotid stump syndrome. J Vasc Surg. 2003; 38:593–595.4. Nano G, Dalainas I, Casana R, Malacrida G, Tealdi DG. Endovascular treatment of the carotid stump syndrome. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2006; 29:140–142.5. Carrafiello G, Delodovici ML, Piffaretti G, Castelli P. Endovascular treatment of carotid stump syndrome. Vasc Endovascular Surg. 2009; 43:277–279.6. Suh DC, Kim JK, Choi CG, Kim SJ, Pyun HW, Ahn C, et al. Prognostic factors for neurologic outcome after endovascular revascularization of acute symptomatic occlusion of the internal carotid artery. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007; 28:1167–1171.7. Choi BS, Park JW, Shin JE, Lü PH, Kim JK, Kim SJ, et al. Outcome evaluation of carotid stenting in high-risk patients with symptomatic carotid near occlusion. Interv Neuroradiol. 2010; 16:309–316.8. Macdonald S, Lee R, Williams R, Stansby G. Delphi Carotid Stenting Consensus Panel. Towards safer carotid artery stenting: a scoring system for anatomic suitability. Stroke. 2009; 40:1698–1703.9. Broadbent LP, Moran CJ, Cross DT 3rd, Derdeyn CP. Management of ruptures complicating angioplasty and stenting of supraaortic arteries: report of two cases and a review of the literature. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003; 24:2057–2061.10. Lownie SP, Pelz DM, Lee DH, Men S, Gulka I, Kalapos P. Efficacy of treatment of severe carotid bifurcation stenosis by using self-expanding stents without deliberate use of angioplasty balloons. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005; 26:1241–1248.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Self-expandable Graft Stenting in an Iatrogenic Fistula between Common Carotid Artery and Internal Jugular Vein
- Subacute In-stent Thrombosis after Carotid Artery Stenting: A Case Report
- Two cases of self expandable stent implantation in patient with occlusive restenosis of brachiocephalic vein stent
- Stent-Graft Repair of Common Carotid Pseudoaneurysms in Behcet's Syndrome
- Covered Stenting Is an Effective Option for Traumatic Carotid Pseudoaneurysm with Promising Long-Term Outcome